MitoBright ROS Deep Red - Mitochondrial Superoxide Detection

Mitochondrial Superoxide Detection
*Same product as Product code 'MT14'
- Allow to detecting mitochondrial superoxide with a long wavelength(Deep Red)
- Allow to co-staining with a green or red fluorescent probe
- High selectivity to superoxide
-
Product codeMT16 MitoBright ROS Deep Red - Mitochondrial Superoxide Detection
| Unit size | Price | Item Code |
|---|---|---|
| 100 nmol x 1 | Find your distributors | MT16-10 |
| 100 nmol x 3 | Find your distributors | MT16-12 |
| 100 nmol x 1 | ||
|---|---|---|
| 100 nmol x 3 |
Description
The mitochondrion is an important organelle that uses oxygen to synthesize ATP, producing the necessary energy for living cells to thrive. Decreased mitochondrial activity and mitochondrial dysfunction are associated with cancer, aging, and neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Mitochondrial mass (MM), mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), and mitochondrial ROS (mtROS) have been widely studied as promising targets for mitochondria-related diseases. Since these mitochondrial attributes are dynamic, simultaneous analysis using multiple staining in a single sample is required.
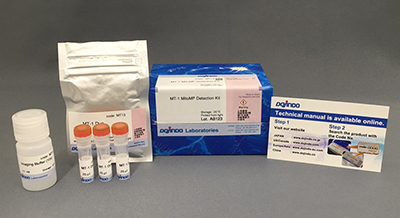
Company T' product Red has widely been used to detect mitochondrial superoxide. However, the emission wavelength is the common red, which overlaps with other MMP detection probes such as TMRE, and is therefore not applicable for simultaneous staining with these other mitochondrial markers in a single sample.
Dojindo’s MitoBright ROS Deep Red overcomes these limitations. This dye emits deep red fluorescence; its fluorescence does not overlap with emission wavelengths that other red fluorescent markers use. Furthermore, the MitoBright ROS Deep Red is better able to selectively detect superoxide, compared to Company T' product Red.
Altogether, MitoBright ROS Deep Red is a powerful tool for researchers with a limited number of cells and can provide an understanding of how mitochondria are altered during different treatments and physiological or pathological states.
Manual
Technical info
Comparison with other products
MitoBright ROS Deep Red has higher superoxide selectivity than Company T's existing product Red.
.png)
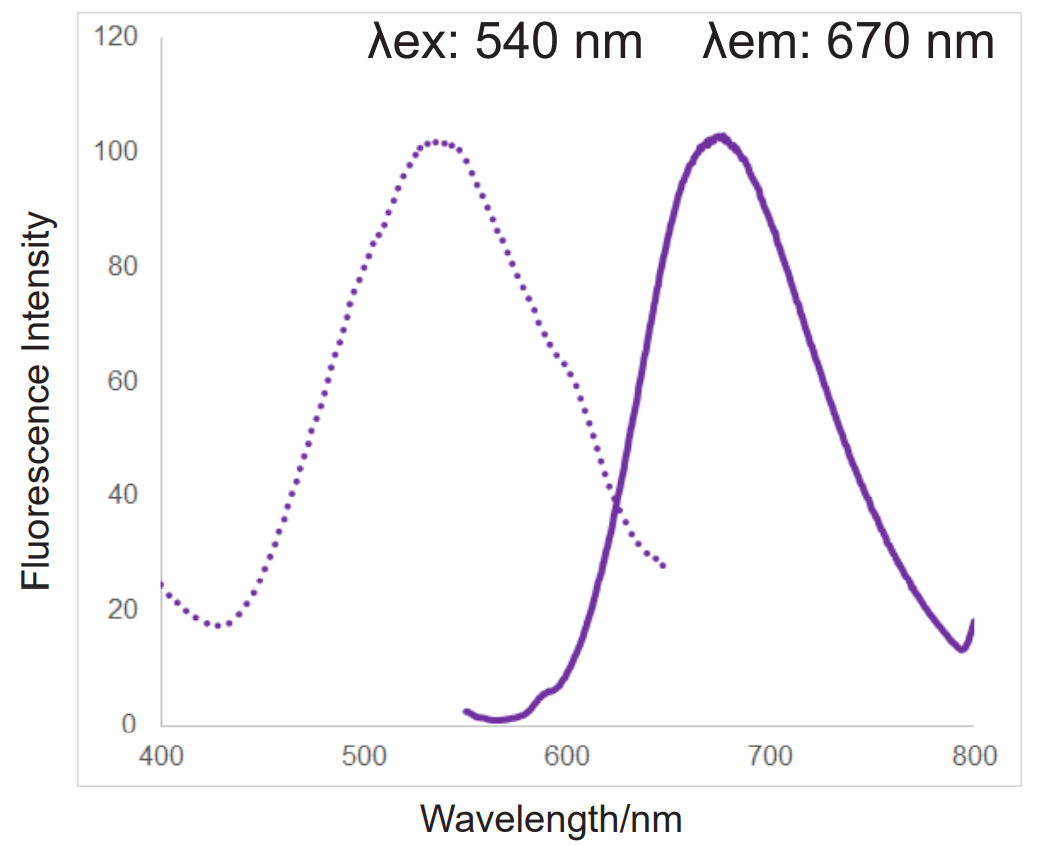
In addition, MitoBright ROS Deep Red has a special fluorescence spectrum (λex: 540 nm, λem: 670 nm), making it possible to co-staining with mitochondrial membrane potential reagent (JC-1, code: MT09, TMRE, MT-1, code: MT13), which is difficult for others mitochondrial superoxide reagent.
| MitoBright ROS Deep Red | Company T's product Red | |
| Appearance | Solid | Solid |
| Live cell staining | ✓ | ✓ |
| Fixation after staining | NA | NA |
| Fluorescence property | λex : 540 nm , λem : 670 nm | λex : 510 nm , λem : 580 nm |
Company T's product Red tends to localize to DNA in cells, but MitoBright ROS Deep Red does not localize to DNA. This is because MitoBright ROS does not have the ability to bind to DNA. This avoids false positives due to binding to DNA and allows for more accurate observation of mitochondrial superoxide.
Application Data: Simultaneously evaluation of mitochondrial superoxide and membrane potential
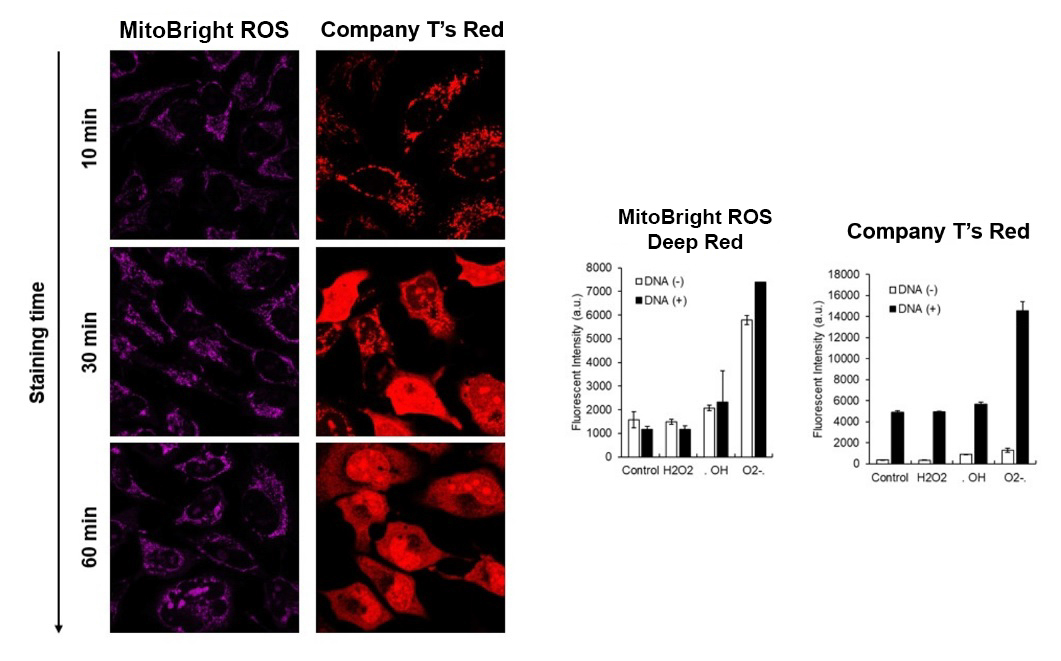
After HeLa cells were washed with HBSS, co-stained with MitoBright ROS Deep Red and mitochondrial membrane potential staining dye (JC-1, code: MT09 or MT-1, code: MT13), and the generated mitochondrial superoxide and membrane potential were observed simultaneously. As a result, the decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential and the generation of mitochondrial superoxide are simultaneously observed.
<General protocol of JC-1>
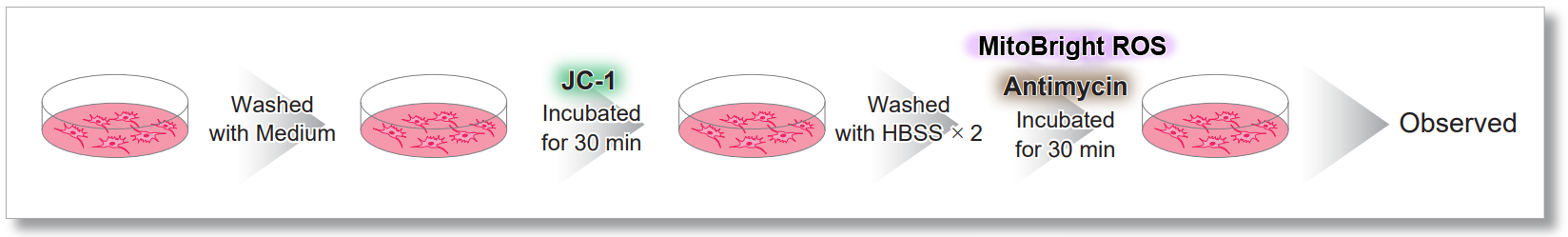
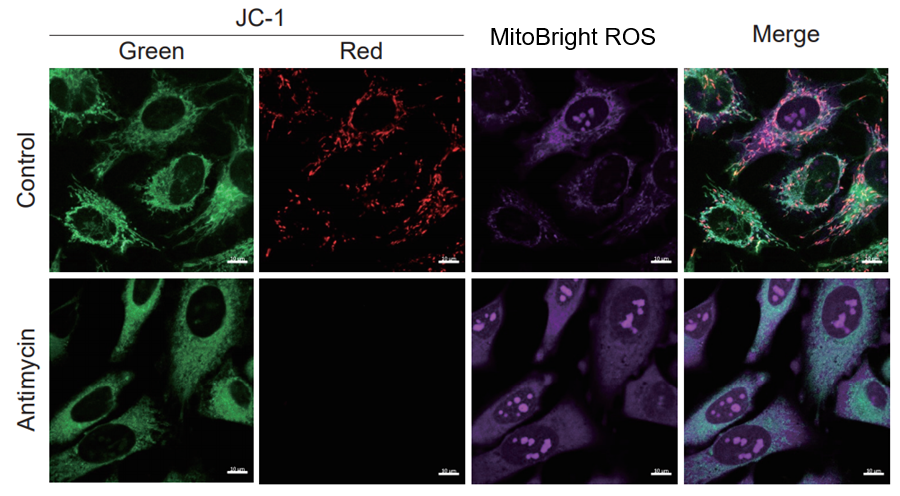

<Imaging Conditions>(Confocal microscopy)
JC-1: Green Ex = 488, Em = 490-520 nm, Red: Ex = 561, Em = 560-600 nm
MitoBright ROS:Ex = 633 nm, Em = 640-700 nm
Scale bar: 10 μm

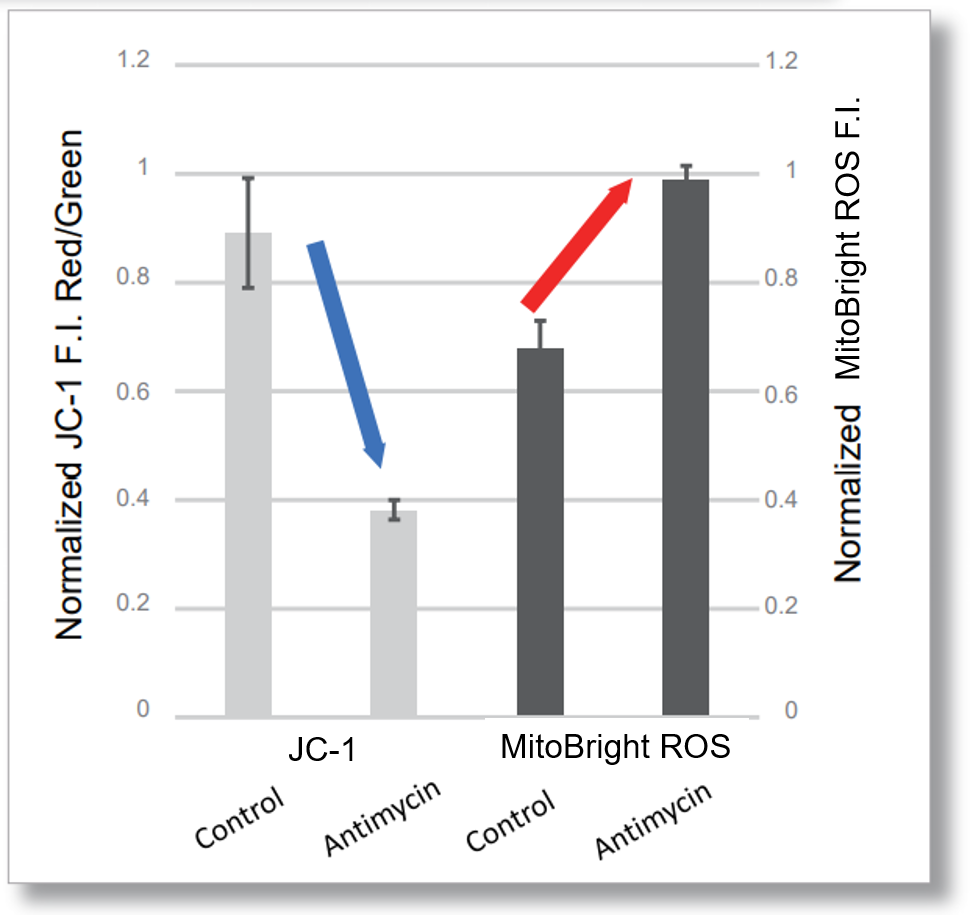
<Examination Conditions>(Plate Reader)Tecan, Infinite M200 Pro
JC-1: Green Ex=480-490 nm, Em=525-545 nm; Red: Ex= 530-540 nm, Em=585-605 nm
MitoBright ROS : Ex=545-555 nm, Em = 665-685 nm
<General Protocol of MT-1>

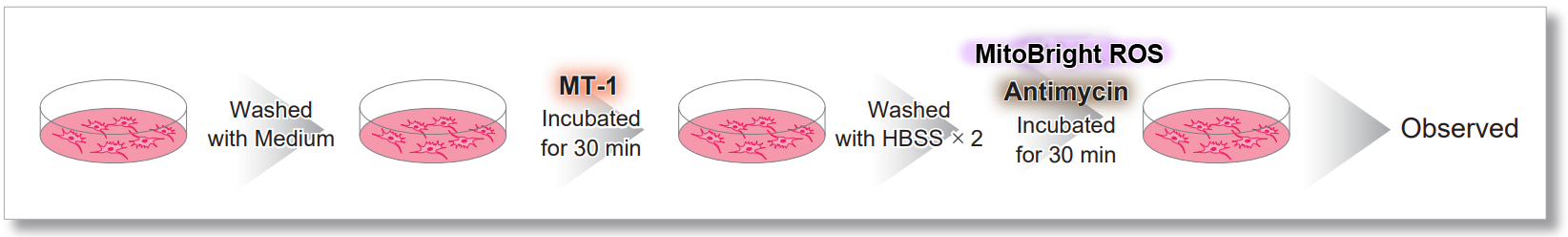

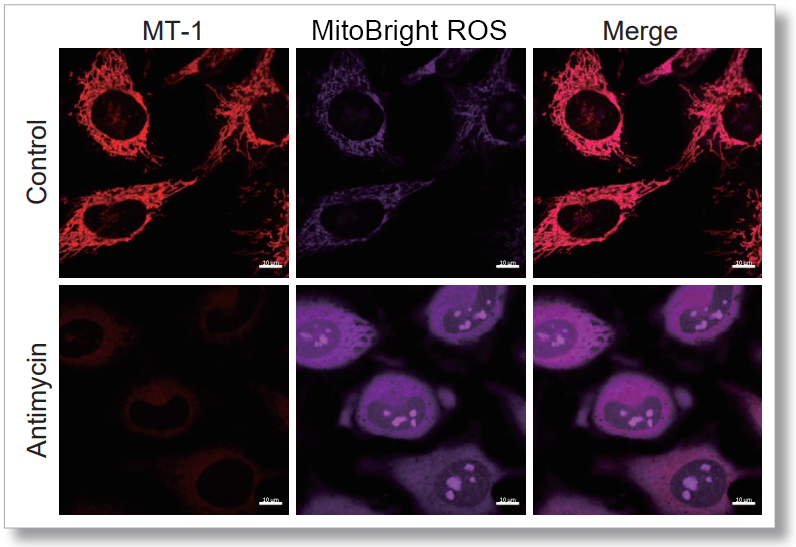
<Imaging Conditions>(Confocal microscope)
MT-1: Ex=561, Em=560-600 nm
MitoBright ROS : Ex=633 nm, Em=640-700 nm
Scale bar: 10 μm

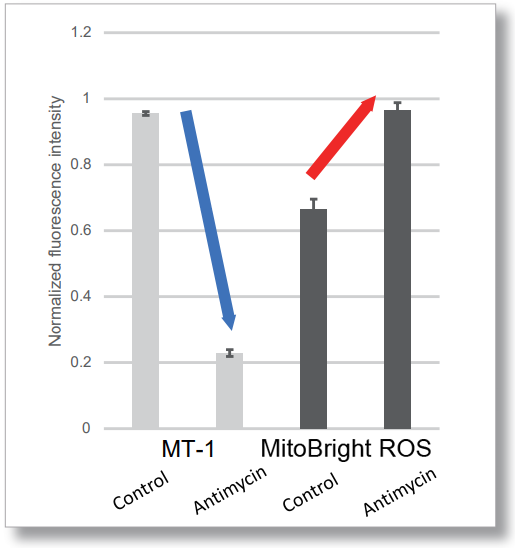
<Examination Conditions>(Plate Reader)Tecan, Infinite M200 Pro
MT-1: Ex=540-550 nm, Em=590-610 nm (Gain=200)
MitoBright ROS : Ex=545-555 nm, Em = 665-685 nm
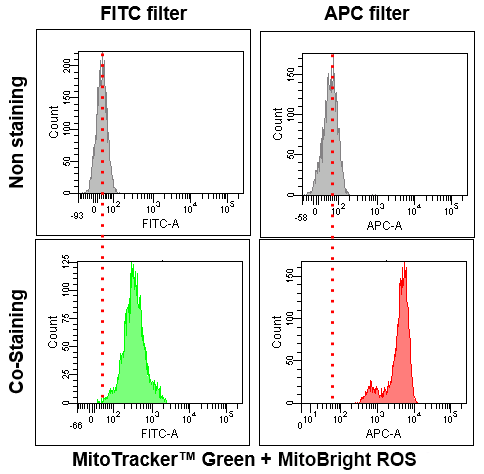
Application Data: Co-Staining with Mitochondrial Fluorescent probe(Company T's Product Green)
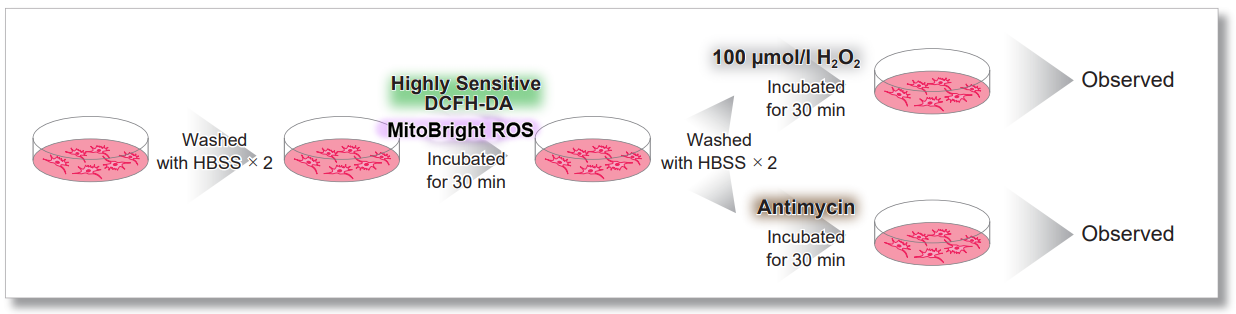
Application Data: Simultaneously evaluation of mitochondrial superoxide and intracellular total ROS
HeLa cells were washed with HBSS and co-stained with MitoBright ROS and intracellular total ROS reagent (ROS Assay Kit -Highly Sensitive DCFH-DA-: code R252), and separately treated with mitochondrial superoxide inducer Antimycin or hydrogen peroxide.
As a result, intracellular total ROS and mitochondrial superoxide were observed separately.
General Protocol

Treated with H2O2
.png)
Treated with Antimycin
.png)
<Imaging Conditions>(Confocal microscopy)
Intracellular ROS: Ex = 488, Em = 490-520 nm
MitoBright ROS : Ex = 633 nm, Em = 640-700 nm
Scale bar: 10 μm
Application Data: Co-staining with DHE(Total ROS Probe)
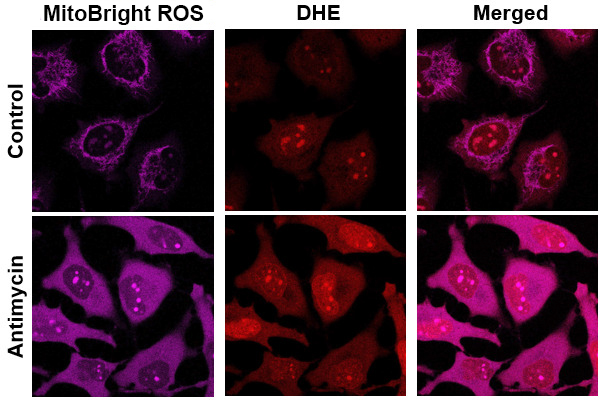
MitoBright ROS Deep Red is applicable for multiple staining with DHE (total ROS probe).
Application Data: Simultaneously evaluate mitochondrial mass, membrane potential and mitochondrial superoxide
HeLa cells stained with nuclear staining reagent (Hoechst33342: code H342), mitochondrial mass detection dye (MitoTrackerTM Green FM), and mitochondrial membrane potential detection dye (Tetramethylrhodamine ethyl ester (TMRE)). The cells were washed with HBSS and stained with MitoBright ROS Deep Red working solution containing Antimycin, and the generated mitochondrial superoxide and membrane potential, mitochondrial mass, and nuclei were observed simultaneously.
As a result, the decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential associated with the generation of mitochondrial superoxide without any change in mitochondrial mass was simultaneously observed.

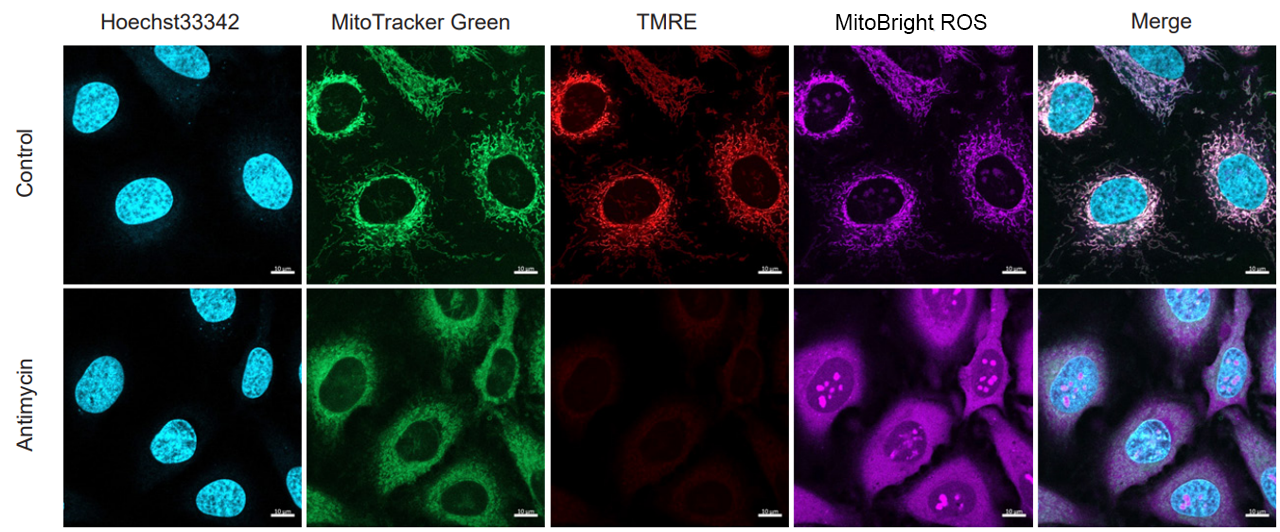
<Imaging Conditions>(Confocal microscopy)
(Blue) Nucleus: Hoechst33342 (Ex=405, Em=450-495 nm)
(Green) Mitochondrial Mass: MitoTrackerTM Green FM (Ex=488 nm, Em=500-550 nm)
(Red) Mitochondrial Membrane Protential: TMRE (Ex=561 nm, Em=560-620 nm)
(Deep Red) Mitochondrial Superoxide: MitoBright ROS Deep Red (Ex=633 nm, Em=640-700 nm
Scale bar: 10 μm
The general number of usable assays per 100 nmol
・96-well plate X 1
・ibidi 8-well plate X 6
・35 mm dish X 5
Application Data: Mitochondrial superoxide detection in senescent cells
-Tips for minimal the endogenous fluorescence from lipofuscin-
Influence of Lipofuscin on Cellular Senescence Research
Senescent cells are known to accumulate oxidatively damaged proteins called lipofuscin, which are not degraded by lysosomes, and mitochondria as insoluble substances in lysosomes, causing an increase in the background during fluorescence observation. In cellular senescence research, it is necessary to minimize the effect of endogenous fluorescence from lipofuscin and other substances.
With a Better Fluorescent Probe
We observed mitochondrial superoxide in proliferating (passage 2) and senescent (passage 14) TIG-1 cells (human fetal lung-derived fibroblasts) using a product from Company T and MitoBright ROS Deep Red - Mitochondrial Superoxide Detection from Dojindo Laboratories.
As a result, in the case of Company T's product (staining concentration: 5 μmol/l), background fluorescence was observed in addition to mitochondrial fluorescence in both proliferating and senescent cells. This background fluorescence was found to be endogenous fluorescence from the images of unstained cells. On the other hand, when MitoBright ROS Deep Red (staining concentration: 1 μmol/l) was used, mitochondria superoxide-derived fluorescence could be observed with less influence of background fluorescence. When observing the mitochondrial superoxide, it is important to compare the sensitivity, wavelength, and channels, then observe with a proper fluorescent probe in order to minimize the endogenous fluorescence.
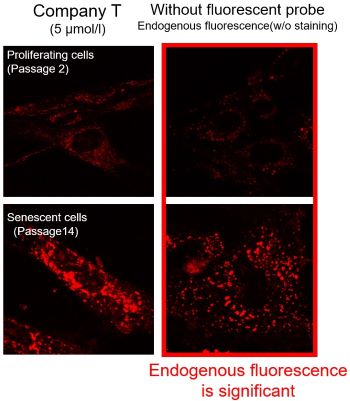
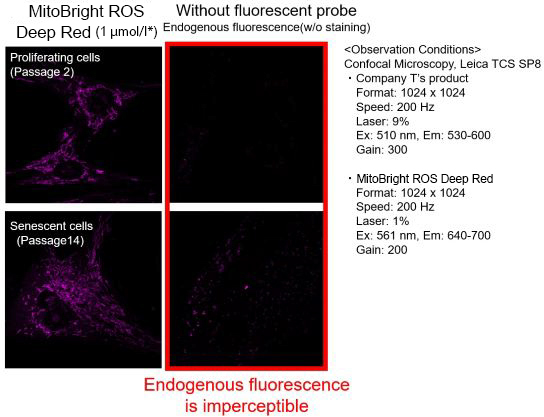
※The optimal concentration of MitoBright ROS varies from cell to cell. For a discussion of the different effects of endogenous fluorescence at different staining concentrations, please refer to the FAQ When I observe senescent cells, I observe fluorescence outside of the mitochondria. What should I watch out for?.
<Experimental Data>
Kindly be provided by Prof. Fujita Yasunori, Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Gerontology.
<Reference>
Y. Fujita, M. Iketani, M. Ito and I. Ohsawa, “Temporal changes in mitochondrial function and reactive oxygen species generation during the development of replicative senescence in human fibroblasts", Exp. Gerontol., 2022, 165, 111866.
Fluorescence spectra

References
| No. | Sample Type | Instrument | Reference (Link) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1) | Cell (NRK52E) |
Microscope | D. Sun, S. Cui, H. Ma, P. Zhu, N. Li, X. Zhang, L. Zhang, L. Xuan, J. Li, "Salvianolate ameliorates renal tubular injury through the Keap1/Nrf2/ARE pathway in mouse kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury", 2022, J. Ethnopharmacol., doi:10.1016/j.jep.2022.115331. |
| 2) | Cell (TIG-1 Cell) |
Microscope | Y. Fujita, M. Iketani, M. Ito, I. Ohsawa, "Temporal changes in mitochondrial function and reactive oxygen species generation during the development of replicative senescence in human fibroblasts", 2022, doi:10.1016/j.exger.2022.111866. |
| 3) | Cell (MIN6-M9) |
Microscope | R. Inoe, T. Tsuno, Y. Togashi, T. Okuyama, A. Sato, K. Nishiyama, M. Kyohara, J. Li, S. Fukushima, T. Kin, D. Miyashita, Y. Shiba, Y. Atobe, H. Kiyonari, K. Bando, A. S. Shapiro, K. Funakoshi, R. N. Kulkarni, Y. Terauchi, and J. Shirakawa, "Uncoupling protein 2 and aldolase B impact insulin release by modulating mitochondrial function and Ca2+ release from the ER", 2022, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2022.104603. |
| 4) | Cell (Endothelial Cell) |
Microscope | A. Patel, M. Simkulet, S. Maity, M. Venkatesan, A. Matzavinos, M. Madesh & B. R. Alevriadou, "The mitochondrial Ca2+ uniporter channel synergizes with fluid shear stress to induce mitochondrial Ca2+ oscillations", 2022, Sci. Rep., doi:10.1038/s41598-022-25583-7. |
| 5) | Cell (BV2 Cell) |
Microscope | Y. Yan, R. Zheng, Y. Liu, Y. Ruan, Z. Lin, N. Xue, Y. Chen, B. Zhang, J. Pu , "Parkin regulates microglial NLRP3 and represses neurodegeneration in Parkinson's disease", Aging Cell, 2023, doi:10.1111/acel.13834. |
| 6) | Cell (B Cell) |
Flow Cytometer | Y. F. Yazicioglu, E. Marin, C. Sandhu, S. Galiani, I. G. A. Rza, Mohammad Ali, B. Kronsteiner, E. B. Compeer, M. Attar, S. J. Dunachie, M. L. Dustin, A. J. Clarke, "Dynamic mitochondrial transcription and translation in B cells control germinal center entry and lymphomagenesis", Nat. Immunol., 2023, doi:10.1038/s41590-023-01484-3. |
Q & A
-
Q
What is the detection principle of MitoBright ROS Deep Red?
-
A
MitoBright ROS Deep Red is a fluorescent dye that is selectively oxidized by superoxide.
This dye localizes to intracellular mitochondria in a membrane-potential-dependent manner, allowing for the specific detection of mitochondrial superoxide.
When mitochondrial membrane potential disappears following superoxide induction, dye is dispersed throughout the nucleolus and cytoplasm.
-
Q
Is it possible to prepare the working solution with buffers other than culture medium?
-
A
Yes, the working solution can be produced using HBSS or PBS
-
Q
What instruments are available, and what filters are appropriate?
-
A
The signal can be detected via confocal microscopy, epi-fluorescence microcopy, microplate reader, and flow cytometry.
・Confocal laser microscopy
Ex: 561, Em: 640-670 nm (Single staining)
Ex: 633, Em: 640-670 nm (Co-staining with red fluorescent dye)
・Epi-fluorescence microscopy
Texas Red filter
・Microplate reader
Ex/Em: 550/675 nm (Bottom reading)
・Flow cytometry
APC filter
-
Q
Is it possible to stain after stimulation/superoxide induction?
-
A
This is possible under conditions where the mitochondrial membrane potential does not decrease.
This dye accumulates in mitochondria in a membrane-potential-dependent manner. Thus, if the membrane potential is decreased via stimulation, the dye cannot accumulate in the mitochondria. Therefore, the dye cannot detect accurate superoxide, as the stain will be inaccurate.
Thus, we recommend pre-stimulus staining.
-
Q
What is the difference in mitochondrial specificity between MitoBright ROS Deep Red and MitoSOX™ Red?
-
A
MitoSOX™ Red tends to accumulate in the nucleus as the staining time increases, whereas MitoBright ROS Deep Red does not accumulate in the nucleus.
However, depending on the type of drug treatment, localization may be seen in nucleolus and other non-mitochondrial organelles.
(Signal change similar to that of MitoSOX™ Red)
Detection of superoxide in HeLa cells treated with antimycin by MitoBright ROS Deep Red and MitoSOX™ Red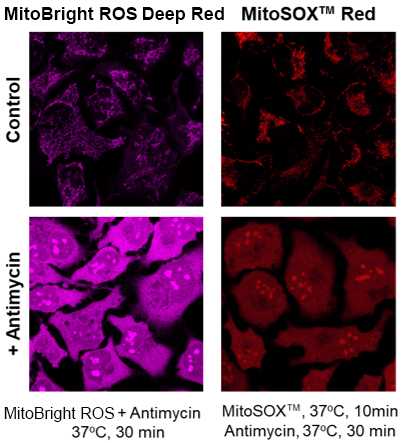
-
Q
When I observe senescent cells, I observe fluorescence outside of the mitochondria. What should I watch out for?
-
A
Please check the following two experimental conditions.
(1)Observation Conditons
Prepare stained and unstained cells and observe under conditions with a minimized endogenous fluorescence.(2)Probe Concentration
The optimal concentration of MitoBright ROS depends on the cells; consider a range of 1-10 μmol/l as a guide.(For your reference)
TIG-1 cells (human fetal lung-derived fibroblasts, step 14) were stained with 1, 10 μmol/l MitoBright ROS and observed. 1 μmol/l cells were observed with less endogenous fluorescence.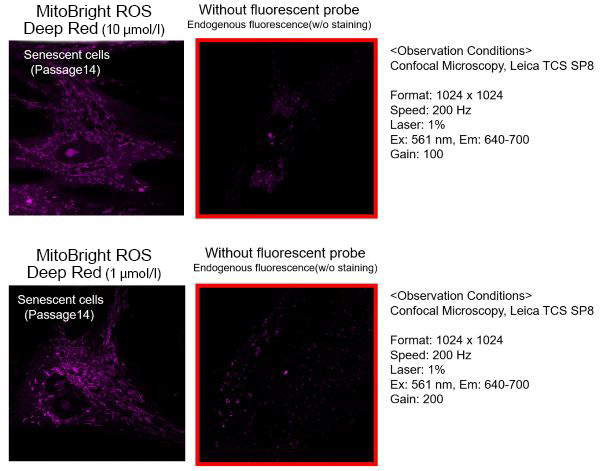
<Experimental Data>
Kindly be provided by Prof. Fujita Yasunori, Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Gerontology.
Handling and storage condition
| 0-5°C |