Detect Cell Death: Apoptosis, Necrosis & Ferroptosis
Science Note
Cell Death Membrane Features in Vesicles [Feb 10, 2026] Previous Science Note
|
Cell death involves plasma membrane rupture or remodeling and the release of cell derived material into the extracellular space. Extracellular vesicles can serve as carriers for such material, and how death associated membrane features are incorporated into vesicles and influence the local response after cell death is an important mechanistic question. Recent work shows that pyroptotic cells release vesicles bearing preformed gasdermin D pores, and these pores can transfer to neighboring nonpyroptotic cells and trigger lytic membrane disruption. A separate study shows that adherent apoptotic cells leave actin rich remnants that later round up into large phosphatidylserine positive vesicles that are engulfed by macrophages. Together, these findings indicate that membrane features generated during cell death can be externalized via extracellular vesicles and linked to the local response after cell death. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Summary: Pyroptosis is an inflammatory form of cell death in which gasdermin D (GSDMD) forms pores in the plasma membrane, leading to membrane rupture. In this study, pyroptotic cells were shown to release extracellular vesicles (EVs) carrying pre-formed GSDMD pores, which can transplant these pores onto nearby cells not undergoing pyroptosis, causing lytic membrane disruption and suggesting how tissue injury and inflammation may spread in vivo. Highlighted technique: To test whether membrane pores generated during pyroptosis can spread to neighboring cells via EVs, the authors used a transwell system and confirmed that pyroptotic cells can induce cell death in physically separated, non-contact cells. They then isolated EVs from pyroptotic cell supernatants by ultracentrifugation and size-exclusion chromatography, analyzed EV populations containing fluorescently labeled GSDMD by flow cytometry, and confirmed that these EVs can induce cell death in nearby cells. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Summary: When adherent cells undergo apoptosis, they leave actin-rich “footprints of death” (FOOD) that remain anchored at the death site and later round up into large extracellular vesicles (EV) exposing phosphatidylserine. By keeping an “eat-me” signal fixed at the site of cell death and generating vesicles that are engulfed by macrophages, FOOD can act as a local flag that promotes clearance of apoptotic debris. Highlighted technique: To observe the formation of “footprints of death” (FOOD) and their conversion into FOOD-derived apoptotic extracellular vesicles (F-ApoEV), the authors performed live-cell 3D time-lapse imaging of apoptotic adherent cells after membrane labeling, while monitoring phosphatidylserine exposure with Annexin V and visualizing nuclei. This approach allowed them to track flat FOOD structures that remain beneath cells as they shrink and detach, and to follow their local rounding on the surface into large vesicles (F-ApoEV) at the site of cell death. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cell Death Indicators (click to open/close)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Application Note (click to open/close)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Topics
- What is Cell Death?
- Cell death detection methods
- Multiple cell death indicators can be measured in combination with Dojindo's kits!
- Experimental Example: Changes in various indicators of cell death induced by drugs
- Experimental Example: Evaluation using apoptosis inhibitors
- Experimental Example: Evaluation using Erastin-treated cells
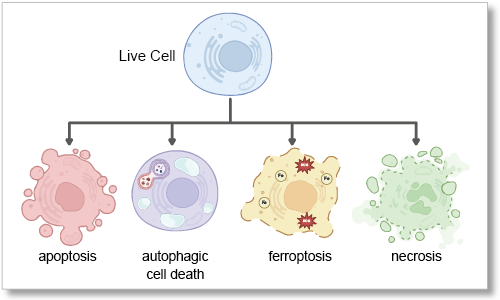
What is Cell Death?
|
Cell death is a fundamental biological process essential for tissue homeostasis and stress response. Traditionally, programmed cell death, known as apoptosis, has been recognized as a key mechanism, while necrosis has been considered an unregulated response to injury. However, recent research has identified additional forms of programmed cell death, including ferroptosis, driven by iron-dependent lipid peroxidation, and autophagy-dependent cell death, resulting from excessive self-digestion of cellular components. Dysregulation of these pathways contributes to various cell death diseases, such as cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and ischemic injury, where either evasion or excessive activation of cell death disrupts normal function. Understanding these mechanisms provides new therapeutic insights for cancer and other cell death-related diseases.
|
Cell death detection methods
Cell viability /Cytotoxicity Assay
| Category | Detection method | Principle | Dojindo products |
| Cell viability /Cytotoxicity Assay | WST assay | The WST-8 is reduced by dehydrogenase activities in cells to give a yellow-color formazan dye, which is soluble in culture media. | Cell counting Kit-8 |
| Calcein assay | The amount of the fluorescent dye, calcein, hydrolyzed by esterases in cells is directly proportional to the number of viable cells. | Cell counting kit-F | |
| MTT Assay | MTT can pass through a cell membrane and is reduced by mitochondria to form a purple color formazan dye. | MTT | |
| LDH detection assay |
LDH leaks from dead cells after cell membrane breakdown. |
Cytotoxicity LDH Assay Kit-WST | |
| Extracellular ATP Assay | Extracellular ATP, known as damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), are released from stressed or activated cells. | Extracellular ATP Assay Kit-Luminescence | |
| Live / dead cell staining | Stain cells with calcein, which stains live cells, and PI, which stains dead cells, to determine whether cells are live or dead. | -Cellstain- Double Staining Kit |
Apoptosis
| Category | Detection method | Principle | Dojindo products |
| Apoptosis | Annexin V binding assay | Annexin V detection of phosphatidylserine, a hallmark of apoptosisAccurate plate assay without the need for washing. | Annexin V Apoptosis Plate Assay Kit |
| ADP/ATP Ratio Assay | It is known that ATP increases from ADP during the apoptotic process. | ADP/ATP Ratio Assay Kit-Luminescence | |
| DNA fragmentation | DNA fragmentation occurs due to the activation of the caspase cascade. | - | |
| p53 activity detection | p53 promotes apoptosis through transcription-dependent and independent mechanisms. | - | |
| Caspase activity | Apoptosis transitions to the execution phase, which is triggered by caspase-3 activation. | - | |
| Cytochrome c release | Release of cytochrome c form mitochondria to cytosol is considered sign of apoptosis. | - |
Necrosis
| Category | Detection method | Principle | Dojindo products |
| Necrosis | LDH detection assay | LDH leaks from dead cells after cell membrane breakdown. | Cytotoxicity LDH Assay Kit-WST |
| Nucleus staining | Non-membrane permeable nuclear staining dyes accumulate in the nucleus of cells with damaged cell membranes. | -Cellstain- DAPI solution -Cellstain- PI solution |
|
| RIP/RIP3/MLKL | Marker proteins involved in the necrosis pathway | - |
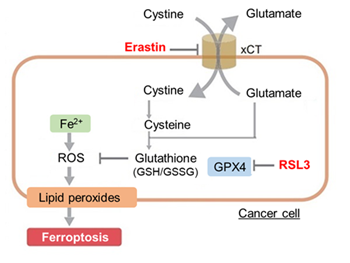
Ferroptosis
| Category | Detection method | Principle | Dojindo products |
| Ferroptosis | Ferrous ion detection | The dye stains Fe²⁺ that induces lipid peroxidation, a key factor in ferroptosis. | FerroOrange |
| Mitochondrial ferrous ion detection | The dye stains mitochondrial Fe²⁺, which is a key factor in ferroptosis. | Mito-FerroGreen | |
| Lipid peroxides detection | The dye Specifically detects lipid peroxides, an inducer of ferroptosis. | Liperfluo | |
| GSH/GSSH | Glutathione is present in cells in either the reduced form (GSH) or the oxidized form (GSSG) and protects cells from oxidative stress. | GSSG/GSH Quantification Kit | |
| Cystine detection | Cystine is imported into cells via the xCT transporter and reduced to cysteine, an important precursor for glutathione (GSH) synthesis. | Cystine Uptake Assay Kit | |
| GPX4 / SCL7A11 / Ferritin / NRF2 | Ferroptosis protein markers | - |
Autophagy-dependent cell death
| Category | Detection method | Principle | Dojindo products |
| Autophagy-dependent cell death | Autophagosome & Autolysosome Detection | Non-apoptotic autophagy-dependent cell death shows autophagic vacuolar structures. |
Autophagy Flux Assay Kit |
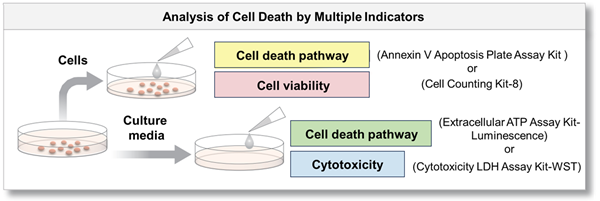
Multiple cell death indicators can be measured in combination with Dojindo's kits!
Same sample can be evaluated with multiple indicators.
By using cells and supernatant to measure each with different indicators, a more detailed analysis of cell death can be achieved.
Experimental example: Changes in various indicators of cell death induced by drugs
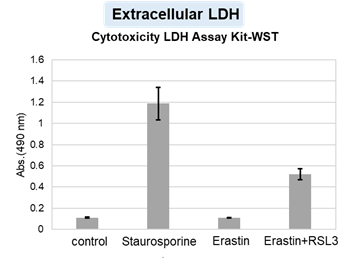
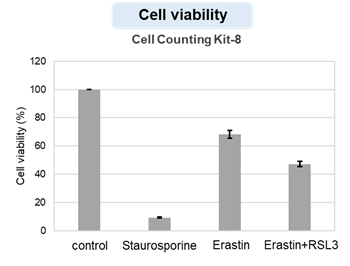
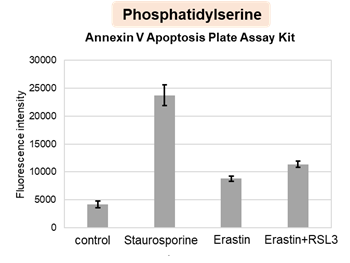
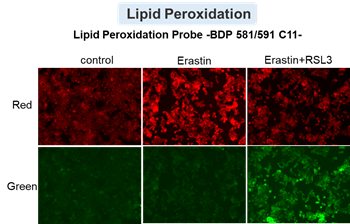
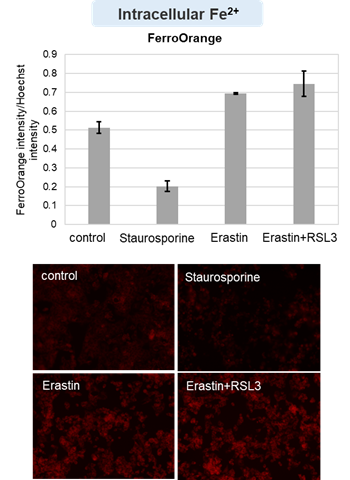
HepG2 cells treated with the apoptosis-inducing agent staurosporine or the ferroptosis-inducing agents Erastin and RSL3. After treatment, extracellular LDH, phosphatidylserine, cell viability, intracellular Fe2+ and lipid peroxidation were determined.
The results showed that apoptosis-induced cells treated with staurosporine showed an increase in phosphatidylserine, a decrease in cell viability and an increase in extracellular LDH, indicating that cell death had occurred. On the other hand, intracellular Fe2+, an indicator of ferroptosis, remained unchanged. In cells treated with Erastin, a ferroptosis inducer, intracellular Fe2+ increased and cell viability decreased, but extracellular LDH and lipid peroxidation (lipid peroxidation: decrease in red fluorescence and increase in green fluorescence) did not increase. In cells in which ferroptosis was more strongly induced by co-treatment with RSL3 in addition to Erastin, increased intracellular Fe2+ and lipid peroxidation were observed. Moreover, decreased cell viability and increased dead cells were detected. Meanwhile, phosphatidylserine showed a lower rate of increase during ferroptosis induction compared to apoptosis-induced cells. These results suggest that cell death can be distinguished by evaluating a combination of cell death indicators.
[Products in use]
Extracellular LDH : Cytotoxicity LDH Assay Kit-WST (Product code: CK12)
Phosphatidylserine: Annexin V Apoptosis Plate Assay Kit(Product code: AD12)
Cell viability : Cell Counting Kit-8 (Product code: CK04)
Intracellular Fe2+ : FerroOrange (Product cose: F374) *Normalized with Hoechst 33342 fluorescence intensity
Lipid peroxidation : Lipid Peroxidation Probe -BDP 581/591 C11- (Product code: L267)
[Experimental conditions]
Cell type: HepG2 cell(2×104 cells/well)
Drugs: Staurosporin(5 μmol/l), Erastin(25 µmol/l), Erastin+RSL3(both 25 µmol/l) *Diluted in serum-free medium
Experimental Example: Evaluation using apoptosis inhibitors
Jurkat cells were treated with or without Z-VAD, an apoptosis inhibitor, and then treated with staurosporine. After treatment, changes in extracellular ATP release, cell viability and extracellular LDH release were assessed over time. The results showed that cell death was inhibited by Z-VAD, but extracellular ATP released during the initial phase of apoptosis increased over time.
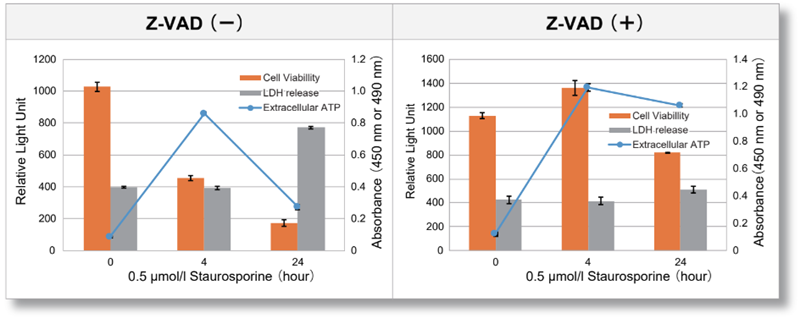
<Product in use>
Extracelluar ATP : Extracellular ATP Assay Kit-Luminescence (code:E299)
Extracellular LDH : Cytotoxicity LDH Assay Kit-WST(code:CK12)
Cell viability : Cell Counting Kit-8(code:CK04)
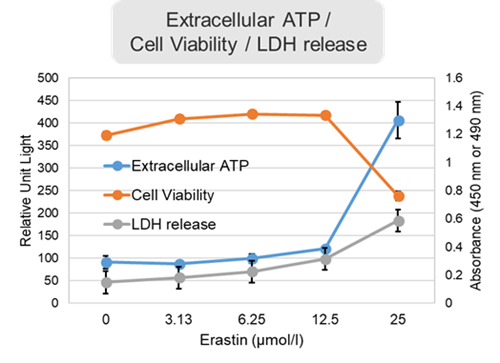
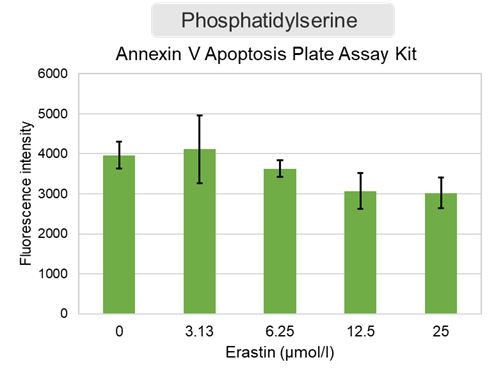
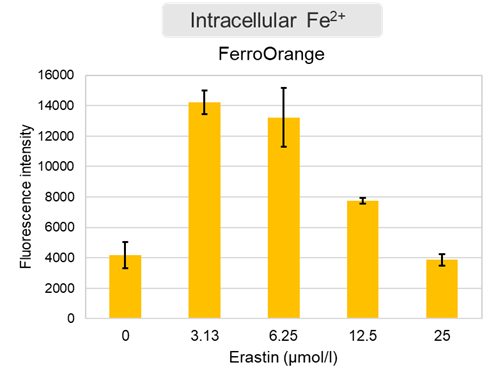
Experimental Example: Evaluation using Erastin-treated cells
-
Changes in extracellular ATP release, cell viability, extracellular LDH release, phosphatidylserine, and intracellular Fe2+ were evaluated in HeLa cells treated with various concentrations of Erastin, a ferotosis inducer, for 24 hours. The results showed that cell viability decreased and extracellular ATP release and extracellular LDH increased in cells treated with Erastin concentration of 25 μmol/l, indicating that cell death was induced under high concentration conditions. Interestingly, the increase in extracellular ATP in the early phase of stimulation, which was observed with the apoptosis inducer Staurosporine, was not observed with Erastin (See Experimental Example: Evaluation using apoptosis inhibitors.). Although the apoptosis-related marker phosphatidylserine was not significantly altered by Erastin treatment at any concentration. The amount of intracellular Fe2+, a ferroptosis-related marker, was significantly increased under the low-concentration treatment condition, indicating that it tends to increase before actual cell death occurs.
<Product in use>
Extracellular ATP : Extracellular ATP Assay Kit-Luminescence (code:E299)
Extracellular LDH : Cytotoxicity LDH Assay Kit-WST(code:CK12)
Cell viability : Cell Counting Kit-8(code:CK04)
Phosphatidylserine : Annexin V Apoptosis Plate Assay Kit(code:AD12)
Intracellular Fe2+ : FerroOrange(code:F374)