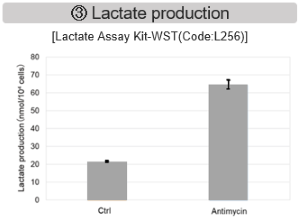
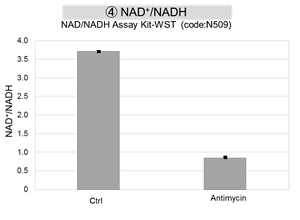
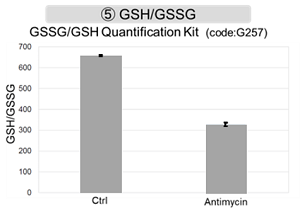
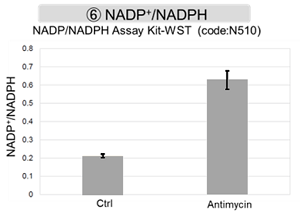
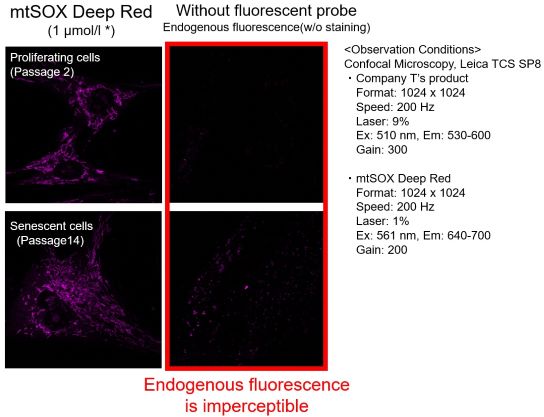
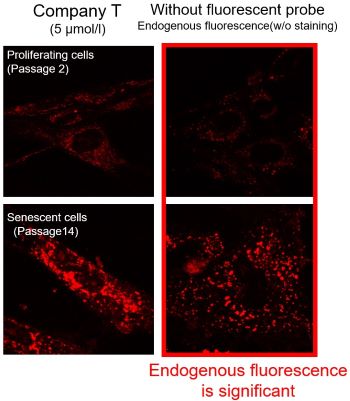
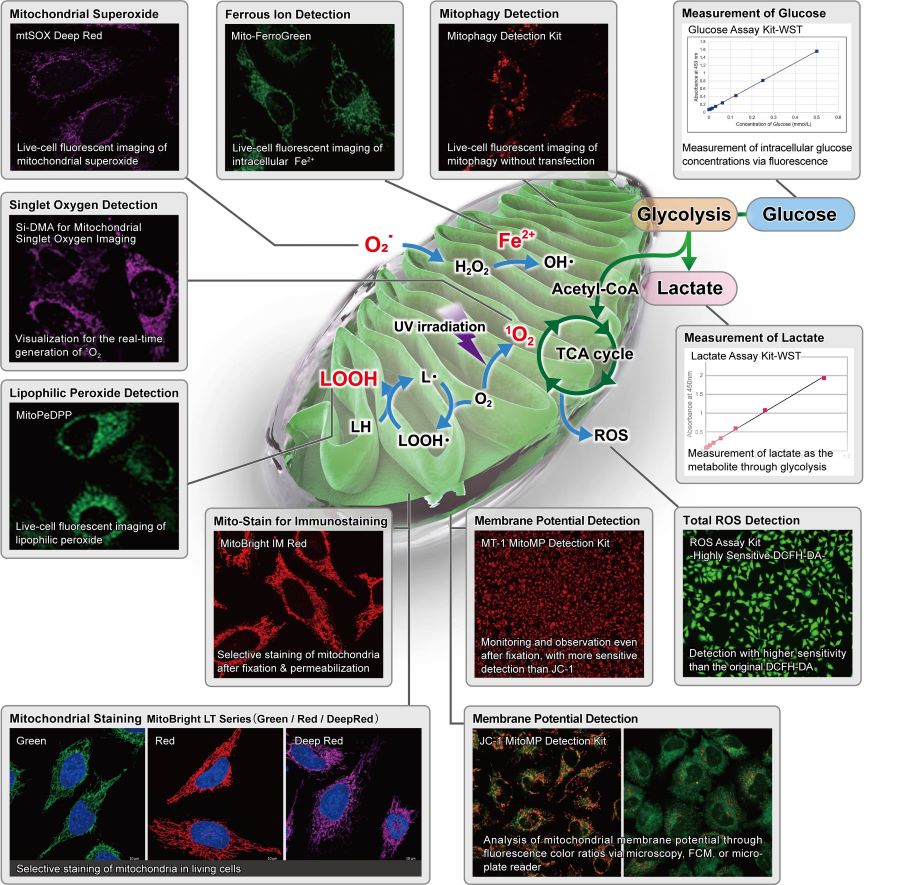
Mitochondrial Metabolism and Oxidative Stress
| Mitochondrial metabolism involves the biochemical processes within mitochondria that convert nutrients into energy and building blocks necessary for cell function, primarily through the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. This energy production produces adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cell's primary energy currency. Oxidative stress occurs when there's an imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the mitochondria and the cell's ability to detoxify these harmful byproducts or repair the resulting damage. Over time, excessive oxidative stress can lead to cellular damage that contributes to aging and several diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders and cancer. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Autoregulatory control of mitochondrial glutathione homeostasis Click here for the original article: Yuyang Liu, et. al., Science, 2023. |
ApoE enhances mitochondrial metabolism via microRNA-142a/146a-regulated circuits that suppress hematopoiesis and inflammation in hyperlipidemia Click here for the original article: Tuan Anh Phu et. al., Cell Reports, 2023. |
Mitochondrial protein C15ORF48 is a stress-independent inducer of autophagy that regulates oxidative stress and autoimmunity |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Point of Interest
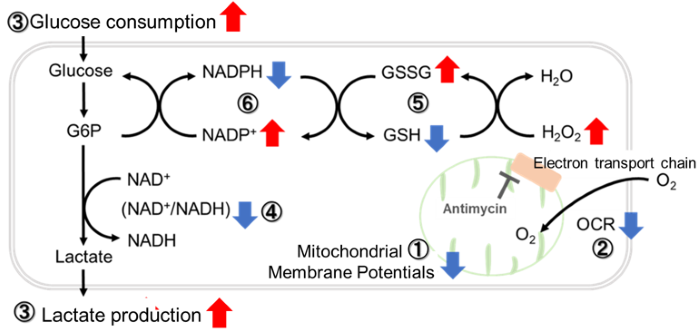
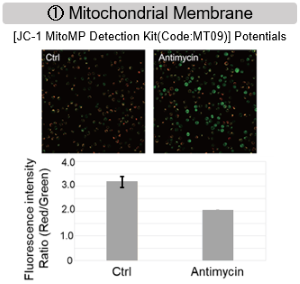
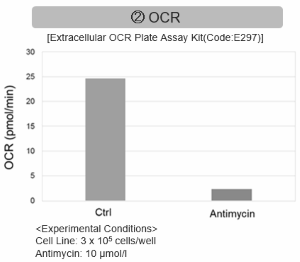
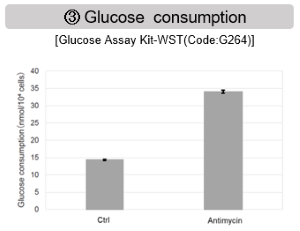
- The mitochondrial glutathione (GSH) transporter, SLC25A39, undergoes rapid degradation by the mitochondrial protease AFG3L2. - Depletion of GSH dissociates AFG3L2 from SLC25A39, which triggers enhancement in the uptake of GSH by mitochondria. - This regulatory mechanism is dependent on a putative iron-sulfur cluster within SLC25A39, linking the control of mitochondrial iron homeostasis to GSH import. |
Point of Interest
- Apolipoprotein E (ApoE) elevates the levels of miR-146a in myeloid cells and hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells, leading to decreased glucose absorption and glycolysis. - By diminishing miR-142a levels, ApoE enhances fatty acid oxidation, thereby improving mitochondrial metabolism. - ApoE plays a critical role in regulating immune cell metabolism, influencing hematopoiesis and inflammation in conditions of hyperlipidemia. |
Point of Interest
- The mitochondrial protein C15ORF48 reduces mitochondrial membrane potential and intracellular ATP levels, resulting in the activation of Unc-51-like kinase 1. - C15ORF48-dependent induction of autophagy upregulates intracellular glutathione levels and promotes cell survival by reducing oxidative stress. - Mice deficient in C15orf48 show a reduction in stress-independent autophagy in thymic epithelial cells (TECs). - C15orf48-/- mice develop autoimmunity, suggesting that stress-independent autophagy in TECs is critical for thymic self-tolerance. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Related Applications | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||