|
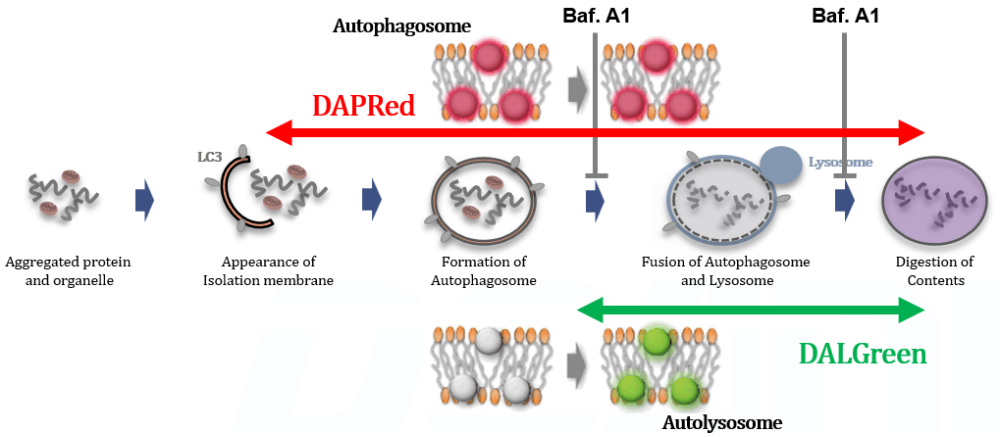
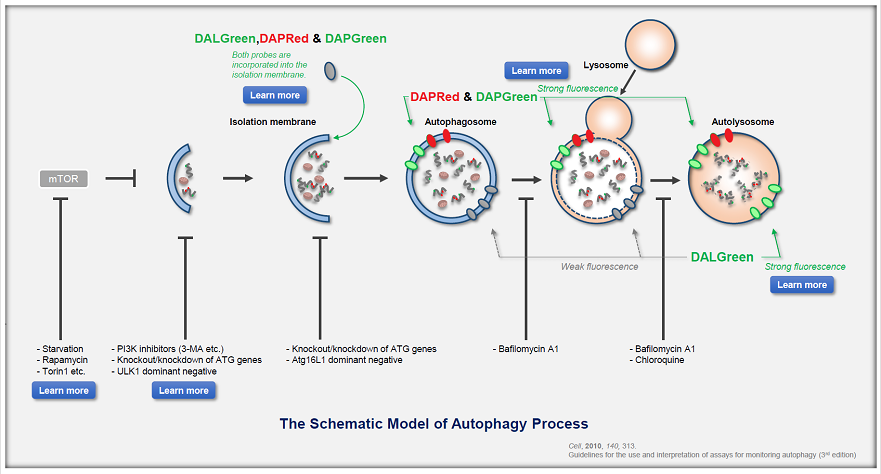
Autophagy is a cellular process that involves the degradation and recycling of cellular components through the formation of autophagosomes, which subsequently fuse with lysosomes for content degradation. In the context of cancer, autophagy plays a dual role; it can suppress tumor initiation by eliminating damaged organelles and proteins, but can also promote tumor survival and growth under metabolic stress by providing nutrients through the recycling of cellular components. |
||||
|
Carnosine regulation of intracellular pH homeostasis promotes lysosome-dependent tumor immunoevasion |
Response to Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitors in aggressive lymphomas linked to chronic selective autophagy Click here for the original article: James D. Phelan, et. al., Cancer Cell, 2024. |
In vivo CRISPR knockout screen identifies p47 as a suppressor of HER2+ breast cancer metastasis by regulating NEMO trafficking and autophagy flux Click here for the original article: Mingang Hao, et. al., Cell Reports, 2024. |
||
|
Point of Interest - Carnosine synthase, CARNS2, promotes carnosine synthesis under hypoxia. - Carnosine controls lysosomal subcellular distribution, acidification, and activity by maintaining intracellular pH homeostasis. - By maintaining lysosomal activity, carnosine facilitates NFX1 degradation, which triggers galectin-9 and T-cell-mediated immune escape and tumorigenesis. |
Point of Interest - Chronic selective autophagy suppresses NF-κB signaling in MCD-type Diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL). - MCD-type DLBCL develops genetic and epigenetic alterations that attenuate selective autophagy. - Disruption of selective autophagy leads to the accumulation of ubiquitinated MYD88L265P. - BTK and mTOR inhibitors interfere with the My-T-BCR pathway by enhancing the autophagic degradation of MYD88L265P. |
Point of Interest - An in vivo CRISPR screen identifies p47 as a suppressor of HER2+ breast cancer metastasis. - Depletion of p47 reduces NEMO endosomal trafficking and enhances NF-κB signaling. - Ablation of p47 impairs lysosomal repair and autophagic flux, leading to increased metastasis. - Lower expression of p47 correlates with increased metastasis in human breast cancer. |
||
| Related Applications | ||||
Analysis of autophagic flux without transfection |
||||
|
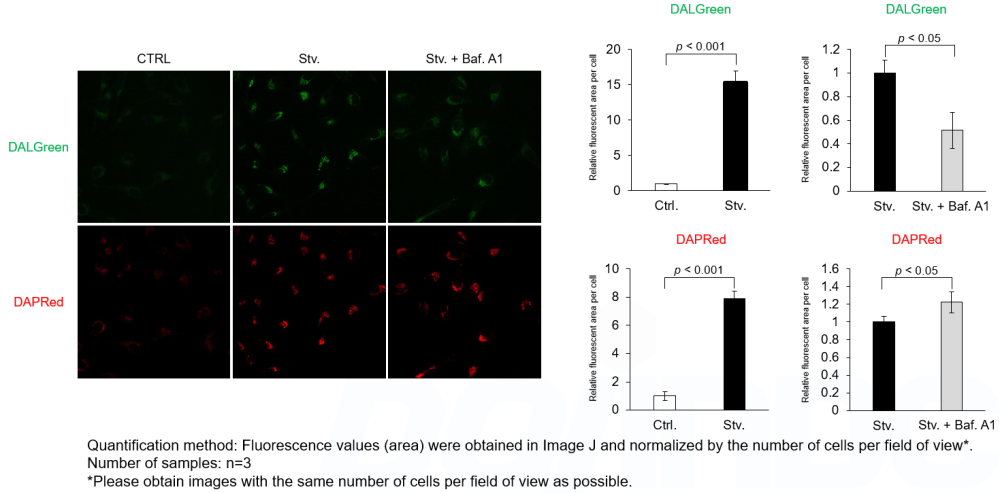
Detection Principle DALGreen and DAPRed labeled HeLa cells were used to evaluate changes in autophagic flux induced by the lysosomal acidification inhibitor bafilomycin A1 (Baf. A1). Compared to starvation conditions, the fluorescence signals of DALGreen were decreased under inhibited conditions of autolysosome formation by the addition of Baf. A1. In contrast, the fluorescence signals of DAPRed were increased under the same conditions, indicating that Baf. A1 led to the accumulation of autophagosome. Experimental Data
Experimental Conditions Procedure Products in Use |
||||
| Related Techniques | ||||
| First-time autophagy research | Autophagic Flux Assay Kit |
|||
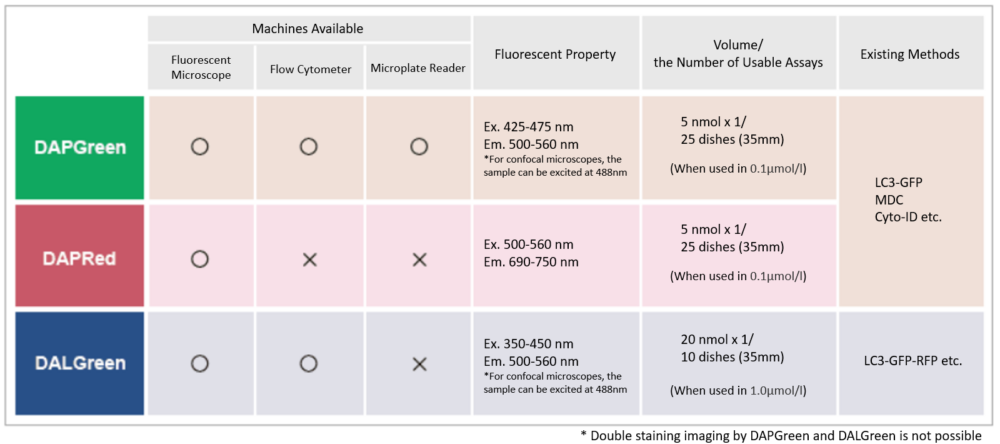
| Autophagy detection dyes for imaging | DAPRed (Autophagosome detection), DALGreen (Autolysosome detection) | |||
| Autophagy detection for Flow cytometry / plate assay | DAPGreen (Autophagosome detection) | |||
| Mitophagy detection dye | Mitophagy Detection Kit and Mtphagy Dye | |||
| Lysosomal pH and mass detection | Lysosomal Acidic pH Detection Kit-Green/Red and Green/Deep Red |
|||
| Accurate detection of endocytosis by pH changes | ECGreen-Endocytosis Detection | |||
| Glycolysis/Oxidative phosphorylation Assay | Glycolysis/OXPHOS Assay Kit | |||