Science Note
[Oct. 9, 2024]
Understanding Cell Death: New Targets for Disease Treatment
In recent years, different types of cell death have been reported and their association with neurodegenerative diseases and potential application in cancer treatment research is anticipated. Understanding the mechanisms of cell death is crucial to the development of these studies. Here are some of the studies that have recently revealed the mechanisms of cell death.Celll death is a fundamental biological process that plays a critical role in maintaining tissue homeostasis and development. Dysregulation of cell death, whether excessive or insufficient, is associated with several diseases. For example, uncontrolled cell death can lead to neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's, while impaired cell death mechanisms are often involved in the development of cancer, allowing abnormal cells to proliferate. Understanding the mechanisms of cell death, such as apoptosis, necrosis and ferroptosis, is crucial to the development of therapies for these diseases. |
||
|
Creation of distinctive Bax-lipid complexes at mitochondrial membrane surfaces drives pore formation to initiate apoptosis |
7-Dehydrocholesterol is an endogenous suppressor of ferroptosis |
Oxylipins and metabolites from pyroptotic cells act as promoters of tissue repair |
|
Point of Interest - Mitochondria store cytochrome C in cristae, which is released through pores formed by Bax upon induction of apoptosis, triggering cell death. - The apoptotic protein Bax first rapidly adsorbs to the mitochondrial membrane surface, initiating the pore formation process. - Bax then extracts lipids, forming Bax-lipid clusters that are deposited on the membrane, leading to pore formation and apoptosis. |
Point of Interest - 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase (DHCR7) has proferroptotic activity, while its substrate 7-dehydrocholesterol (7-DHC) unexpectedly promotes cancer cell survival by preventing lipid autoxidation. - 7-DHC accumulation protects lipids from peroxidation in cancer cells, leading to ferroptosis resistance and a more aggressive tumour phenotype. - Accumulation of 7-DHC in neuroblastoma and Burkitt's lymphoma promotes ferroptosis resistance and contributes to tumour aggressiveness. |
Point of Interest - Pyroptosis is a form of cell death that limits the spread of infection and is associated with sterile inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, involving inflammasome activation and secretion of IL-1β. - A study of macrophages undergoing pyroptosis without IL-1β or IL-1α shows that the secretome of these cells enhances fibroblast and macrophage migration, improves wound closure and promotes tissue repair through oxylipins and metabolites. - In particular, prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), which is synthesized during pyroptosis, and is a key contributor to tissue repair by promoting immune cell infiltration and macrophage polarization. |
| Related Techniques | ||
| Apoptosis detection in multiple samples | Annexin V Apoptosis Plate Assay Kit NEW | |
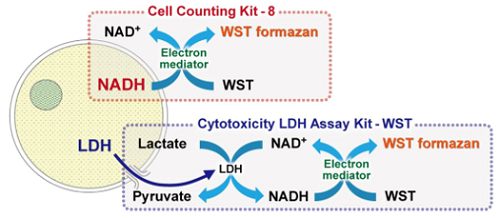
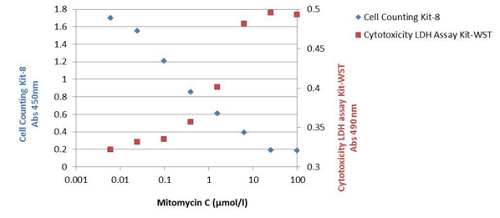
| Cell proliferation/ cytotoxicity assay | Cell Counting Kit-8, Cytotoxicity LDH Assay Kit-WST | |
| Intracellular / mitochondrial ferrous ion (Fe2+) detection | FerroOrange, Mito-FerroGreen | |
| Intracellular / mitochondrial lipid peroxidation detection | Liperfluo, MitoPeDPP | |
| Mitochondrial membrane potential detection | JC-1 MitoMP Detection Kit, MT-1 MitoMP Detection Kit | |
| Mitochondrial superoxide detection | MitoBright ROS Deep Red - Mitochondrial Superoxide Detection | |
| Oxygen consumption rate assay | Extracellular OCR Plate Assay Kit | |
| Glycolysis/Oxidative phosphorylation Assay | Glycolysis/OXPHOS Assay Kit | |
| Total ROS detection | Highly sensitive DCFH-DA or Photo-oxidation Resistant DCFH-DA | |
| Related Applications | ||
|
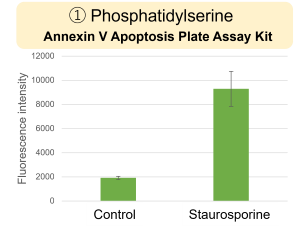
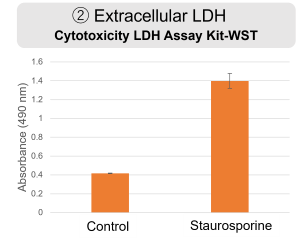
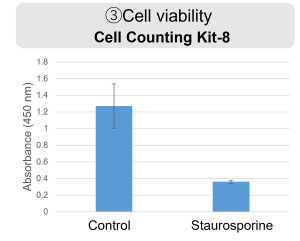
Inhibition of Mitochondrial Electron Transport Chain HepG2 cells were treated with staurosporine to induce apoptosis, and phosphatidylserine, extracellular LDH and cell proliferation were detected. Phosphatidylserine was measured as an apoptosis marker using the Annexin V Apoptosis Plate Assay Kit, extracellular LDH was measured as an indicator of dead cells using the Cytotoxicity LDH Assay Kit-WST , and cell proliferation was measured using the Cell Counting Kit-8. The results showed that staurosporine treatment increased phosphatidylserine and extracellular LDH, and decreased cell proliferation. |
||






 Please watch this video for comparison between MTT and Cell Counting Kit-8.
Please watch this video for comparison between MTT and Cell Counting Kit-8.