|
Chronic inflammation drives immune decline and age-related diseases, creating a vicious cycle with senescence. This week, we introduce a review of the link between senescence and inflammation, along with recent discoveries. Cellular senescence and inflammation are linked, as senescent cells secrete pro-inflammatory factors that perpetuate chronic inflammation and tissue dysfunction. Chronic inflammation drives immune decline and age-related diseases, creating a vicious cycle with senescence. In this note, we introduce a review article of the link between senescence and inflammation, along with recent findings on anti-IL-17 and anti-IL-11 treatment for anti-senescence. Anti-IL-17 drugs are already approved, and anti-IL-11 therapy is in trials for fibrotic lung disease, suggesting that these treatments may soon help delay aging. |
|||
|
Review Article Inflammation and aging: signaling pathways and intervention therapies |
Inhibition of IL-11 signalling extends mammalian healthspan and lifespan |
Targeting lymphoid-derived IL-17 signaling to delay skin aging Click here for the original article: Paloma Solá, et. al., Nature Aging, 2024. |
|
|
Point of Interest - Inflammaging creates a vicious cycle of inflammation and senescence, suggesting the elimination of inflammation as a potential anti-aging strategy. - The paper reviews inflammaging, aging models, single-cell technologies, and anti-aging strategies to combat disease and improve quality of life. |
Point of Interest - Genetic deletion of IL-11 or use of anti-IL-11 improves metabolism, reduces frailty and extends lifespan by over 20% in mice. - Anti-IL-11 therapy, currently in clinical trials for fibroinflammatory diseases, may extend health and lifespan in humans with promising safety. |
Point of Interest - Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals increased IL-17 signaling in aged skin, which drives inflammation and impairs homeostasis. - Blocking IL-17 signaling reduces skin inflammation and delays age-related features, suggesting a potential anti-aging skin therapy. |
|
| Related Techniques | |||
| Cellular senescence detection | SPiDER-βGal for live-cell imaging or flow cytometry / microplate reader / tissue samples NEW SPiDER-βGal Blue for fixed cell and for multiple staining with immunostaining and other methods |
||
| Oxygen Consumption Rate(OCR) Plate Assay | Extracellular OCR Plate Assay Kit | ||
| Total ROS detection | Highly sensitive DCFH-DA or Photo-oxidation Resistant DCFH-DA | ||
| Glycolysis/Oxidative phosphorylation Assay | Glycolysis/OXPHOS Assay Kit | ||
| First-time autophagy research | Autophagic Flux Assay Kit | ||
| Lysosomal function | Lysosomal Acidic pH Detection Kit-Green/Red and Green/Deep Red | ||
| Apoptosis detection in multiple samples | Annexin V Apoptosis Plate Assay Kit | ||
| Cell proliferation/ cytotoxicity assay | Cell Counting Kit-8 and Cytotoxicity LDH Assay Kit-WST | ||
| Related Applications | |||
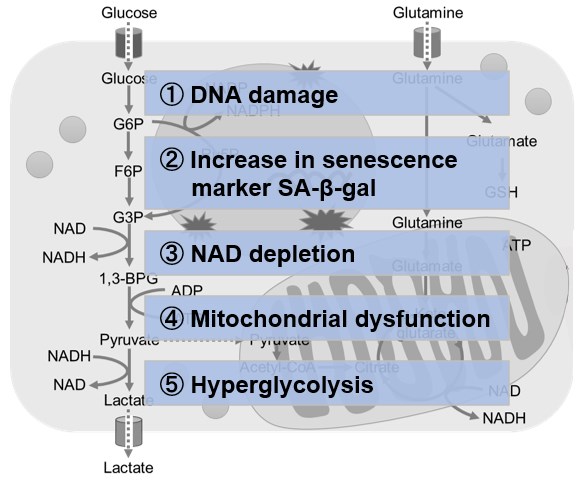
Metabolic shift to glycolysis in senescenct cells |
|||
|
|
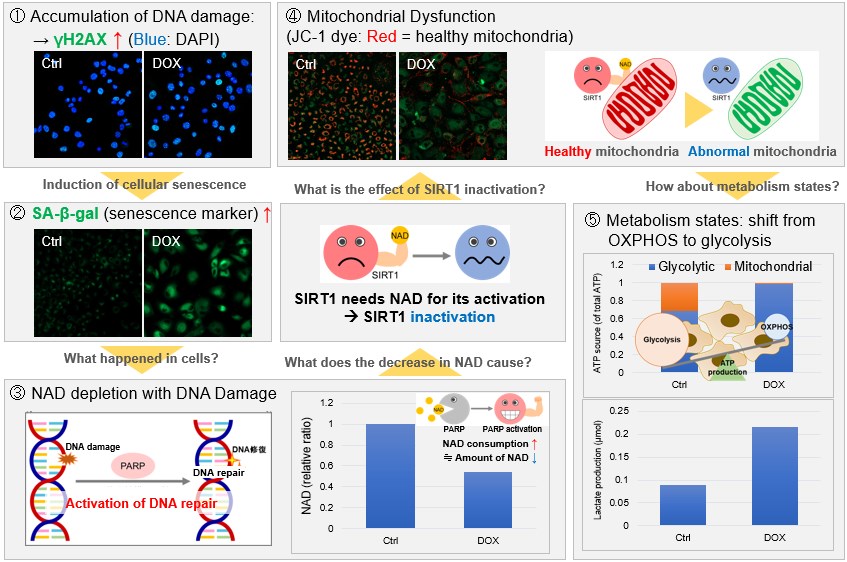
NAD(+) levels decline during the aging process, causing defects in nuclear and mitochondrial functions and resulting in many age-associated pathologies*. Here, we try to redemonstrate this phenomenon in the doxorubicin (DOX)-induced cellular senescence model with a comprehensive analysis of our products. *S. Imai, et al., Trends Cell Biol, 2014, 24, 464-471
|
||
 |
|||
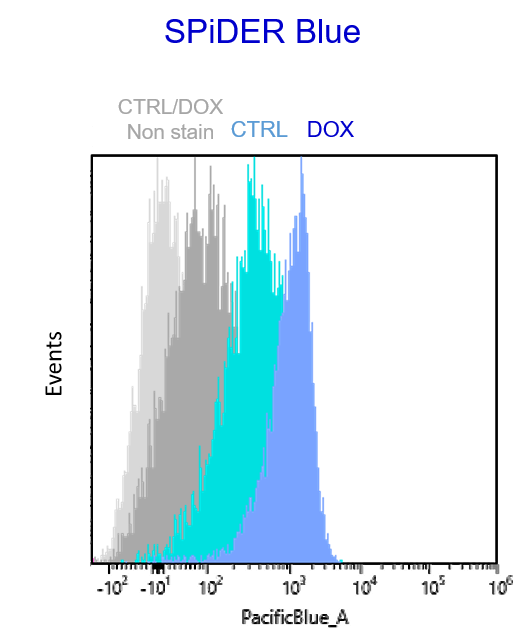
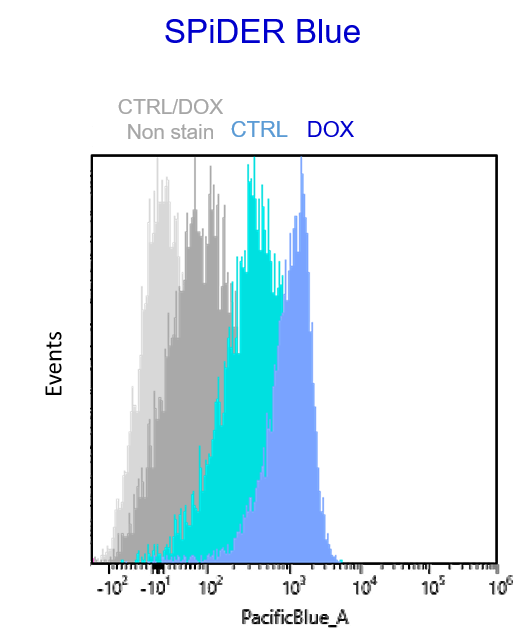
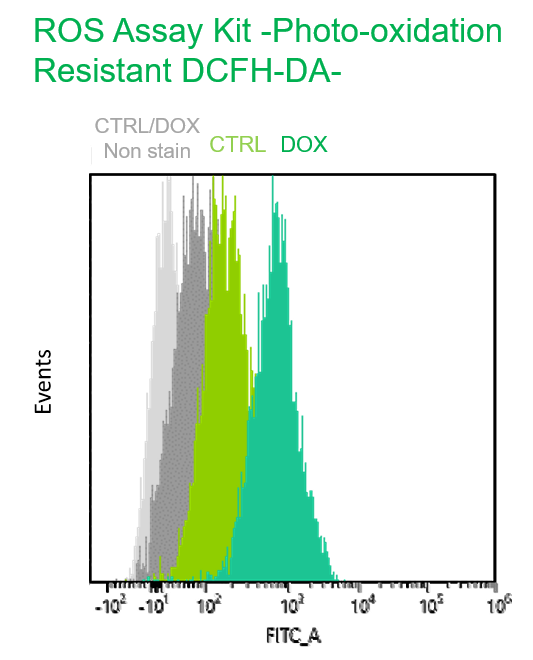
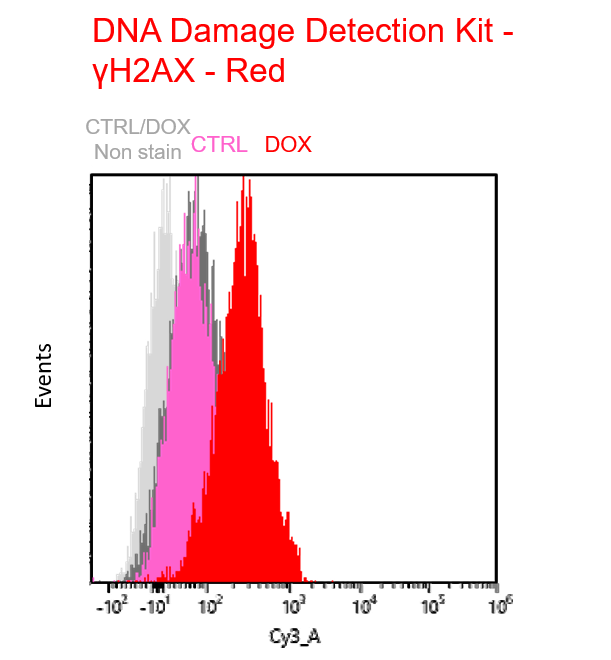
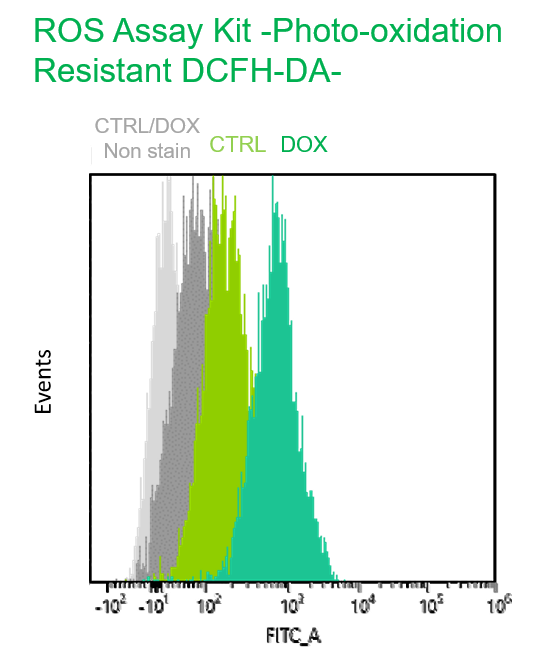
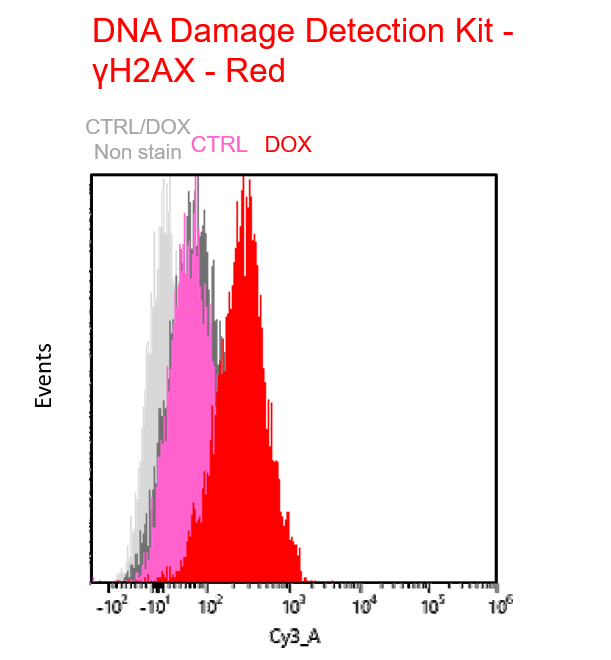
Multiple staining with oxidative stress-related markers using Doxorubicin-induced senescent cells(flow cytometry) |
|||
|
Using A549 cells induced to senescence by doxorubicin (DOX) and normal cells (CTRL), changes in oxidative stress-related markers in senescent cells were analyzed by flow cytometry with multiple staining. SA-βGal as a senescence marker was detected by Cellular Senescence Detection Kit - SPiDER Blue, total ROS as an oxidative stress marker was detected by ROS Assay Kit - Photo-oxidation Resistant DCFH-DA-, and γH2AX as a DNA damage marker was detected by DNA Damage Detection Kit - γH2AX-Red. As a result, total ROS and γH2AX were increased in SA-βGal-positive senescent cells, and the increase in oxidative stress-related markers associated with cellular senescence could be detected by multiple staining. <Experimental Procedure> |
|||