Science Note: Lysosome
Lysosomal Dysfunction Drives Cell Senescence and Damage [Nov. 12, 2024]
Open / Close the Article
|
Recent research shows that lysosomal dysfunction in cells leads to toxic accumulation, causing stress responses, cell senescence and cell death. Here are some of the papers showing that lysosomal homeostasis is important for disease prevention. Lysosomal dysfunction disrupts essential cellular processes and leads to the promotion of several diseases, including neurodegenerative diseases and senescence. In neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, impaired lysosomal activity leads to the accumulation of toxic proteins that contribute to neuronal death and disease progression. Lysosomal dysfunction is also associated with cellular senescence, where it impairs the degradation of damaged cellular components, leading to the accumulation of senescent cells and promoting age-related diseases. Therapeutic strategies targeting lysosomal function are being explored to alleviate these conditions and improve overall cellular health. |
||||||||||
|
PLD3 and PLD4 synthesize S,S-BMP, a key phospholipid enabling lipid degradation in lysosomes |
Modeling Parkinson’s disease pathology in human dopaminergic neurons by sequential exposure to α-synuclein fibrils and proinflammatory cytokines |
HKDC1, a target of TFEB, is essential to maintain both mitochondrial and lysosomal homeostasis, preventing cellular senescence |
||||||||
|
Point of Interest - PLD3 and PLD4 synthesize lysosomal S,S-bis(monoacylglycero)phosphate (BMP), which is critical for lipid degradation and brain health. - Lysosomal S,S-BMP is essential for lipid degradation; its synthesis by PLD3/4 prevents gangliosidosis and supports cellular health. - Mutations in PLD3 associated with neurodegenerative diseases reduce its activity, affecting S,S-BMP levels and contributing to lysosomal dysfunction. |
Point of Interest - Immune-induced lysosomal dysfunction promotes Lewy body (LB) formation in dopaminergic neurons, mimicking Parkinson's disease (PD) pathology. - α-Synuclein fibrils and immune challenges (e.g., interferon-γ treatment) induce LD-like inclusions in iPSC-derived dopaminergic neurons. - LB formation in PD may result from lysosomal-autophagic dysfunction, exacerbated by immune challenge and α-synuclein accumulation. |
Point of Interest - Mitochondrial and lysosomal functions are linked, with transcription factor EB (TFEB) and hexokinase domain containing 1 (HKDC1) playing critical roles in their regulation and maintenance. - HKDC1, regulated by TFEB, is essential for mitophagy and lysosomal repair, independent of its glycolysis function. - Loss of HKDC1 accelerates cellular senescence by causing mitochondrial hyperfusion and lysosomal damage. |
||||||||
| Related Techniques | ||||||||||
| Lysosomal function | Lysosomal Acidic pH Detection Kit -Green/Red and Green/Deep Red | |||||||||
| Mitophagy detection | Mitophagy Detection Kit | |||||||||
| First-time autophagy research | Autophagic Flux Assay Kit | |||||||||
| Autophagy detection | DAPGreen/ DAPRed (Autophagosome detection), DALGreen (Autolysosome detection) | |||||||||
| Cellular senescence detection | SPiDER-βGal for live-cell imaging or flow cytometry / microplate reader / tissue samples | |||||||||
| SPiDER-βGal Blue for multiple staining with immunostaining and others | ||||||||||
| Lipid Droplet Staining | Lipi-Blue/ Green/ Red/ Deep Red | |||||||||
| Mitochondrial membrane potential detection | JC-1MitoMPDetection Kit,MT-1MitoMPDetection Kit | |||||||||
| Glycolysis/Oxidative phosphorylation Assay | Glycolysis/OXPHOS Assay Kit, Extracellular OCR Plate Assay Kit | |||||||||
| Total ROS detection | Highly sensitive DCFH-DA or Photo-oxidation Resistant DCFH-DA | |||||||||
| Mitochondrial superoxide detection | MitoBright ROS Deep Red - Mitochondrial Superoxide Detection | |||||||||
| Related Applications | ||||||||||
|
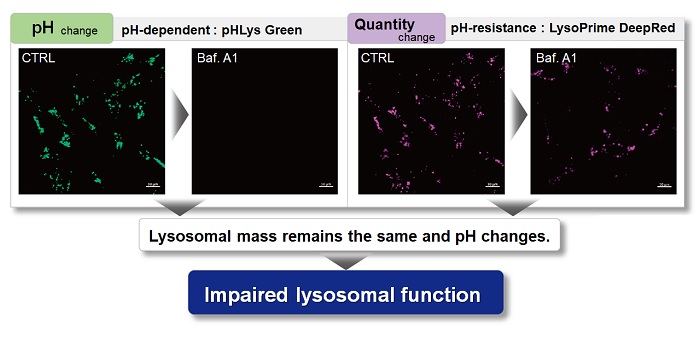
Lysosomal Function Analysis With existing reagents, it was difficult to determine whether lysosomal mass or their function (pH) fluctuated because the discussion was based on changes in the fluorescence brightness of a single dye. This kit contains pHLys Green, which is highly specific to lysosomes and shows pH-dependent changes in fluorescence, and pH-resistant LysoPrime Deep Red. Using these two dyes, lysosomal pH and volume of the same sample can be measured for a detailed analysis of lysosomal function. |
||||||||||
|
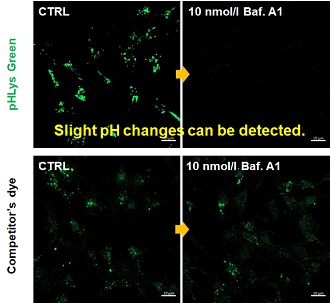
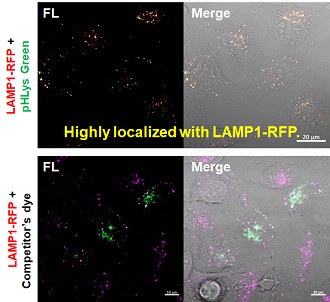
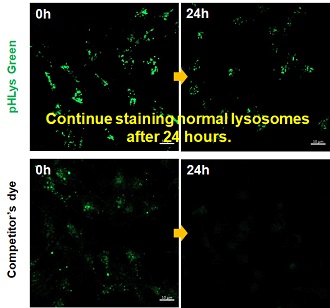
Accurate Measurement for Lysosomal pH changes Existing lysosomal pH detection reagents have issues with dye localization, pH sensitivity, and retention. pHLys Green is a dye that solves these issues. The improved dye retention and localization enable detection of normal lysosomes, and the improved pH sensitivity enables detection of slight pH changes.
Product in Use: Related Product:
|
||||||||||
Lysosomal Dysfunction: A Key Factor in Alzheimer's Progression [Oct. 1, 2024]
Open / Close the Article
|
Some research on Alzheimer's disease (AD) shows that lysosomal dysfunction is observed in the early stages of AD and affects the progression of AD. Here are some of the studies that show one of the mechanisms of lysosomal dysfunction in AD and ideas for therapy. Lysosomes play a critical role in the removal and degradation of cellular waste, including the degradation of proteins and damaged organelles by autophagy. Lysosomal dysfunction is commonly observed in Alzheimer's disease (AD), contributing to the accumulation of amyloid beta plaques and tau tangles that are hallmarks of the disease. Impaired lysosomal activity disrupts cellular homeostasis, leading to the accumulation of toxic proteins and organelle damage, further exacerbating neurodegeneration. Restoring lysosomal function has emerged as a potential therapeutic target for slowing or ameliorating the progression of Alzheimer's disease. |
||
|
Accumulation of APP C-terminal fragments causes endolysosomal dysfunction through the dysregulation of late endosome to lysosome-ER contact sites |
Urolithin A improves Alzheimer's disease cognition and restores mitophagy and lysosomal functions |
Rescue of ApoE4-related lysosomal autophagic failure in Alzheimer’s disease by targeted small molecules |
|
Point of Interest - Endolysosomal collapse in Alzheimer's disease (AD), initiated by decreased lysosomal calcium and increased cholesterol, is triggered by γ-secretase inhibition, with APP depletion rescuing these dysfunctions. - APP C-terminal fragments (CTFs) are localized to late endosome-lysosome-ER contacts, and excess APP CTFs cause lysosomal Ca2+ deficits, leading to cholesterol accumulation at endosome-lysosome-ER contacts. - Failure to maintain balanced APP-CTF levels perpetuates signaling, causing lysosomal dysfunction and contributing to early AD pathology. |
Point of Interest - Long-term treatment with urolithin A (UA) improves learning, memory and olfactory function in Alzheimer's disease mice. - UA reduces amyloid beta and tau pathology and improves mitophagy by restoring lysosomal function through cathepsin Z regulation. - UA shows therapeutic potential for Alzheimer's disease by improving lysosomal function and modulating immune responses and Alzheimer's disease-related pathways. |
Point of Interest - The APOE ε4 allele increases the risk of Alzheimer's disease by impairing autophagy by blocking the transcription of autophagy genes. - Small molecules have been identified that bind ApoE4 and restore autophagy gene transcription, thereby reducing amyloid aggregation in models. - These findings suggest that ApoE4-targeted drugs could be used to rescue lysosomal autophagy in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's. |
| Related Techniques | ||
| Lysosomal function | Lysosomal Acidic pH Detection Kit -Green/Red and Green/Deep Red | |
| First-time autophagy research | Autophagic Flux Assay Kit | |
| Autophagy detection | DAPGreen/ DAPRed (Autophagosome detection), DALGreen (Autolysosome detection) | |
| Mitophagy detection | Mitophagy Detection Kit | |
| Mitochondrial membrane potential detection | JC-1MitoMPDetection Kit,MT-1MitoMPDetection Kit | |
| Glycolysis/Oxidative phosphorylation Assay | Glycolysis/OXPHOS Assay Kit, Extracellular OCR Plate Assay Kit | |
| Oxygen consumption rate assay | Extracellular OCR Plate Assay Kit | |
| Intracellular calcium ion detection | Fura 2-AM | |
| Glutathione Quantification | GSSG/GSH Quantification Kit | |
| Cell Proliferation / Cytotoxicity Assay | Cell Counting Kit-8, Cytotoxicity LDH Assay Kit-WST | |
| Related Applications | ||
|
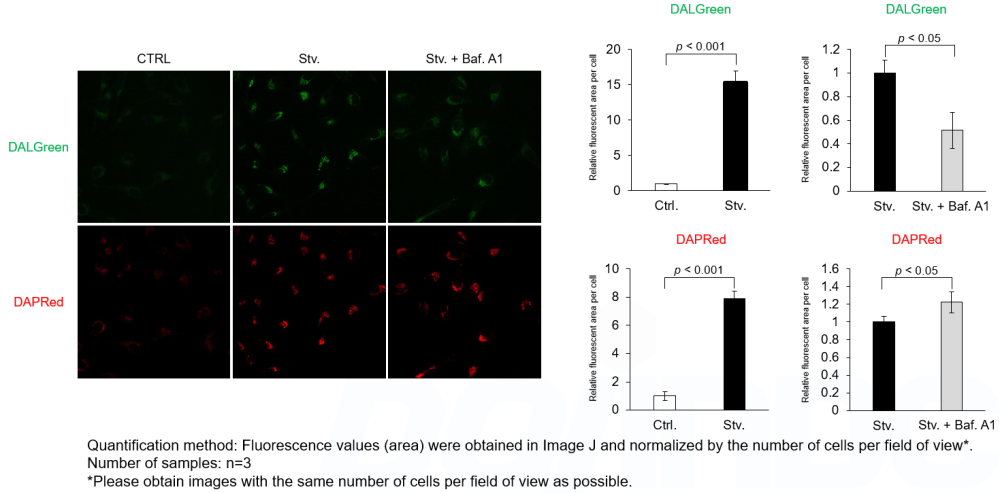
Analysis of autophagic flux without transfection DALGreen and DAPRed labeled HeLa cells were used to evaluate changes in autophagic flux induced by the lysosomal acidification inhibitor bafilomycin A1 (Baf. A1). Compared to starvation conditions, the fluorescence signals of DALGreen were decreased under inhibited conditions of autolysosome formation by the addition of Baf. A1. In contrast, the fluorescence signals of DAPRed were increased under the same conditions, indicating that Baf. A1 led to the accumulation of autophagosome. Experimental Conditions Products in Use |
||
Lysosomes in the Regulation of Metabolism and Organelle [Jan. 3, 2024]
Open / Close the Article
|
Lysosomal dysfunction is increasingly recognized as a critical factor in the development and progression of several neurological diseases. In neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's and Alzheimer's, impaired lysosomal function leads to the accumulation of misfolded proteins and neuronal toxicity, contributing to cell death and disease progression. Although rare, lysosomal storage diseases often have significant neurological manifestations due to the accumulation of undigested substances in neurons, impairing their function and survival. Therefore, understanding and targeting lysosomal pathways is emerging as a promising therapeutic approach to treat and potentially prevent a range of neurological disorders. |
||||||||||||
|
Lysosomes mediate the mitochondrial UPR via mTORC1-dependent ATF4 phosphorylation |
ARL8B mediates lipid droplet contact and delivery to lysosomes for lipid remobilization |
Nutrient-regulated control of lysosome function by signaling lipid conversion |
||||||||||
|
Point of Interest - This phosphorylation of ATF4 triggers the mitochondrial unfolded protein response (UPRmt). - Interfering with the ability of mTORC1 to phosphorylate ATF4 inhibits the UPRmt. - The phosphorylation of ATF4 prevents ROS-induced cell death under mitochondrial stress. |
Point of Interest - ARL8B in its GDP-bound state associates with LDs, whereas ARL8B-GTP is predominantly associated with lysosomes. - ARL8B facilitates the contact between LDs and lysosomes, with both its GDP- and GTP-bound states forming a complex. - The ARL8B-mediated lysosomal lipolysis of LDs represents a pathway for the turnover of neutral lipids in macrophages. |
Point of Interest - Cells possess diverse lysosome populations, distinguished by the presence of either PI(3)P or PI(4)P. - A lipid switch, regulated by nutrient availability, facilitates the interconversion between these distinct lysosome populations. - mTORC1 signaling and the synthesis of lysosomal PI(4)P are mutually inhibitory, each suppressing the other's activity. |
||||||||||
| Related Techniques | ||||||||||||
| Lysosomal function | Lysosomal Acidic pH Detection Kit-Green/Red and Green/Deep Red | |||||||||||
| Autophagy detection | DAPGreen / DAPRed (Autophagosome detection), DALGreen (Autolysosome detection) | |||||||||||
| Endocytosis detection | ECGreen-Endocytosis Detection | |||||||||||
| Phagocytosis detection | AcidSensor Labeling Kit – Endocytic Internalization Assay and -Cellstain- Calcein-AM solution | |||||||||||
| Mitophagy Detection | Mitophagy Detection Kit and Mtphagy Dye | |||||||||||
| Mitochondrial superoxide detection | MitoBright ROS Deep Red - Mitochondrial Superoxide Detection | |||||||||||
| Oxygen consumption rate assay | Extracellular OCR Plate Assay Kit | |||||||||||
| Antibody/Protein labeling - fast and high recovery | Fluorescein, Biotin, and Peroxidase Labeling Kit - NH2 | |||||||||||
| Related Applications | ||||||||||||
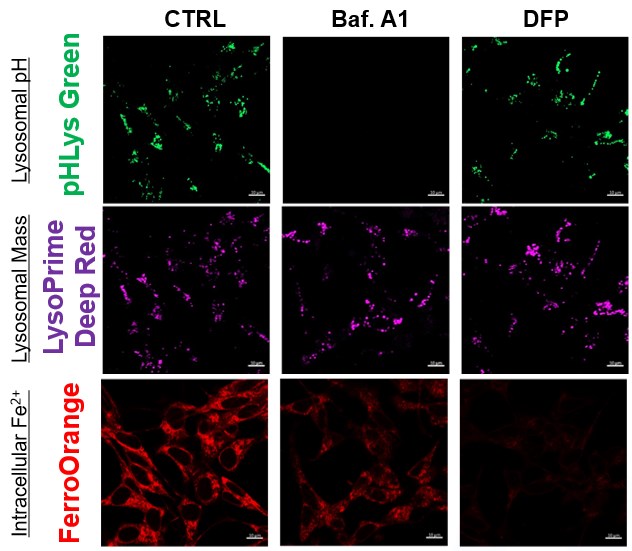
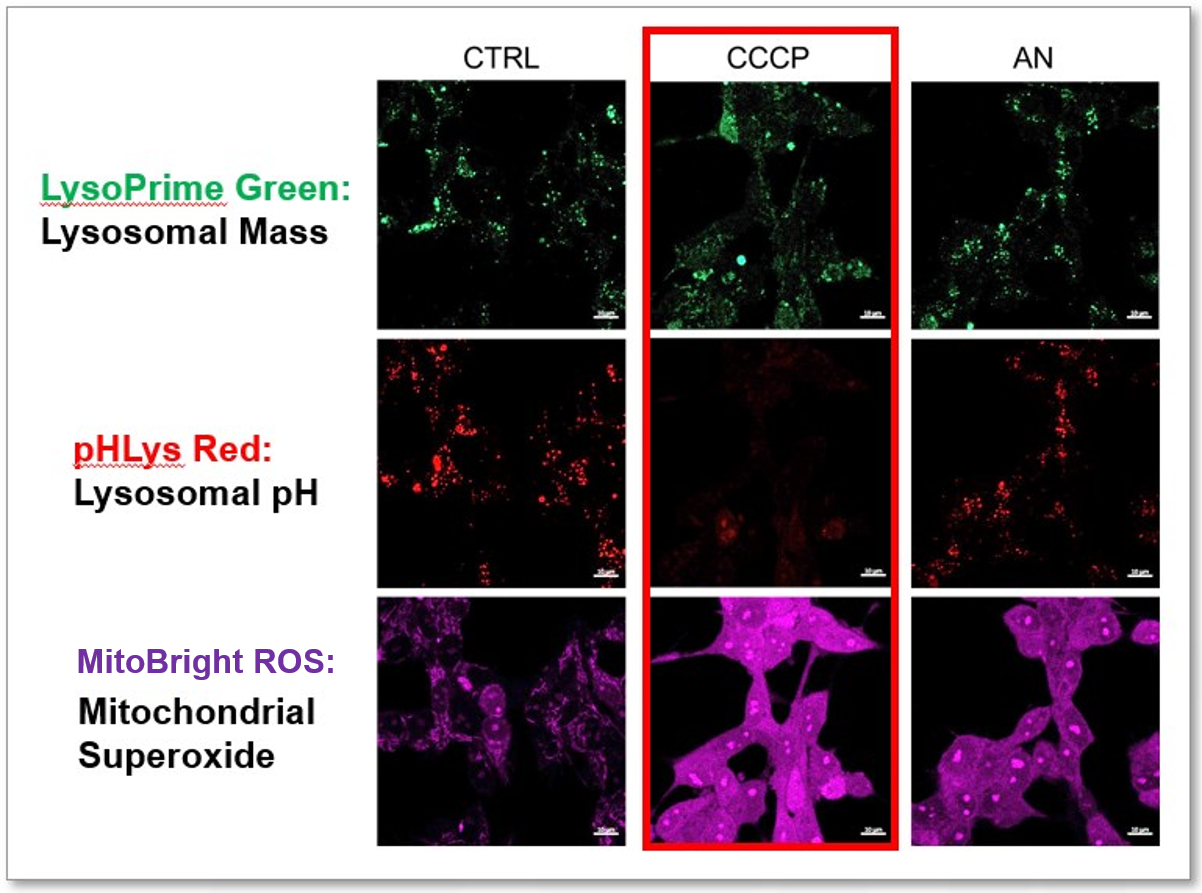
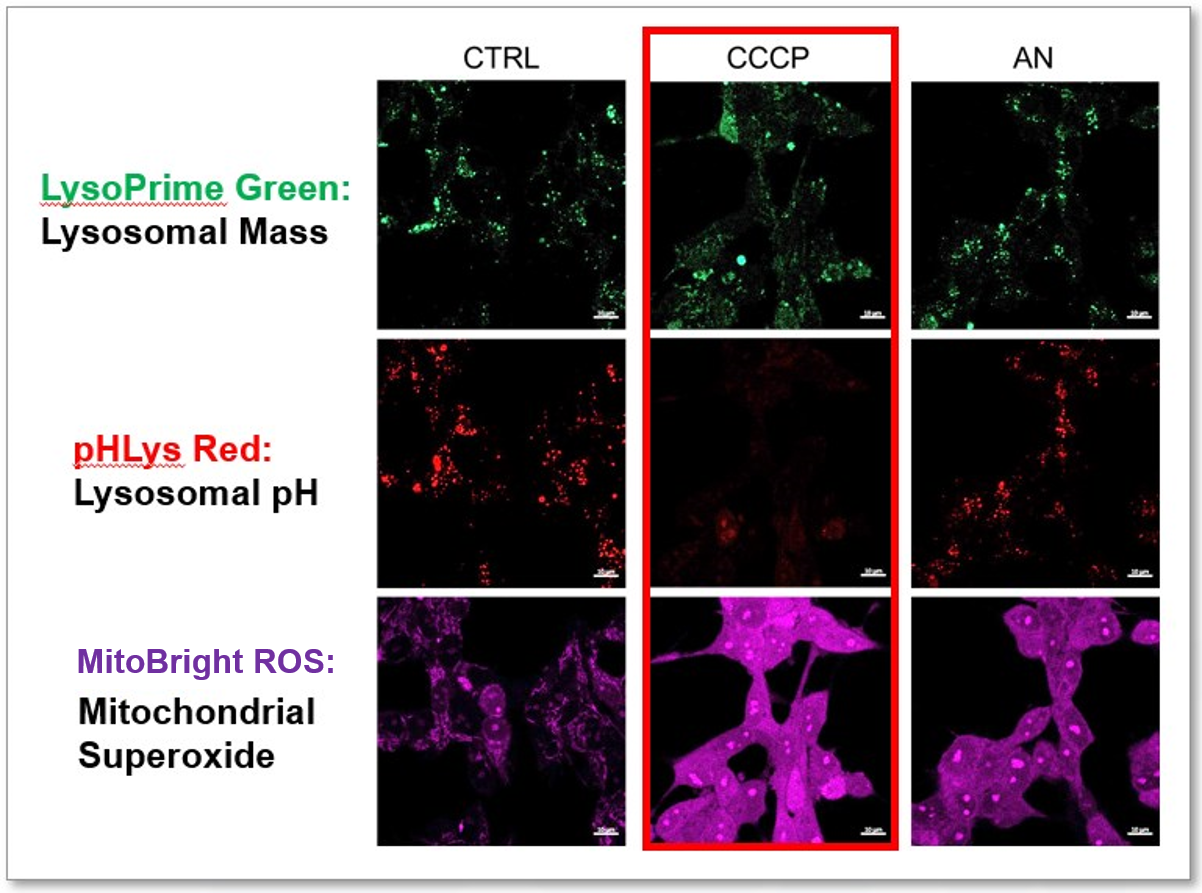
The simultaneous detection of lysosomal function with Mitochondrial ROS and intracellular Fe2+
|
||||||||||||
Lysosomal pH regulated by LAMP proteins [July 11, 2023]
Open / Close the Article
|
Through a combination of various scientific methods, this research reveals the vital role of human lysosome-associated membrane proteins (LAMP-1 and LAMP-2) in maintaining lysosomal pH balance. Despite being mainly recognized as lysosomal markers, LAMP-1 and LAMP-2 directly influence the lysosomal cation channel TMEM175, aiding the acidification of lysosomes to a pH level that optimizes hydrolase activity. Interruptions to the interaction between LAMP and TMEM175 can increase lysosomal pH, impairing their hydrolytic function. |
|
|
Lysosomal LAMP proteins regulate lysosomal pH by direct inhibition of the TMEM175 channel Point of Interest |
|
| Related Techniques | |
| Lipid droplets detection | Lysosomal Acidic pH Detection Kit-Green/Red, Green/Deep Red |
| Lysosome staining | pH-dependent (Red) and pH-independent (Green / Deep Red) probes |
| Autophagy detection | DAPGreen / DAPRed (Autophagosome detection), DALGreen (Autolysosome detection) |
| Endocytosis detection | ECGreen |
| Endocytic internalization assay | AcidSensor Labeling Kit |
| Plasma membrane staining | PlasMem Bright Green / Red |
| Total ROS detection | Highly sensitive DCFH-DA or Photo-oxidation Resistant DCFH-DA |
| Related Applications | |
Accurate Measurement for Lysosomal pH changesExisting lysosomal pH detection reagents have issues with dye localization, pH sensitivity, and retention. pHLys Green is a dye that solves these issues. The improved dye retention and localization enable detection of normal lysosomes, and the improved pH sensitivity enables detection of slight pH changes.
Product in Use: Related Product: |
|
Link Lysosomal Failure to Ferroptosis in Human Neurons [May 9, 2023]
Open / Close the Article
| Here, the scientists reveal an unexpected role for the lysosomal protein prosaposin (PSAP), the knockdown of which caused the formation of lipofuscin, a hallmark of aging, which traps iron, generating reactive oxygen species and triggering ferroptosis. Intriguingly, PSAP deficiency caused these dramatic phenotypes only in neurons, but not in other cells. Learn how the authors used Dojindo's Ferroptosis-related products, FerroOrange and Liperfluo for detecting Iron levels and lipid peroxidation, in their study. | |||||
|
Genome-wide CRISPRi/a screens in human neurons link lysosomal failure to ferroptosis Ruilin Tian, et. al., Nature Neuroscience (2022) Point of Interest |
|||||
| Related Techniques | |||||
| Intracellular lipid peroxidation measurement | Liperfluo | ||||
| Mitochondria lipid peroxidation measurement | MitoPeDPP | ||||
| Intracellular ferrous ion (Fe2+) detection | FerroOrange | ||||
| Mitochondria ferrous ion (Fe2+) detection | Mito-FerroGreen | ||||
| Mitochondrial superoxide detection | MitoBright ROS Deep Red - Mitochondrial Superoxide Detection | ||||
| Lysosomal function assay | Lysosomal pH and mass detection Kit | ||||
| Cellular senescence detection (Live cell imaging or FCM) | Cellular Senescence Detection Kit | ||||
| Cellular senescence detection (Plate reader) | Cellular Senescence Plate Assay Kit | ||||
| Related Applications | |||||
The simultaneous detection of lysosomal function with Mitochondrial ROS and intracellular Fe2+
|
|||||
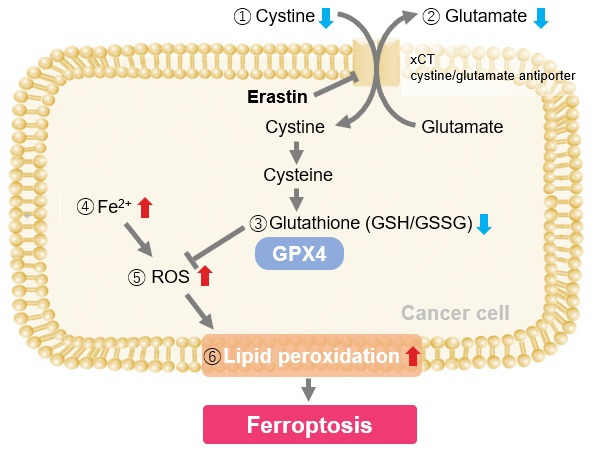
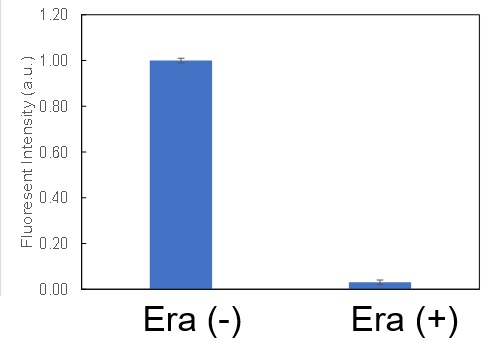
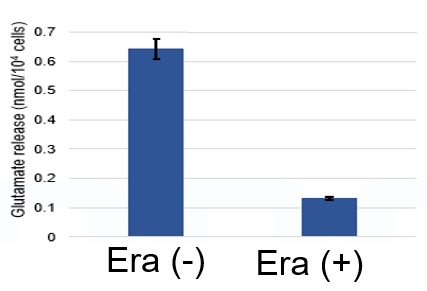
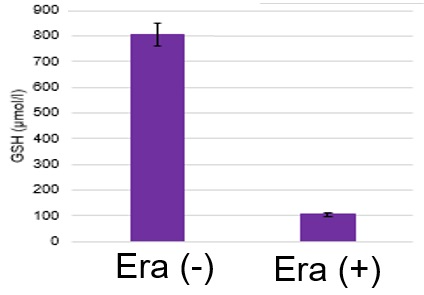
Induction of Ferroptosis by ErastinErastin is a known inducer of ferroptosis. By inhibiting the cystine transporter (xCT), erastin inhibits the uptake of cystine. Cystine is the raw material for GSH. Therefore, Erastin ultimately decreases the amount of GSH. Decreased GSH then results in lipid peroxide accumulation and induction of ferroptosis. Using erastin-treated A549 cells, we measured intracellular Fe2+, ROS, lipid peroxide, glutathione, glutamate release into the extracellular space, and cystine uptake. As a result, inhibition of xCT by elastin was observed and also the release of glutamate and uptake of cystine were decreased. Furthermore, elastin treatment decreased intracellular glutathione while it increased intracellular Fe2+ , ROS, and lipid peroxides.
|
|||||
Various Functional Pathways in Lysosomes [Feb. 7, 2023]
Open / Close the Article
| Lysosomes play a critical role in cellular metabolism and waste management. They are essential for maintaining cellular health and preventing the buildup of cellular waste, which can lead to disease and dysfunction. Understanding the functions of lysosomes is critical for developing treatments for a variety of diseases and disorders. Today, we introduce you to three highlighted articles focusing on lysosomal exocytosis, lysosomal AMPK pathway, and lysosomal pH optimization. | ||
|---|---|---|
| Lysosomal exocytosis in synucleinopathy models | Metformin and lysosomal AMPK pathway | Lysosomal pH optimum and Parkinson's disease |
| Lysosomal exocytosis releases pathogenic α-synuclein species from neurons in synucleinopathy models (Ying Xue Xie, et al., Nature Communications, 13, 4918, 2022) |
Low-dose metformin targets the lysosomal AMPK pathway through PEN2 (Teng Ma, et al., Nature, 603, 159-165, 2022) |
Parkinson’s disease-risk protein TMEM175 is a proton-activated proton channel in lysosomes (Meiqin Hu, et al., Cell, 185, 2292-2308, 2022) |
|
|
|
| Related Technique in This Topic | ||
| Lysosomal function assay | Lysosomal pH and mass detection Kit HOT | |
| Lysosome staining | pH-dependent (Red) and pH-independent (Green / Deep Red) probes HOT | |
| Autophagy detection | DAPGreen / DAPRed (Autophagosome detection), DALGreen (Autolysosome detection) | |
| Endocytosis detection | ECGreen | |
| Endocytic internalization assay | AcidSensor Labeling Kit HOT | |
| Extracellular vesicles labeling | ExoSparkler Exosome Membrane Labeling Kit-Green, Red, Deep Red | |
| Extracellular vesicles Isolation | ExoIsolator Exosome Isolation Kit HOT | |
| Total ROS detection | High Sensitive DCFH-DA HOT or Compatible with Immunostaining HOT | |
Learn more about application data with multiple products here