| [Jun. 13, 2023] | Previous Science Note |
|
Scientists have unveiled that VDAC2, a mitochondrial pore protein, as a PI3K-binding protein and show that endosomes positive for Ras PI3K complexes are tethered to mitochondria through PI3K-VDAC2 interaction. These researchers have further elucidated that this mitochondrion-endosome association fosters endosome maturation. Learn more about how the authors detected this mitochondria-endosome interaction using ECGreen for endosome labeling, and PlasMem Bright Red for plasma membrane labeling, which served as a negative control (please refer to Figures 5C - E and 5F - G). |
|
|
Related Techniques |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Related Applications |
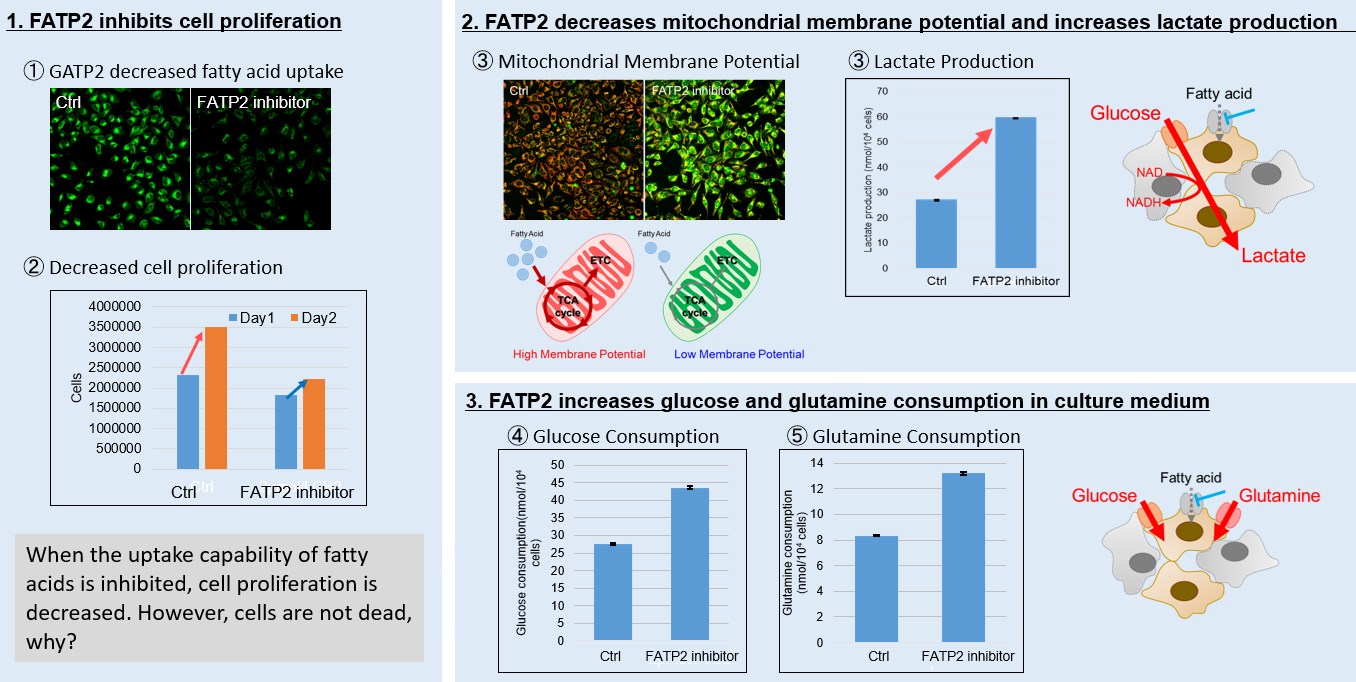
Fatty acid starvation induced by uptake inhibitor evoke reprogramming of cellular metabolism
Mitochondrial fatty acid β-oxidation and oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) are crucial biochemical processes that metabolize fats and sugars to produce ATP, the cell's primary energy source. In this section, we underscored the significance of fatty acid starvation and energy pathways, with an emphasis on the fatty acid uptake inhibitor, FATP2. Here are the key findings from our experiments conducted on HeLa cells: ・Inhibition of fatty acid uptake results in reduced cell proliferation, though it does not lead to cell death. This was determined through the use of a Cell Counting Kit-8 and Fatty Acid Uptake Kit (Image 1). ・Fatty acid starvation shifts cellular metabolism from OXPHOS to glycolysis, as indicated by the Glycolysis/JC-1 MitoMP Assay Kit. (Image 2) ・When fatty acid uptake is inhibited, a compensatory increase in glucose and glutamine uptake occurs to preserve cell viability, as observed using the Glucose Assay Kit and Glutamine Assay Kit. (Image 3) Products in Use for Cell Proliferation/Cytotoxicity Assay for Glycolysis Assay and Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Detection for Glucose and Glutamine Consumption Assay |