-Bacstain- CFDA solution
Bacterial Staining
- Fluorescence detection
- Ready-to-use solution
-
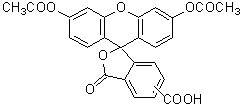
Product codeBS03 -Bacstain- CFDA solution
-
CAS No.79955-27-4(CFDA:5-isomer)
-
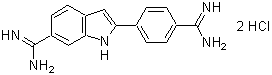
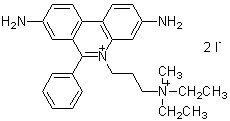
Chemical name5(6)-Carboxyfluorescein diacetate, solution, DMSO solution
| Unit size | Price | Item Code |
|---|---|---|
| 100 assays | $235.00 | BS03-10 |
Required Equipment and Materials
10 μl, 1000 μl pipettes, incubator, Microscope (blue excitation filter and red emission filter) or flow cytometer (488 nm blue laser)
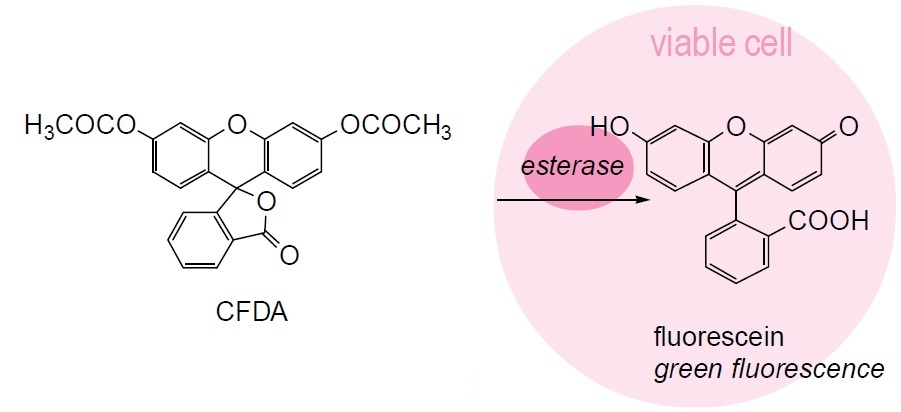
Fig. 1 Cell staining mechanism
Manual
Technical info
1. Allow CFDA solution to stand at room temperature for 30 minutes to thaw. Solution should be protected from light.
2. Resuspend the organism with an appropriate buffer (phosphate buffer, saline, etc.) a) and adjust the number of cells to 106 cells/ml(flow cytometry) or 108-109 cells/ml(microscopy).
3. Add CFDA solution into the microbial cell suspension and vortex gently to mix. Use 5 μl for flow cytometry and 15 μl for microscopy analysis. The maximum wavelengths of the dye are 493 nm for excitation and 515 nm for emission.
4. Incubate the microbial cell at 37°C for 5 minutes b).
5. Fix the microbial cell by addition of formaldehyde (1-4% final concentration).
6. Remove the buffer by filtration or centrifugation, and resuspend with buffer.
7. Analyze the stained-cells by a flow cytometer or a microscope.
a) Gram-negative bacteria tend to exhibit lower fluorescence intensity than Gram-positive bacteria because of their cell structure (outer membrane impedes penetration of CFDA). For the staining of Gram-negative bacteria, use 0.1 M phosphate buffer, 0.9 M NaCl, 0.5 mM EDTA, pH 8.5.
b) If CFDA staining is not sufficient with 5 minutes of incubation, increase the incubation time.
Staining Data
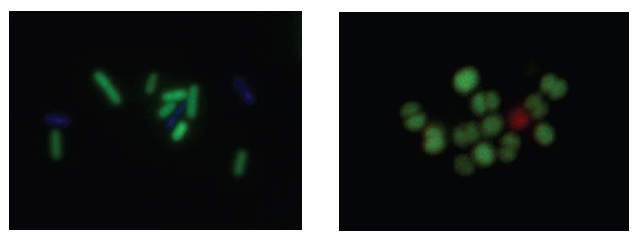
Fig. 2 B. cereus stained with CFDA and DAPI (left). S. epidermidis stained with CFDA and PI (right).
References
1) N. Yamaguchi and M. Nasu, " Flow cytometric analysis of bacterial respiratory enzymatic activity in the natural aquatic environment ".Journal of Appl. Microbiol., 1997, 83, 43.
2) M. Kawai, N. Yamaguchi and M. Nasu, “Rapid enumeration of physiologically active bacteria in purified water used in the pharmaceutical manufacturing process ", Journal of Appl. Microbiol.,1999, 86, 496.
3) T. Someya et al.,” Fluorescence Direct Count of Bacteria in Various Manures and Composts as Compared with Plate Count(Program for 2005 Annual Meeting of Japanese Society of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition)”, Journal of the science of soil and manure, Japan, 2005, 76(4), 401.
Handling and storage condition
| Appearance: | Colorless liquid |
|---|---|
| Dye content: | To pass test |
| 0-5°C, Protect from light | |
|
Danger / harmful symbol mark |

|
|---|---|