Neurodegeneration & LLPS
What is Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation (LLPS)?
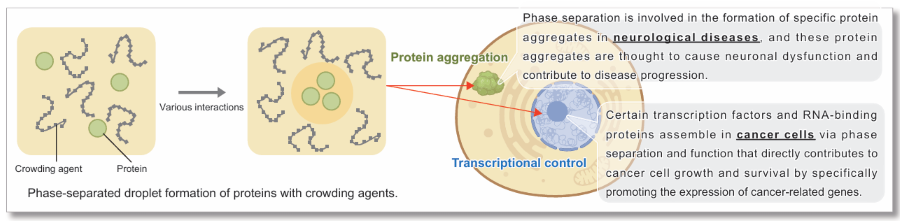
Liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) is a phenomenon in which certain molecules assemble locally within a cell to form aggregates (droplets) of biomolecules with liquid-like properties. In recent years, LLPS has attracted much attention as it has been shown to affect many biological processes in the cell. Although the study of droplets formed by phase separation is still in its infancy, elucidating how these biological phenomena affect cellular functions and the pathogenesis of disease is considered key to the development of new therapeutic strategies.
Reference: Dolgin, E. Nature, 2018, DOI: 10.1038/d41586-018-03070-2.
Protein aggregation is a hallmark of neurodegenerative disease. Many proteins found in pathological inclusions are known to undergo LLPS, a reversible process of molecular self-assembly. Recent evidence suggests that dysregulated LLPS may act as a precursor to protein aggregation in neurodegeneration. Ongoing research aims to elucidate the underlying mechanisms and explore strategies for modulation.


Reference: Zbinden, A. Developmental Cell, 2020, DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2020.09.014.
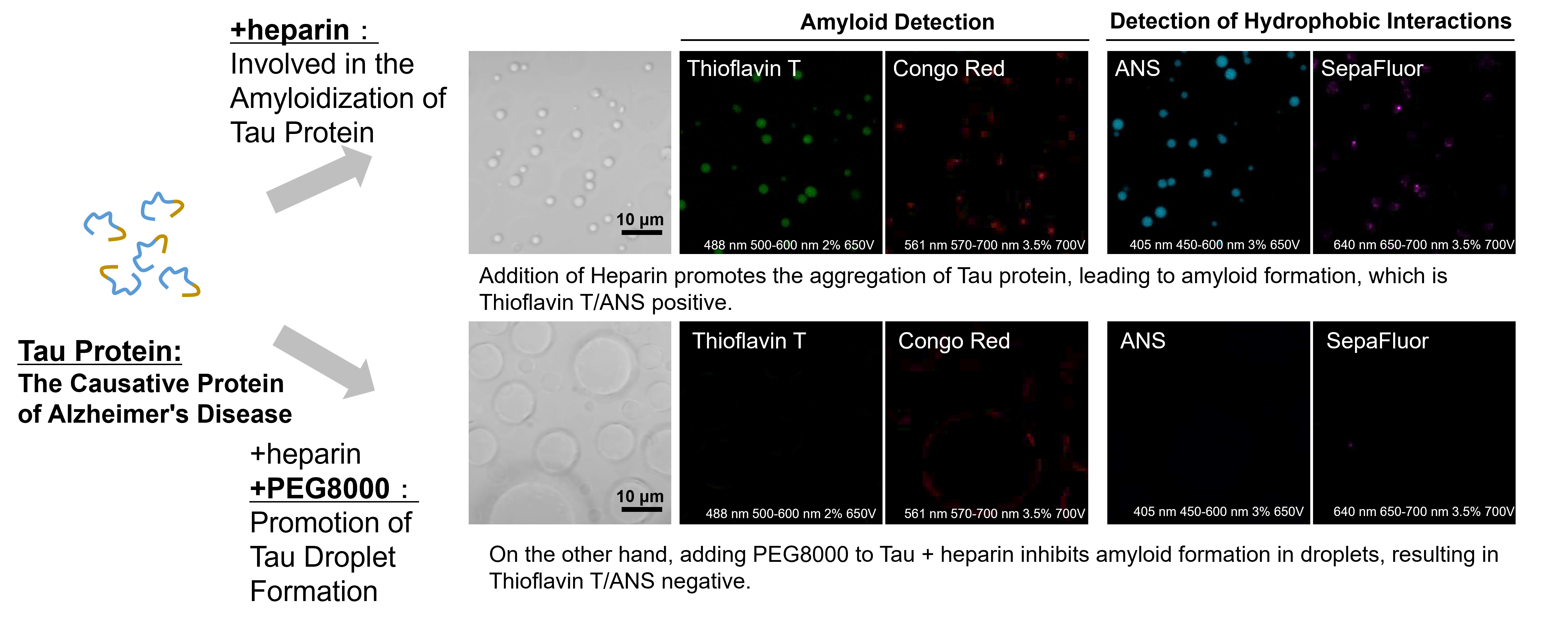
Experimental example: effect of crowding agents on the properties of Tau protein droplets.
LLPS Characterization-dye Set was used to investigate the properties of tau protein droplets: when heparin, a scaffold, was added to the tau protein, tau protein droplets were observed and were positive with both amyloid staining dyes, Thioflavin T and Congo Red.
The droplets were also positive with both ANS and SepaFluo dyes, which fluoresce in a hydrophobic environment, suggesting an amyloid-like aggregation structure.
On the other hand, under the condition of adding the crowding agent PEG8000, the tau protein droplets were enlarged and the fluorescence signals of all dyes were weakened.
These results suggest that the enhancement of phase-separated droplet formation by the crowding agent may affect the properties of the tau protein droplets.
-
<Experimental conditons>
Tau 441(WT):10 μmol/l
Heparin:20%
PEG8000:10 %
Buffer: 10 mmol/l HEPES (pH 7.4), 150 mmol/l NaCl
Dye:10 μmol/l Thioflavin T, Congo Red, ANS, 100 nmol/l SepaFluor
Incubate (37℃):7 days
Fluorescence microscope :Zeiss LSM800