Lysosome Function Analysis - Selection Guide for Detection and Imaging Reagent / Probe / Kit
Science Note
[Jun. 24, 2025] Previous Science Note
Why Lysosomes Deserve Your Attention in Cancer and Neurodegeneration
|
Lysosomal Dysfunction Directly Contributes to Disease Progression Recent studies have shown that lysosomal dysfunction plays an active role in disease mechanisms. In Alzheimer’s disease, impaired lysosomal acidification prevents the clearance of amyloid-beta, leading to autophagic vacuole buildup and toxic plaque formation. In cancer, dysregulated lysosomal iron triggers lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis, offering a path to eliminate treatment-resistant cells. These findings position lysosomes as key players in both pathological progression and therapeutic response. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Summary: Lysosomal dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease impairs acidification, disrupting the breakdown of amyloid-beta (Aβ) and related proteins. As a result, autophagic vacuoles build up and form flower-like structures, leading to cell death and plaque formation. Highlighted technique: This study used a neuron-specific transgenic fluorescent protein (mRFP-eGFP-LC3) to monitor lysosomal acidification. Because eGFP loses its signal in acidic environments while mRFP remains stable, reduced acidification could be detected by comparing the two signals using confocal and electron microscopy. Related technique Accurate lysosomal detection / Autophagic Flux Assay Kit |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Activation of lysosomal iron triggers ferroptosis in cancer (Nature, 2025) Summary: When lysosomes lose control of iron activity, they can trigger damaging reactions that lead to ferroptosis. This hidden malfunction offers a new way to target treatment-resistant cancer cells, positioning lysosomes as a key focus in drug development. Highlighted technique: This study visualized lysosomes using LAMP1 immunostaining and Lysosome specific probes, allowing detection of structural and acidification changes. In addition, lipid peroxidation and iron accumulation were monitored together with lysosomes to evaluate their involvement in ferroptosis. Related technique Intracellular Iron Detection, Lipid Peroxide Detection (used in this article) |
||||||||||||||||||||||
All Related Techniques (click to open/close)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Application Note (click to open/close)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
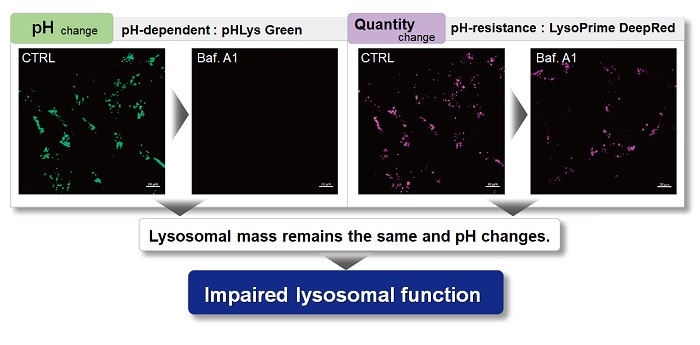
With existing reagents, it was difficult to determine whether lysosomal mass or their function (pH) fluctuated because the discussion was based on changes in the fluorescence brightness of a single dye. This kit contains pHLys Green, which is highly specific to lysosomes and shows pH-dependent changes in fluorescence, and pH-resistant LysoPrime Deep Red. Using these two dyes, lysosomal pH and volume of the same sample can be measured for a detailed analysis of lysosomal function.
|
|||
| Existing lysosomal pH detection reagents have issues with dye localization, pH sensitivity, and retention. pHLys Green is a dye that solves these issues. The improved dye retention and localization enable detection of normal lysosomes, and the improved pH sensitivity enables detection of slight pH changes. | |||
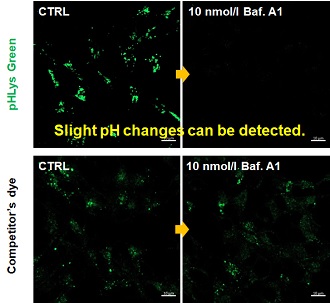
| 1. High sensitive pH detection Comparison of pH response of cells treated with low concentrations of lysosomal acidification inhibitor Bafilomycin A1 |
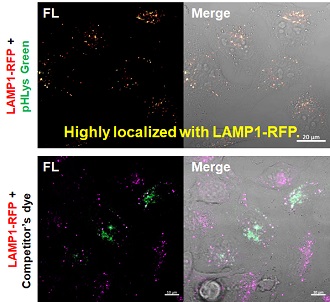
2. High specificity for lysosomes Comparison of specificity for lysosomes using lysosomal marker protein LAMP1-GFP expressing cells |
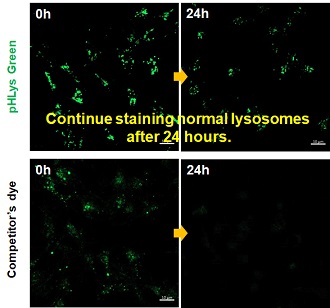
3. High retention in lysosomes Comparison of intracellular retention |
|
 |
 |
 |
|
|
Product in Use: Related Product: |
|||
Topics
- What is Lysosome?
- How to Analyze Lysosomal Function?
- Lysosome Staining Reagents and Kits
- Experimental Example: Effect of lysosomal acidification inhibitor on endocytic vesicle fusion with lysosome
- Experimental Example: Effect of mitochondrial inhibitors on lysosomal function
- Experimental Example: Measurement of intracellular iron changes and lysosomal pH changes
What is Lysosome?
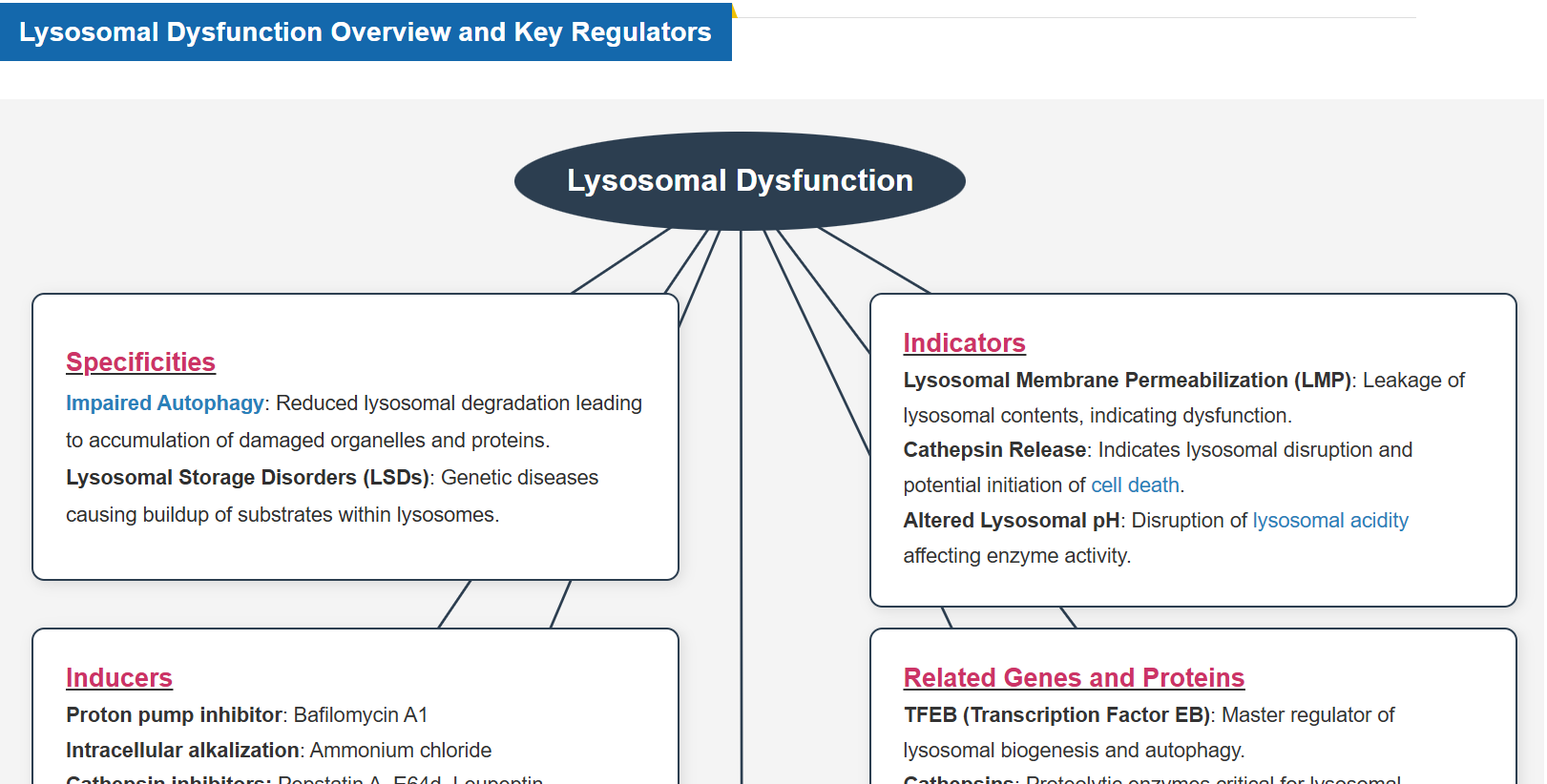
 Lysosomes are essential for maintaining cell homeostasis by degrading and recycling biomolecules, regulating organelle quality control, and facilitating intracellular signaling. Lysosomal function is closely linked to the Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, and nucleus, coordinating cellular metabolism and stress responses. When lysosomal function is impaired, damaged proteins and organelles accumulate, metabolic processes are disrupted, and cell membrane integrity is compromised, leading to various diseases. For example, in neurodegenerative diseases, lysosomal dysfunction leads to the accumulation of toxic aggregates, resulting in neuronal damage and cognitive decline. Understanding lysosomal regulation and its interactions with other organelles is critical for developing therapies to slow disease progression and promote cellular longevity.
Lysosomes are essential for maintaining cell homeostasis by degrading and recycling biomolecules, regulating organelle quality control, and facilitating intracellular signaling. Lysosomal function is closely linked to the Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, and nucleus, coordinating cellular metabolism and stress responses. When lysosomal function is impaired, damaged proteins and organelles accumulate, metabolic processes are disrupted, and cell membrane integrity is compromised, leading to various diseases. For example, in neurodegenerative diseases, lysosomal dysfunction leads to the accumulation of toxic aggregates, resulting in neuronal damage and cognitive decline. Understanding lysosomal regulation and its interactions with other organelles is critical for developing therapies to slow disease progression and promote cellular longevity.
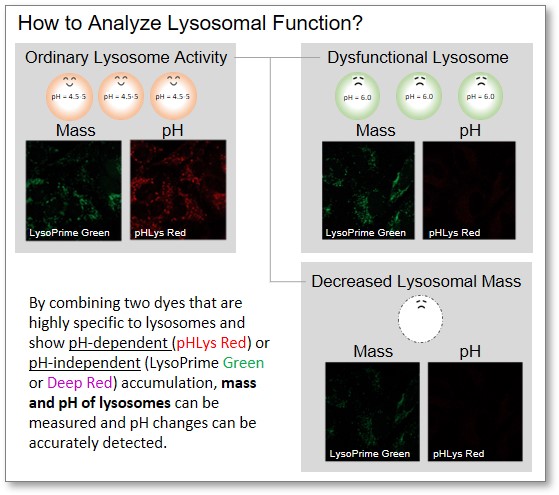
How to Analyze Lysosomal Function?
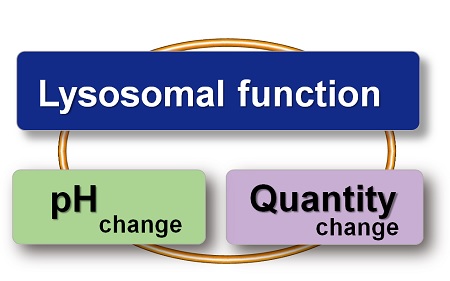
When conventional dyes are used to analyze lysosomal function, it is difficult to determine whether the lysosomal mass or their function (pH) has changed because the analysis is based only on the fluorescence intensity of a single dye.
Dojindo's kits contain two types of dyes: pHLys Red/Green, which shows a lysosomal pH-dependent change in fluorescence intensity, and LysoPrime Green/Deep Red, which is lysosomal pH-resistant. By combining these two dyes, the lysosomal function can be analyzed in detail by simultaneously analyzing lysosomal mass and pH.
Lysosome Staining Reagents and Kits
Explore Dojindo's wide range of lysosomal staining and pH detection dyes. Choose the following kit or reagent that aligns with your experimental requirements.
| Product Name (Item Code) |
Supported Devices | Indicator and Detection Color | Dyes and Fluorescence Properties |
Approximate Number of Use |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
||||
| Lysosomal Acidic pH Detection Kit-Green/Deep Red (L268) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | pH | pHLys Green Ex: 488 nm / Em: 490-550 nm |
[for 1 set] 35 mm dish: 10 dishes μ-Slide 8 well: 10 plates 96-well Plate: 2 plates |
| quantity | LysoPrime Deep Red Ex: 633 nm / Em: 640-700 nm |
|||||
| Lysosomal Acidic pH Detection Kit-Green/Red (L266) | ✓ | Need G/Y Laser G:532 nm Y:561 nm |
✓ | pH | pHLys Red Ex: 561 nm / Em: 560-650 nm |
|
| quantity | LysoPrime Green Ex: 488 nm / Em: 500-600 nm |
|||||
| pHLys Red- Lysosomal Acidic pH Detection (L265) | ✓ | ✓ | pH | pHLys Red Ex: 561 nm / Em: 560-650 nm |
[for 1 tube] 35 mm dish: 10 dishes μ-Slide 8 well: 10 plates 96-well Plate: 2 plates |
|
| LysoPrime Deep Red - High Specificity and pH Resistance (L264) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | quantity | LysoPrime Deep Red Ex: 633 nm / Em: 640-700 nm |
|
| LysoPrime Green- High Specificity and pH Resistance (L261) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | quantity | LysoPrime Green Ex: 488 nm / Em: 500-600 nm |
[for 10 μl] 35 mm dish: 10 dishes μ-Slide 8 well: 10 plates 96-well Plate: 2 plates |
Experimental Example: Effect of lysosomal acidification inhibitor on endocytic vesicle fusion with lysosome
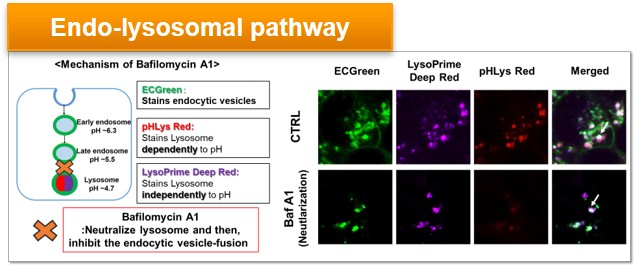
Endocytic vesicles were labeled by ECGreen and the lysosomal mass and pH were detected separately with LysoPrime Deep Red and pHLys Red. Co-staining with ECGreen and Lysosomal dyes showed the inhibition of endocytic vesicle-fusion induced by Bafilmycin A1.
Experimental Example: Effect of mitochondrial inhibitors on lysosomal function
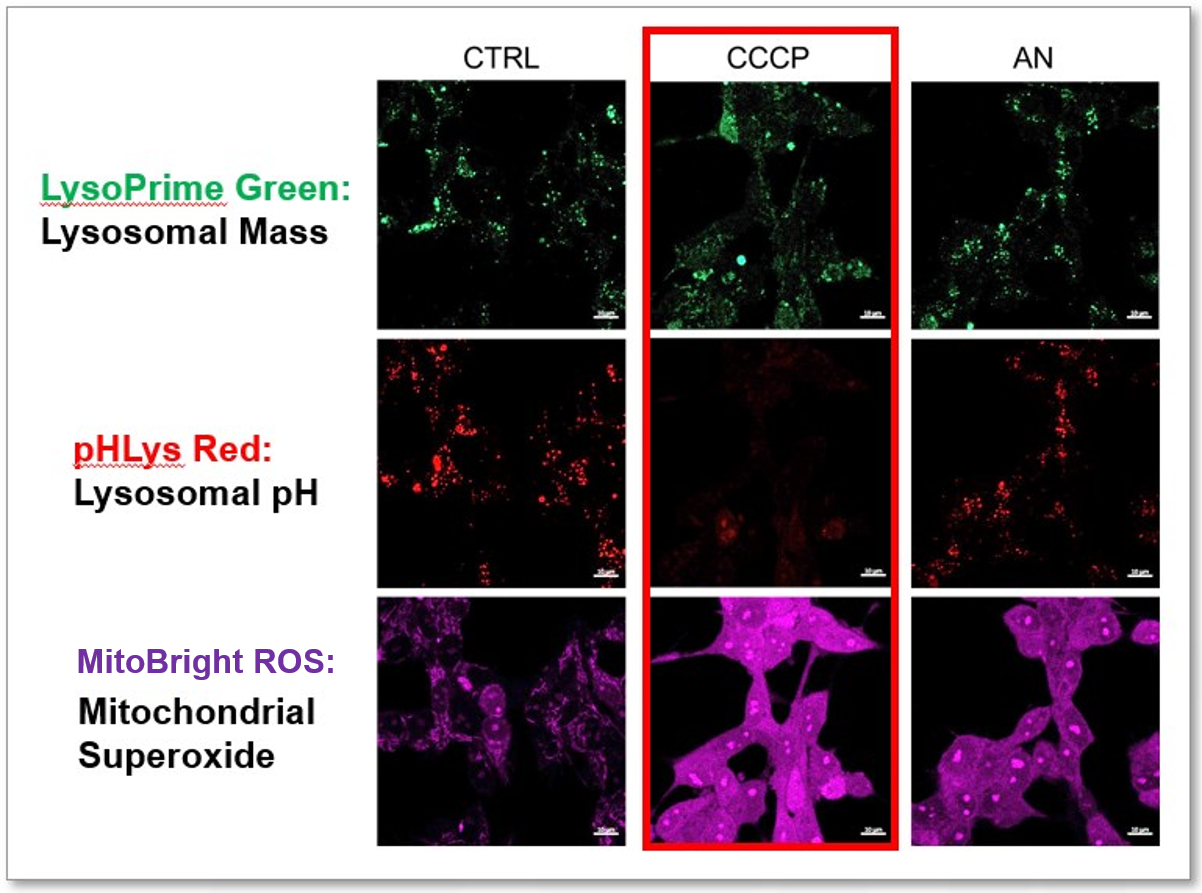
CCCP and Antimycin are recognized inducers of mitochondrial ROS, linked to the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential. Recent studies have shown that CCCP induces not only mitochondrial ROS but also lysosomal dysfunction. To observe mitochondrial ROS, HeLa cells were labeled with MitoBright ROS Deep Red for Mitochondrial Superoxide Detection, and the lysosomal mass and pH were independently detected with LysoPrime Green and pHLys Red. Co-staining with MitoBright ROS and Lysosomal dyes revealed that CCCP, unlike Antimycin, triggers concurrent lysosomal neutralization and mitochondrial ROS induction.
Reference: Benjamin S Padman, et. al., Autophagy (2013)
Products in Use
- LysoPrime Green
- pHLys Red
- Lysosomal Acidic pH Detection Kit
- MitoBright ROS Deep Red - Mitochondrial Superoxide Detection
Related Products
- Mitophagy Detection Kit and Mtphagy Dye
Experimental Example: Measurement of intracellular iron changes and lysosomal pH changes
In neurodegenerative diseases, the relationship between lysosomal function and iron has attracted attention, and it has been reported* that lysosomal neutralization prevents the breakdown of iron stores (Transferrin or Ferritin), resulting in a decrease in intracellular iron.
Lysosomal pH changes and intracellular iron changes in the same sample were detected using SH-SY5Y cells supplemented with lysosomal acidification inhibitor (Bafilomycin A1) or iron chelator (Deferipron (DFP)). (Lysosomal pH: Lysosomal Acidic pH Detection kit - Green/Deep Red, Intracellular iron: FerroOrange [Code:F374])
The results showed that the addition of Bafilomycin A1 decreased the fluorescence of FerroOrange, confirming the decrease in intracellular iron. The fluorescence of LysoPrime DeepRed remained almost unchanged, while the fluorescence of pHLys Green decreased due to lysosomal neutralization. These results suggest that there is a relationship between changes in intracellular iron and lysosome function.
*Mol Cell., 2020, 77(3), 645-655.
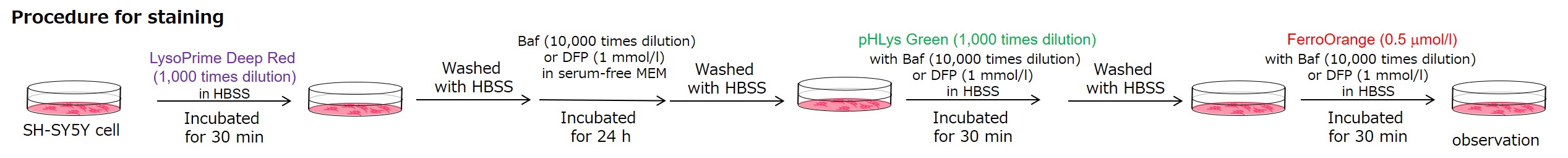
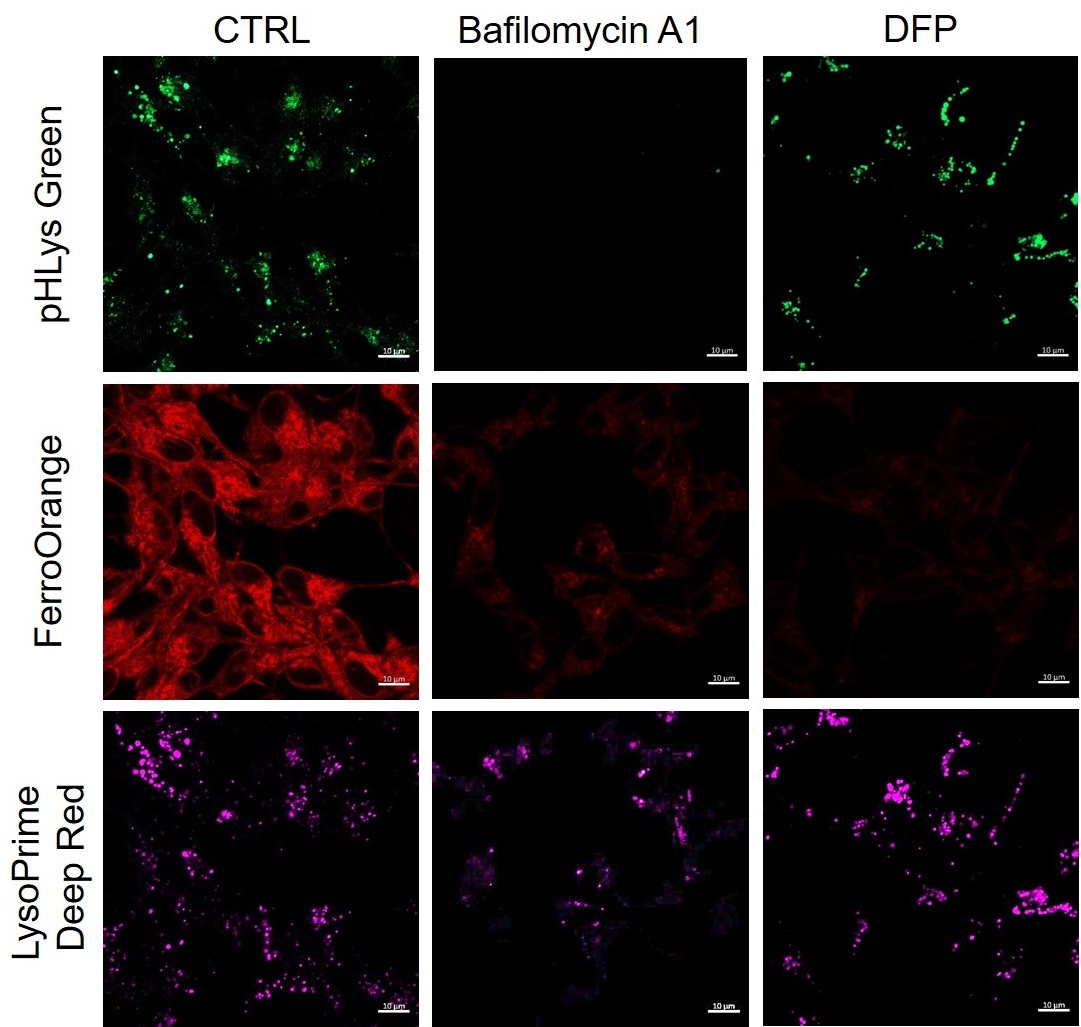
<Condition>
pHLys Green (Green) : Ex=488 nm, Em=486-574 nm
FerroOrange (Red) : Ex=561 nm, Em=550-650 nm
LysoPrime Deep Red (Violet) : Ex=633 nm, Em=599-700 nm