|
In recent years, apoptosis, along with other distinct types of cell death, such as ferroptosis and pyroptosis, have been identified, making the classification and pathways of cell death increasingly complex. This Science Note introduces a review of cell death pathways and highlights recent findings on the induction of apoptosis and the clearance of apoptotic cells.
|
|
Cell death Review Article
Kim Newton, et. al., Cell, 2024.
Frequently cited throughout 2024, this review provides a comprehensive overview of apoptosis, ferroptosis, and other cell death processes, as well as their associated diseases. It will be a helpful resource for researchers beginning to study cell death and seeking to understand its complex pathways.
|
|
Stem cells tightly regulate dead cell clearance to maintain tissue fitness
Katherine S. Stewart, et. al., Nature, 2024.
Stem cells are non-motile and non-professional phagocytes, yet they possess the ability to engulf apoptotic corpses.A commonly used method to detect phagocytosis, as described in this paper, is to label the engulfing and engulfed cells with different fluorophores and to detect double-positive cells.
|
|
Acute suppression of mitochondrial ATP production prevents apoptosis and provides an essential signal for NLRP3 inflammasome activation
Benedikt S. Saller, et. al., Immunity, 2025.
Apoptosis and NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis are distinct cell death pathways, but mitochondrial signals determine which pathway the cell follows. This paper describes the preparation methods for various primary cells, including PBMCs, thymocytes, microglia, and Kupffer cells, which will be useful to researchers performing immune cell experiments.
|
Related Techniques (click to open/close)
|
Application Note (click to open/close)
> Changes in various indicators of cell death induced by drugs
|
|
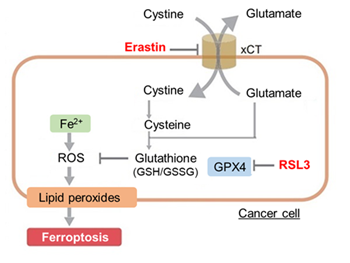
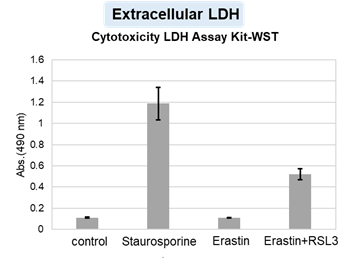
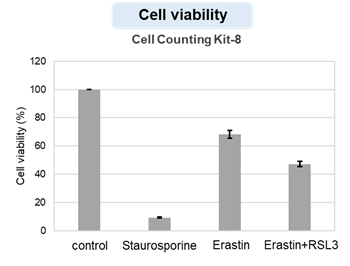
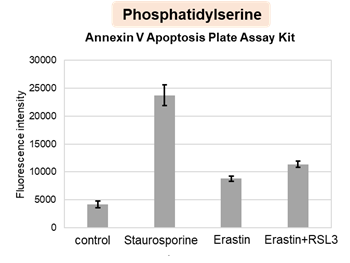
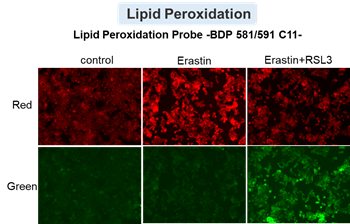
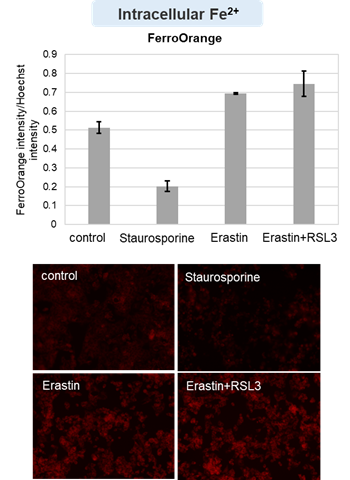
HepG2 cells treated with the apoptosis-inducing agent staurosporine or the ferroptosis-inducing agents Erastin and RSL3. After treatment, extracellular LDH, phosphatidylserine, cell viability, intracellular Fe2+ and lipid peroxidation were determined.
The results showed that apoptosis-induced cells treated with staurosporine showed an increase in phosphatidylserine, a decrease in cell viability and an increase in extracellular LDH, indicating that cell death had occurred. On the other hand, intracellular Fe2+, an indicator of ferroptosis, remained unchanged. In cells treated with Erastin, a ferroptosis inducer, intracellular Fe2+ increased and cell viability decreased, but extracellular LDH and lipid peroxidation (lipid peroxidation: decrease in red fluorescence and increase in green fluorescence) did not increase. In cells in which ferroptosis was more strongly induced by co-treatment with RSL3 in addition to Erastin, increased intracellular Fe2+ and lipid peroxidation were observed. Moreover, decreased cell viability and increased dead cells were detected. Meanwhile, phosphatidylserine showed a lower rate of increase during ferroptosis induction compared to apoptosis-induced cells. These results suggest that cell death can be distinguished by evaluating a combination of cell death indicators.
|
|
|
|
 |
|





















