|
Anti-senescence study aims to restore youthful function to aging tissues and organs, often focusing on cellular repair and regeneration. Extracellular vesicles (EVs), including exosomes and microvesicles, play a critical role in cell-to-cell communication by transporting bioactive molecules such as proteins, lipids and RNA. Recent studies suggest that EVs derived from young or healthy cells can have anti-senescence effects on aged cells and tissues, promoting regeneration and repair. These EVs have shown potential to reverse age-related damage and improve tissue function, making them a promising tool in regenerative medicine and anti-aging therapies. |
|||
|
Small extracellular vesicles from young plasma reverse age-related functional declines by improving mitochondrial energy metabolism |
Extracellular vesicles from human urine-derived stem cells delay aging through the transfer of PLAU and TIMP1 Click here for the original article: Shanshan Rao, et. al., Acta Biomaterialia, 2024. |
Rejuvenating effects of young extracellular vesicles in aged rats and in cellular models of human senescence Click here for the original article: Lilian Grigorian Shamagian, et. al., EMBP Reports, 2023. |
|
|
Point of Interest - Proteomic analysis shows young sEVs enhance metabolism and mitochondrial function in aged tissues. - Young sEVs stimulate PGC-1α, reversing age-related dysfunction.
|
Point of Interest - USC-EVs' anti-aging effects are consistent regardless of donor age, gender, or health. - Plasminogen activator urokinase (PLAU) and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 1 (TIMP1) in USC-EVs contribute to the anti-senescent effects of USC-EVs. |
Point of Interest - Young cardiosphere-derived cells (CDC) EVs rejuvenate aged rats, improving heart, lungs, muscles, and kidneys. - Purified EVs from young blood show rejuvenating effects; EV-depleted serum increases senescence. - The treatment also favorably modulates glucose metabolism and anti-senescence pathways, ultimately extending lifespan. |
|
| Related Techniques | |||
| Cellular senescence detection | SPiDER-βGal for live-cell imaging or flow cytometry / microplate reader / tissue samples. | ||
| Exosome Labeling | ExoSparkler Exosome Membrane Labeling Kit - Green / Red / Deep Red | ||
| Exosome purification | ExoIsolator Exosome Isolation Kit, ExoIsolator Isolation Filter | ||
| Glycolysis/Oxidative phosphorylation Assay | Glycolysis/OXPHOS Assay Kit | ||
| Oxygen Consumption Rate(OCR) Plate Assay | Extracellular OCR Plate Assay Kit | ||
| Mitochondrial membrane potential detection | JC-1 MitoMP Detection Kit, MT-1 MitoMP Detection Kit | ||
| Mitochondrial superoxide detection | MitoBright ROS Deep Red - Mitochondrial Superoxide Detection | ||
| Total ROS detection | Highly sensitive DCFH-DA or Photo-oxidation Resistant DCFH-DA | ||
| Endocytosis Detection detection | ECGreen-Endocytosis Detection | ||
| Lysosomal function | Lysosomal Acidic pH Detection Kit-Green/Red and Green/Deep Red | ||
| Related Applications | |||
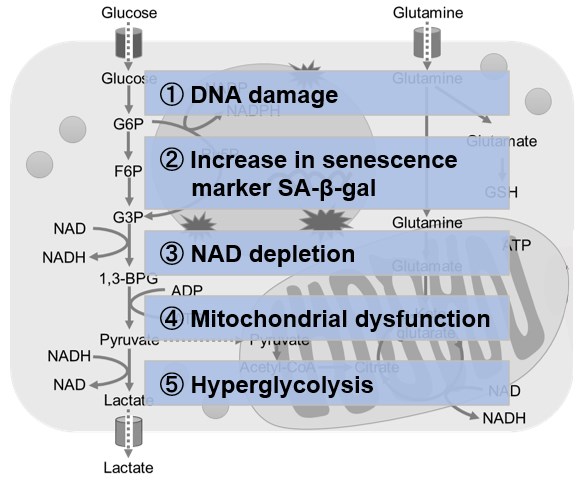
Metabolic shift to glycolysis in senescenct cells |
|||
|
|
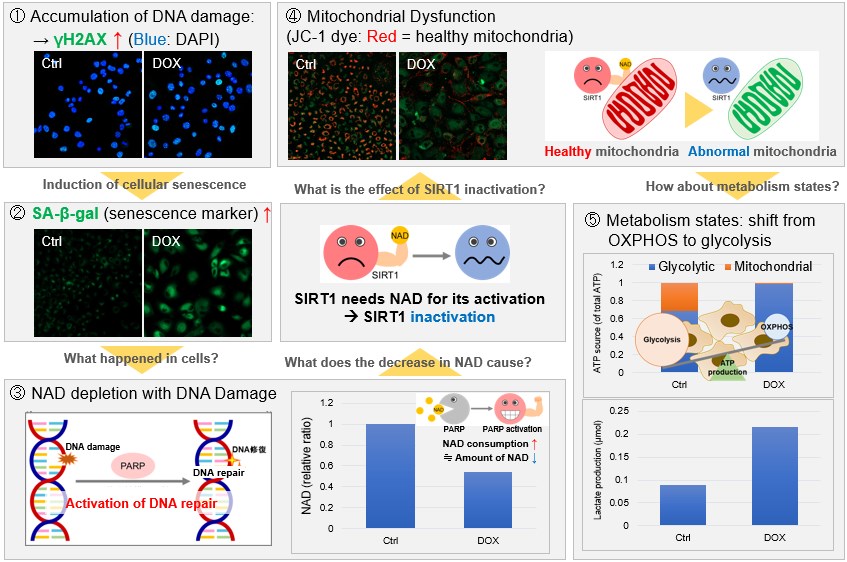
NAD(+) levels decline during the aging process, causing defects in nuclear and mitochondrial functions and resulting in many age-associated pathologies*. Here, we try to redemonstrate this phenomenon in the doxorubicin (DOX)-induced cellular senescence model with a comprehensive analysis of our products. *S. Imai, et al., Trends Cell Biol, 2014, 24, 464-471
|
||
 |
|||