|
Recent research into cancer metastasis shows that cancer cells hijack immune cells, particularly macrophages, to promote metastasis. Here are some of the papers showing how macrophages contribute to cancer metastasis and immune evasion.
Cancer metastasis is the spread of cancer cells from a primary tumor to distant organs, often evading immune surveillance. Immune cells, such as macrophages, can be co-opted by cancer cells to create an immunosuppressive environment that supports tumor growth and metastasis. Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) and other immune cells such as neutrophils and regulatory T cells can promote metastatic progression by facilitating tissue remodeling, angiogenesis and immune evasion. Conversely, enhancing the function of cytotoxic immune cells, such as CD8+ T cells and natural killer (NK) cells, may help to target and eliminate metastatic cancer cells.
|
-
Efferocytosis reprograms the tumor microenvironment to promote pancreatic cancer liver metastasis
Click here for the original article: Yuliana Astuti, et. al., Nature Cancer, 2024.
Point of Interest
- Efferocytosis, the process by which macrophages engulf apoptotic cells, is physiologically used to protect host tissues from immune attack, resulting in local immunosuppression.
- In pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), macrophage reprogramming by efferocytosis supports pancreatic cancer liver metastasis, allowing cancer cells to evade immune detection and grow.
- Macrophage progranulin regulates lysosomal acidification, which is critical for efferocytosis and macrophage conversion during metastasis.
- Blocking efferocytosis or progranulin improves CD8+ T cell function and reduces liver metastasis, suggesting new therapeutic approaches.
-
Necroptosis enhances ‘don’t eat me’ signal and induces macrophage extracellular traps to promote pancreatic cancer liver metastasis
Click here for the original article: Cheng-Yu Liao et. al., Nature Communications, 2024.
Point of Interest
- Mixed lineage kinase domain like pseudo kinase-driven necroptosis in PDAC recruits macrophages, enhances the tumor CD47 "don't eat me" signal and induces CXCL8 activation.
- Necroptosis-induced CXCL8 activation initiates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and endothelial adhesion, promoting PDAC liver metastasis.
- Blocking necroptosis and CD47 reduces PDAC liver metastasis, offering potential for neoadjuvant immunotherapy and radical surgery.
-
Mesothelin Secretion by Pancreatic Cancer Cells Co-opts Macrophages and Promotes Metastasis
Click here for the original article: Teifion Luckett et. al., Cancer Research, 2024.
Point of Interest
- Mesothelin secretion by PDAC cells reprograms macrophages by inducing macrophage VEGFA and S100A9 expression.
- Macrophage-derived VEGFA supports tumor growth, while S100A9 promotes neutrophil infiltration and lung metastasis.
- Mesothelin drives macrophage-neutrophil interactions and promotes PDAC metastasis through extracellular traps and VEGFA signaling.
|
|
Related Techniques
|
- Apoptosis detection in multiple samples
- Annexin V Apoptosis Plate Assay Kit
|
|
|
- Endocytosis Detection detection
- ECGreen-Endocytosis Detection
|
- Lysosomal function
- Lysosomal Acidic pH Detection Kit -Green/Red and Green/Deep Red
-
|
- Mitophagy or autophagy detection
- Mitophagy Detection Kit, Autophagic Flux Assay Kit
|
- Plasma Membrane Staining
- PlasMem Bright Green / Red
|
- Total ROS detection
- Highly sensitive DCFH-DA or Photo-oxidation Resistant DCFH-DA
|
|
Related Applications
|
Phagocytosis assay of labeled apoptotic cells in THP-1 cells
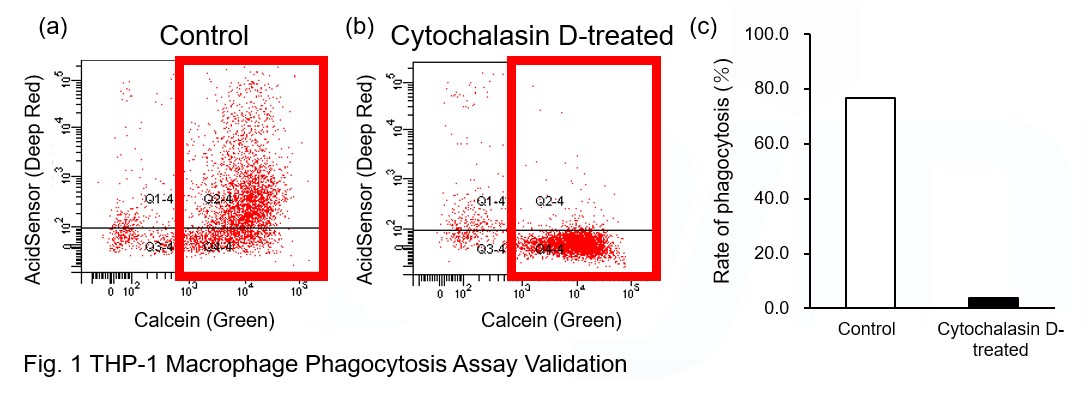
AcidSensor-labeled substances are taken up by cells and their fluorescence increases when they reach acidic organelles such as lysosomes. Taking advantage of this property, we evaluate the phagocytic activity of apoptotic cells by co-culturing AcidSensor-labeled apoptotic cells with Calcein-labeled THP-1 macrophages. As a result, Calcein (Green) / AcidSensor (Deep red) double-positive cells, indicating THP-1 macrophages phagocytosing apoptotic cells, were observed by flow cytometry (Fig. 1a). Furthermore, when the phagocytosis of THP-1 macrophages was inhibited by Cytochalasin D, the percentage of double-positive cells decreased (Fig. 1b and 1c), confirming that the assay system can accurately evaluate phagocytosis.
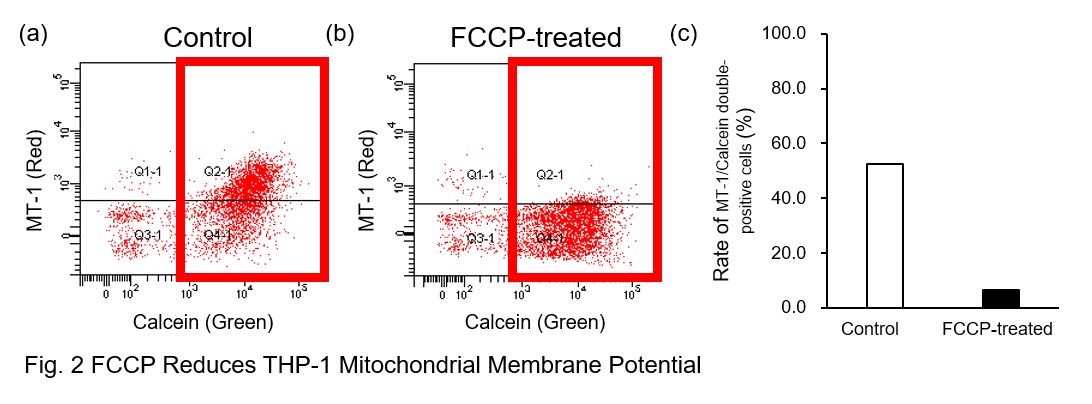
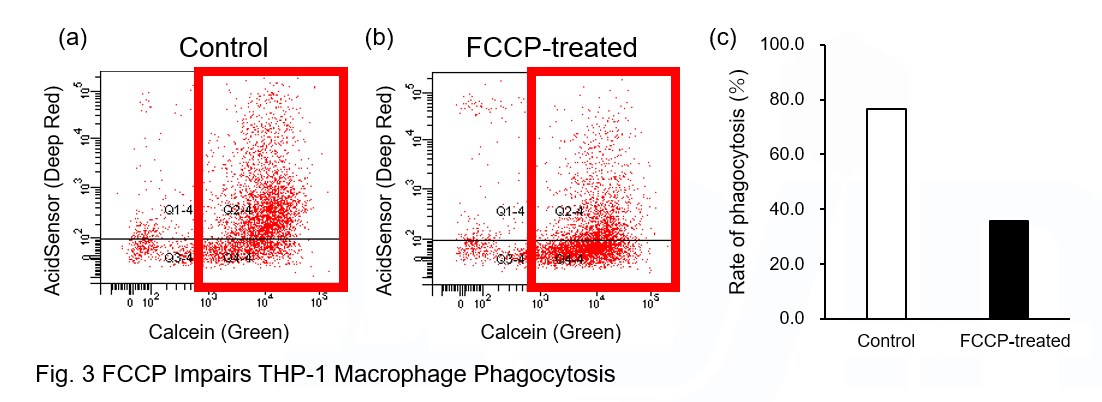
A recent report reveals that inhibition of mitochondrial function induces a switch to glycolysis and reduces phagocytosis in cultured microglia, resident macrophages in the central nervous system*. To replicate this result, phagocytosis assays were performed using mitochondria-inhibited THP-1 macrophages. The results show that FCCP, a potent uncoupler of oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria, decreases mitochondrial membrane potential (MT-1, Red) of THP-1 macrophages (Fig. 2) and reduces phagocytosis (Fig. 3).
*Lauren H. Fairley, et al., PNAS (2023)
Products in Use
① AcidSensor Labeling Kit – Endocytic Internalization Assay [code: A558]
② -Cellstain- Calcein-AM solution [code: C396]
③ MT-1 MitoMP Detection Kit [code: MT13]
|


















