Membrane trafficking involves vital processes such as phagocytosis, endocytosis, and exocytosis, each of which plays a critical role in cellular homeostasis. Phagocytosis and endocytosis allow cells to ingest external particles and fluids, facilitating nutrient uptake and the removal of pathogens or debris, which is critical for cellular health and immune response. Exocytosis, on the other hand, allows cells to expel waste products and secrete signaling molecules that are essential for communication and functional coordination within tissues. These coordinated processes ensure that the cell maintains a balanced internal environment, adapts to changing external conditions, and maintains cellular integrity and function.
|
-
CTLA-4 blockade induces a microglia-Th1 cell partnership that stimulates microglia phagocytosis and anti-tumor function in glioblastoma
Click here for the original article: Dan Chen, et. al., Immunity, 2023.
Point of Interest
- αCTLA-4 therapy promotes the induction of protective CD4+ Th1 cells against mesenchymal glioblastomas.
- IFNγ, derived from Th1 cells, stimulates the induction of MHC-II+ microglia, which sustains Th1-mediated anti-glioma immunity.
- Th1 cells enhance microglial phagocytosis of gliomas through AXL-MER receptor signaling.
- The presence of microglia and MHC-II expression are associated with protective outcomes in human glioblastoma.
-
Stress granules plug and stabilize damaged endolysosomal membranes
Click here for the original article: Claudio Bussi et. al., Nature, 2024.
Point of Interest
- Stress granule formation and membrane stabilization allow efficient repair of damaged endolysosomes.
- This process requires both ESCRT (endosomal sorting complex required for transport)-dependent and independent mechanisms.
- Blocking stress granule formation in human macrophages creates a permissive environment for Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which exploits endomembrane damage to survive in the host.
-
A phosphoinositide switch mediates exocyst recruitment to multivesicular endosomes for exosome secretion
Click here for the original article: Di-Ao Liu et. al., Nature Communications, 2023.
Point of Interest
- A sequential conversion of phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PI(3)P) to phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate (PI(4)P) catalyzed by myotubularin 1.
- Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase type IIα on the surface of MVEs mediates the recruitment of the exocyst complex.
- The exocyst targets MVEs to the plasma membrane for exosome secretion.
- Disruption of PI(4)P generation or exocyst function blocked exosomal secretion of programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1), a key immune checkpoint protein in tumor cells, and led to its accumulation in lysosomes.
|
|
Related Techniques
|
- Endocytosis Detection detection
- ECGreen-Endocytosis Detection
|
|
|
- Lysosomal function
- Lysosomal Acidic pH Detection Kit -Green/Red and Green/Deep Red
|
- Exosome Labeling
- ExoSparkler Exosome Membrane Labeling Kit-Green / Red / Deep Red
-
|
- Plasma Membrane Staining
- PlasMem Bright Green / Red
|
- Lipid droplets detection
- Lipi-Blue / Green / Red / Deep Red
|
- Antibody/Protein labeling with fast and high recovery
- Fluorescein, Biotin, and Peroxidase Labeling Kit - NH2
|
|
Related Applications
|
Phagocytosis assay of labeled apoptotic cells in THP-1 cells
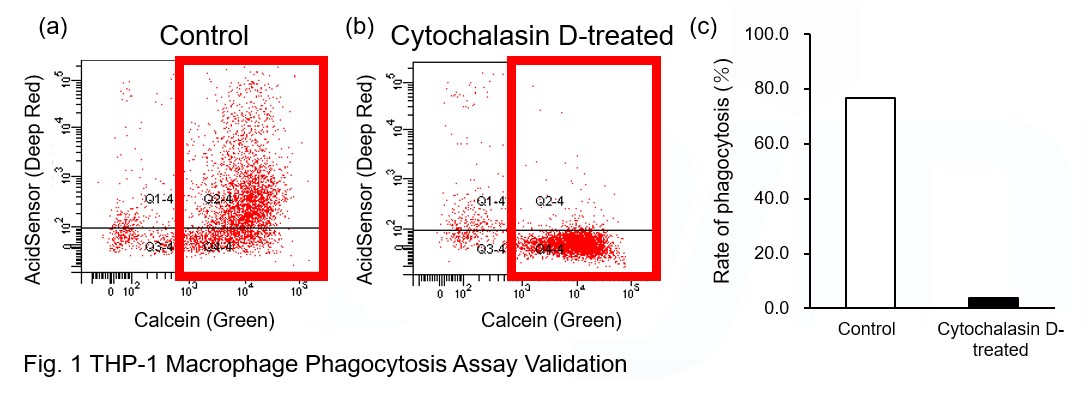
AcidSensor-labeled substances are taken up by cells and their fluorescence increases when they reach acidic organelles such as lysosomes. Taking advantage of this property, we evaluate the phagocytic activity of apoptotic cells by co-culturing AcidSensor-labeled apoptotic cells with Calcein-labeled THP-1 macrophages. As a result, Calcein (Green) / AcidSensor (Deep red) double-positive cells, indicating THP-1 macrophages phagocytosing apoptotic cells, were observed by flow cytometry (Fig. 1a). Furthermore, when the phagocytosis of THP-1 macrophages was inhibited by Cytochalasin D, the percentage of double-positive cells decreased (Fig. 1b and 1c), confirming that the assay system can accurately evaluate phagocytosis.
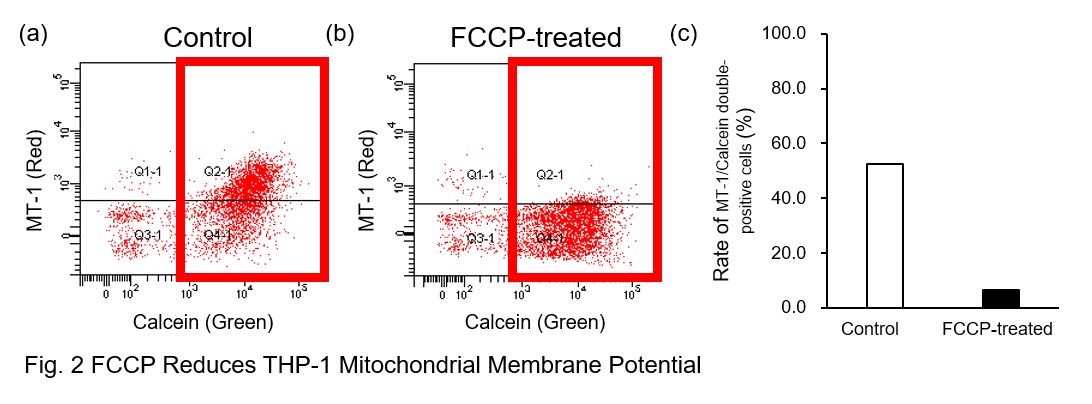
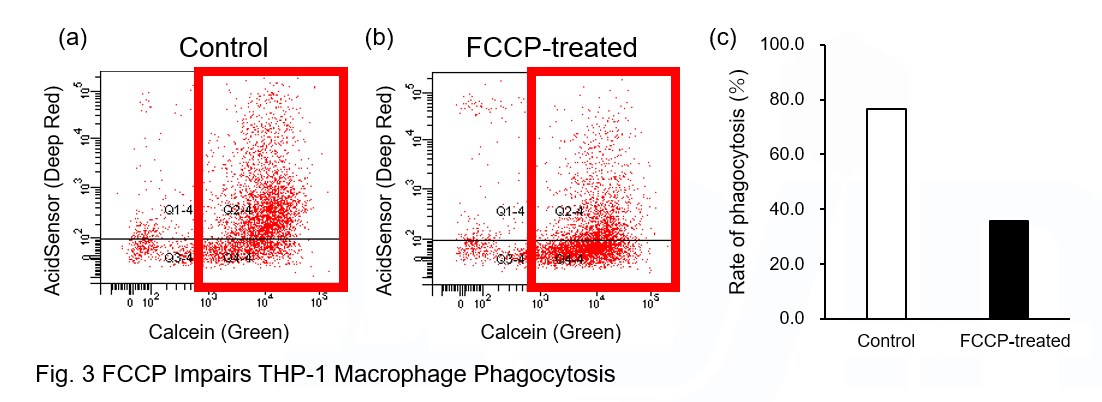
A recent report reveals that inhibition of mitochondrial function induces a switch to glycolysis and reduces phagocytosis in cultured microglia, resident macrophages in the central nervous system*. To replicate this result, phagocytosis assays were performed using mitochondria-inhibited THP-1 macrophages. The results show that FCCP, a potent uncoupler of oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria, decreases mitochondrial membrane potential (MT-1, Red) of THP-1 macrophages (Fig. 2) and reduces phagocytosis (Fig. 3).
*Lauren H. Fairley, et al., PNAS (2023)
Products in Use
① AcidSensor Labeling Kit – Endocytic Internalization Assay [code: A558]
② -Cellstain- Calcein-AM solution [code: C396]
③ MT-1 MitoMP Detection Kit [code: MT13]
|


















