Autophagy : Reagent Selection Guide
Science Note
Employing Autophagy to Eliminate Disease Origins [Jun. 3, 2025]
| Autophagy is increasingly recognized as a key regulator in disease pathogenesis, influencing the mechanisms of protein aggregation, secretion, and cellular clearance. This Science Note introduces three studies highlighting how autophagy suppression by PHGDH, the secretion mechanism of the antioxidant protein PARK7, and p97/VCP-dependent aggrephagy contribute to the progression of neurodegeneration and cancer. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Transcriptional regulation by PHGDH drives amyloid pathology in Alzheimer’s disease (Cell, 2025) Highlighted technique: This study demonstrated that PHGDH increases the expression of IKKα and HMGB1, which are involved in the suppression of autophagy via the mTOR pathway, at both the mRNA and protein levels in brain organoid astrocytes. Impaired autophagy was also confirmed by a reduction in autophagosomes using fluorescent small-molecule probes. Related technique Autophagic Flux Detection, Apoptosis Detection |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Unconventional secretion of PARK7 requires lysosomal delivery via chaperone-mediated autophagy and specialized SNARE complex (PNAS, 2025) Highlighted technique: In this study, autophagy was monitored by expressing LC3 fused with either GFP or mRFP in cells. While both GFP and mRFP fluorescence are visible in autophagosomes, only mRFP remains detectable in autolysosomes due to the quenching of GFP in the acidic environment. Related technique Autophagic Flux Detection Lysosome function |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
p97/VCP is required for piecemeal autophagy of aggresomes (Nature Communications, 2025) Highlighted technique: In this study, retinoic acid-differentiated SH-SY5Y cells, which mimic neuron-like properties and are commonly used to study aggresomes, were utilized as a disease-relevant model. Autophagy was assessed by immunofluorescence staining of LC3, revealing that p97/VCP inhibition blocked aggresome clearance. Related technique Autophagic Flux Detection Mitophagy Detection |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Related Techniques (click to open/close)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Application Note I (click to open/close)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
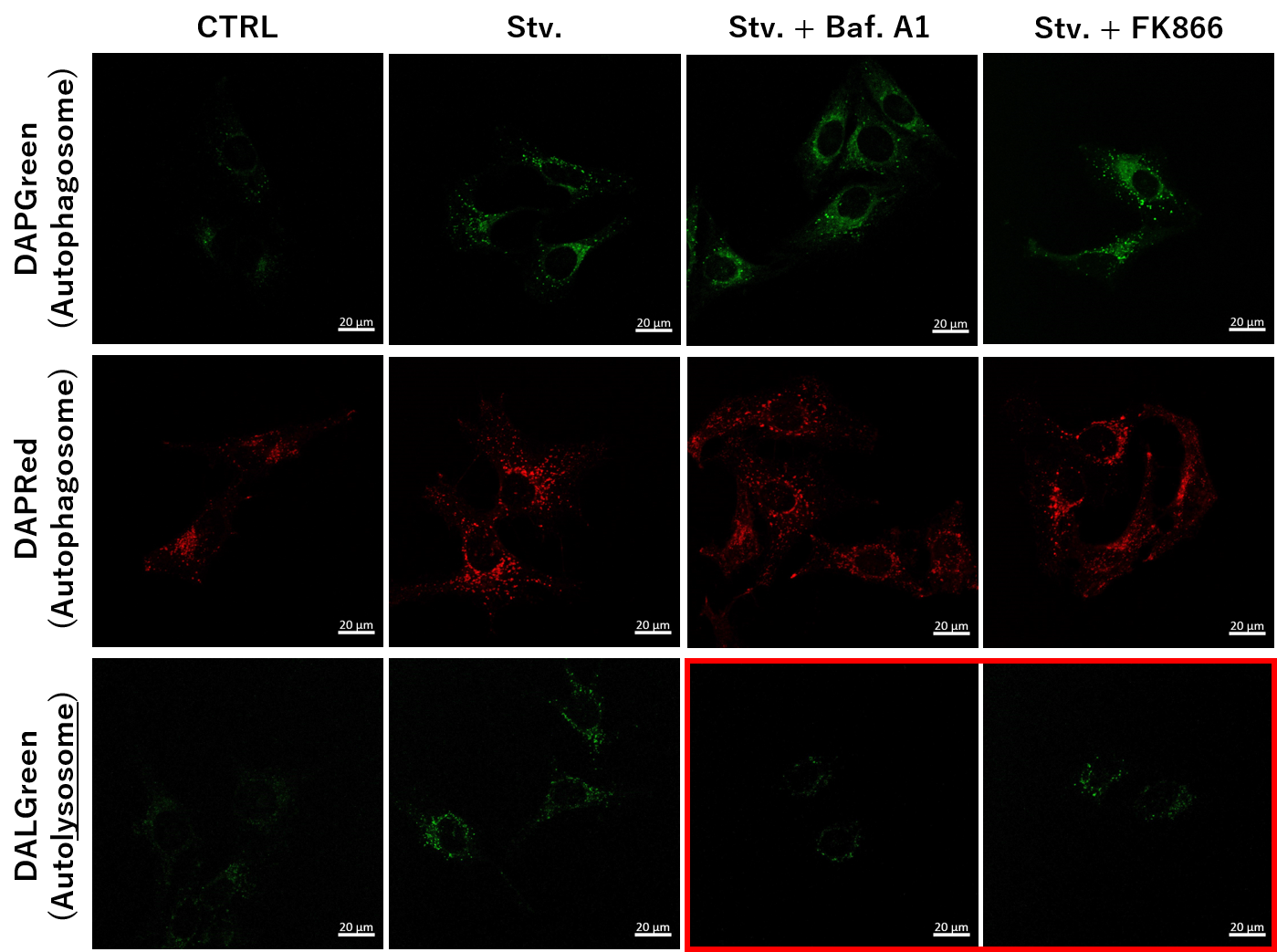
We determined how FK866-induced lysosomal deacidification affects the autophagy-lysosomal pathway. After staining with DAPGreen/DAPRed (for detecting autophagosome), or DALGreen (for detecting autolysosome), HeLa cells were starved in HBSS incubation and then treated with FK866 or Bafilomycin A1. Under the starvation condition, the fluorescent signals from all dyes increased, indicating the proceeding autophagy-lysosomal pathway. On the other hand, only DALGreen's signals were decreased in FK866 and Bafilomycin A1 treated cells with starvation conditions. These results clearly suggested that FK866 inhibits the autophagy-lysosomal pathway by NAD+ depletion-induced lysosomal deacidification. Nampt inhibitor, FK866 inhibits the progress of autophagosome to autolysosome by lysosomal deacidification. A recent finding shows that the dysfunctional condition of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) biosynthetic enzyme, Nampt induces lysosomal deacidification1). In this section, we tried to determine how NAD+ depletion-induced lysosomal deacidification affects the autophagy-lysosomal pathway. 1) Mikako Yagi, et. al., EMBO J., 40(8), e105268 (2021) |
Application Note II (click to open/close)
> Simultaneous Detection of Lysosomal and Mitochondrial Dysfunction
|
|
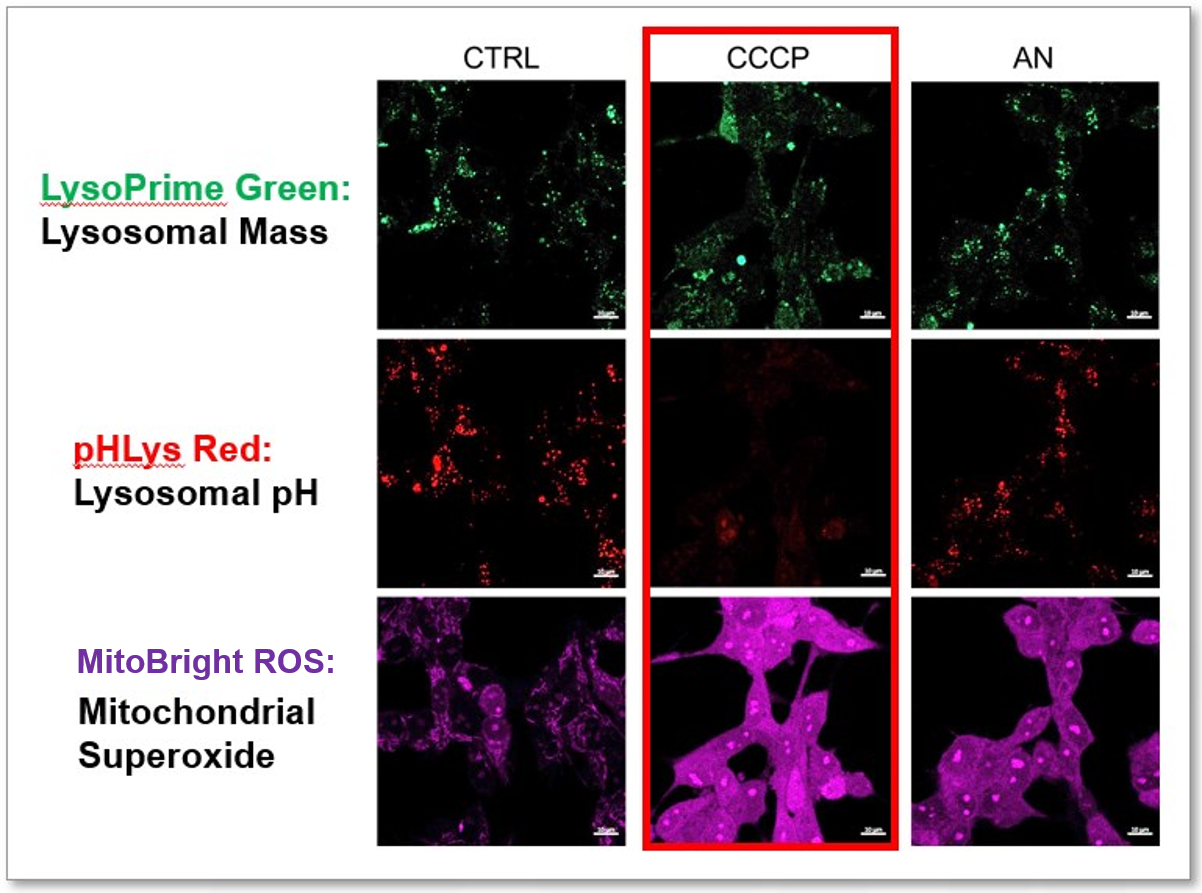
We tried the simultaneous detection of lysosomal and mitochondrial dysfunction in Hela cells treated with CCCP or Antimycin (AN). CCCP and AN are well-known inducers of mitochondrial ROS regarding loss of mitochondrial membrane potential. Recent research showed the result that CCCP induces not only mitochondrial ROS but also lysosomal neutralization. To detect mitochondrial ROS, HeLa cells were labeled by MitoBright ROS Deep Red - Mitochondrial Superoxide Detection, and the lysosomal mass and pH were detected separately with LysoPrime Green and pHLys Red. Co-staining with MitoBright ROS and Lysosomal dyes demonstrated that CCCP causes lysosomal neutralization and mitochondrial ROS induction at the same time. Products in Use
|
Topics
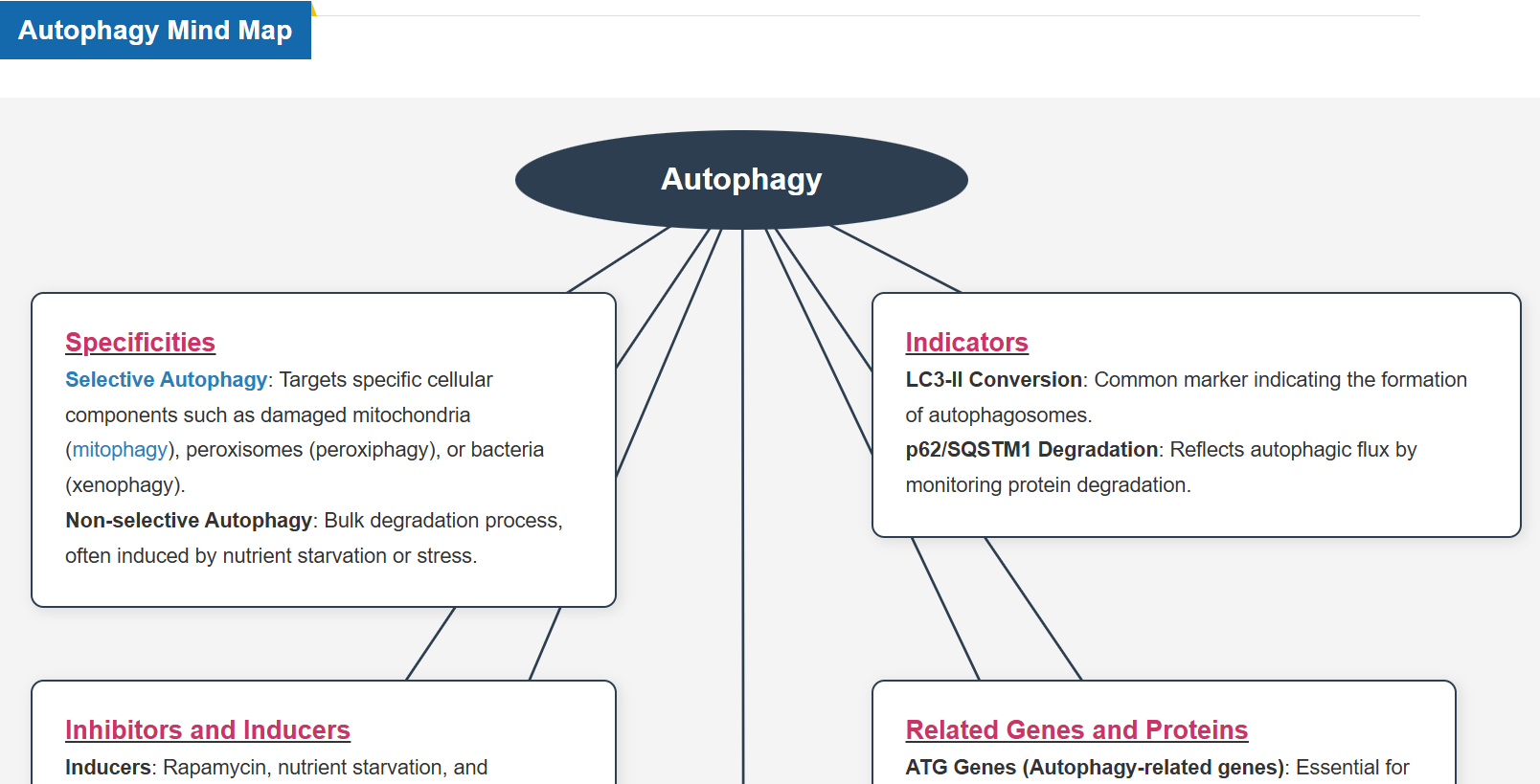
- What is Autophagy?
- Autophagy Reagents Selection Guide
- Principle of Autophagy Reagents
- Typical Examples of Article in Use
- Experimental Example: Analysis of autolysosome formation inhibition using Bafilomycin A1 by confocal fluorescence microscopy
- Experimental Example: Analysis of lysosomal protein degradation inhibition using E64d/Pepstatin A by confocal fluorescence microscopy
- Experimental Example: Time-lapse imaging of autophagy with DALGreen
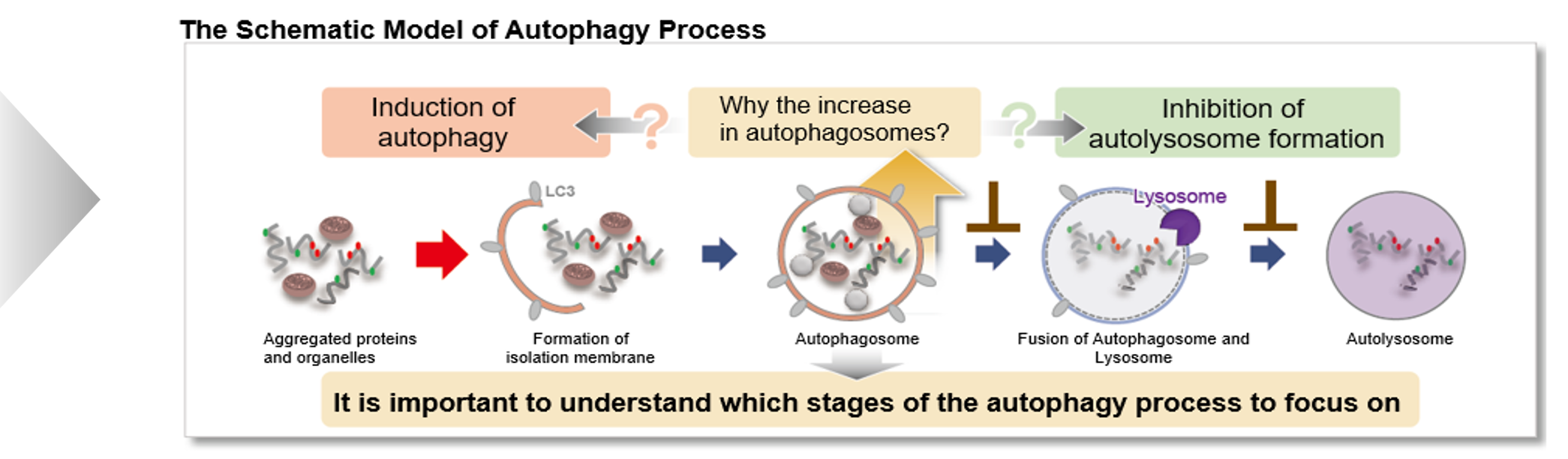
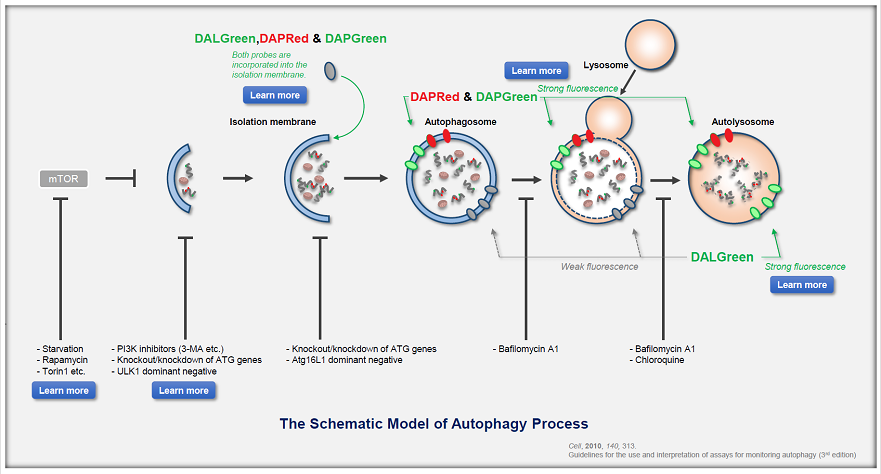
What is Autophagy?
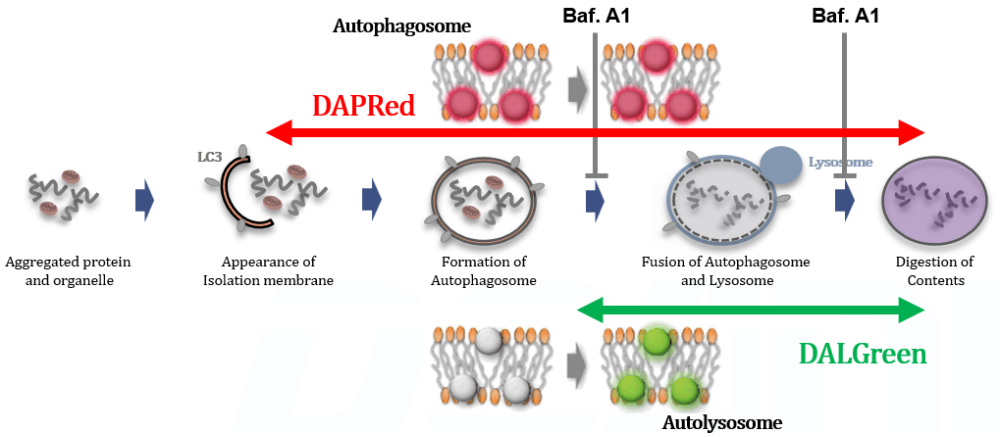
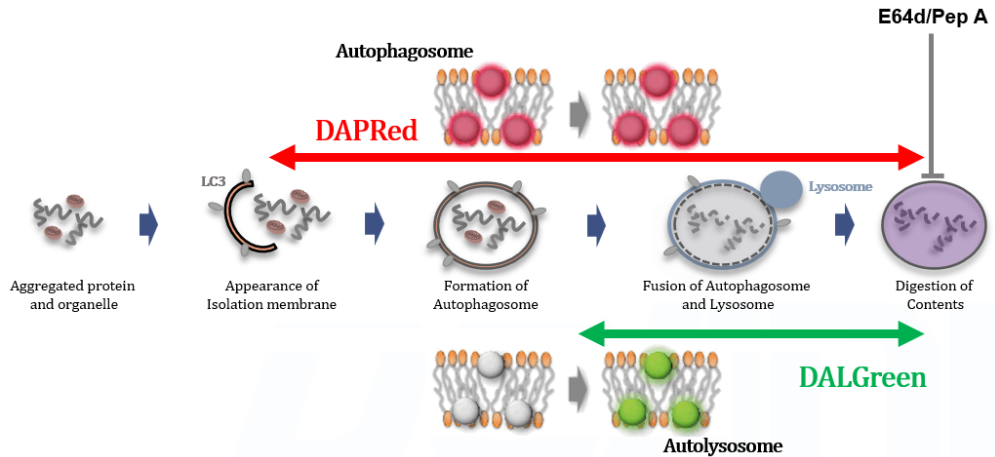
Autophagy is a degradation process of cytoplasmic dysfunctional proteins and organelles. In this process, an isolation membrane composed of a double membrane appears in the cytosol, gradually expands, encloses the aggregated proteins and damaged organelles, and close to form autophagosomes. The autophagosomes are fused with lysosomes to form autolysosomes, which have an acidic environment. The contents in autolysosomes are decomposed by digestive enzymes in lysosomes. Since this cellular function is said to be related to aging as well as neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s disease, a simple autophagy detection method is being required.
Autophagy Reagents Selection Guide
Depending on the method and purpose of autophagy assessment, three types of fluorescent small molecule reagents and kits are available.
Select by targets
| Small Fluorescent Molecules | Fluorescent Protein | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DAPGreen | DAPRed | DALGreen | Autophagic Flux Assay Kit | GFP-LC3 | RFP-LC3 | mRFP-GFP-LC3 | |
| Autophagosome | ✓ | ✓ | - | Autophagosomes and autolysosomes are each detectable. | ✓ | ✓ | Autophagosomes and autolysosomes are each detectable. |
| Autolysosome | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | - | ✓ | ||
| Transfection | No need for transfection | ✓ | |||||
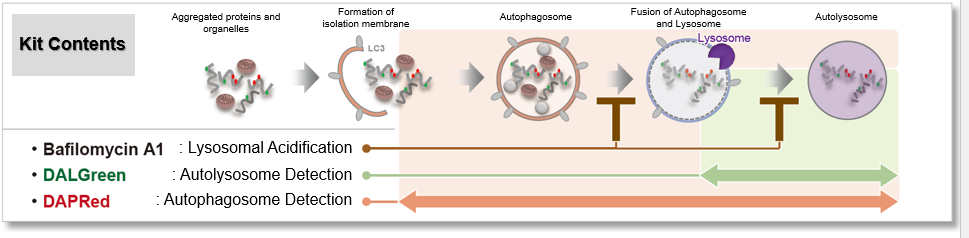
Autophagic Flux Assay Kit: This kit contains autophagosome and autolysosome detection dye (DAPRed), autolysosome detection dye (DALGreen), and lysosomal acidification inhibitor (bafilomycin A1). The Autophagic Flux Assay Kit allows the accurate evaluation of autophagic flux by monitoring autophagosome formation, lysosome fusion, and digestion of contents.
Select by detector and fluorescence propety
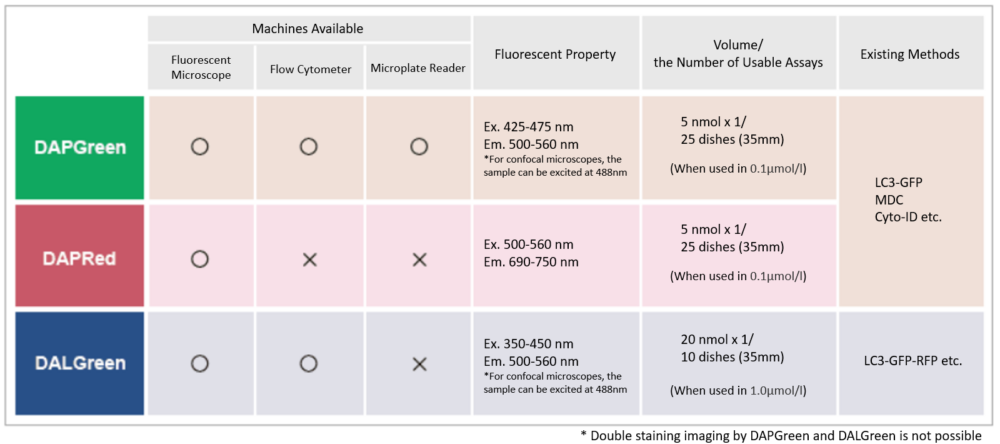
There are several autophagy-related products available, which one to choose?
|
Example: Screen the autophagy activity of a drug
|
Principle of Autophagy Reagents
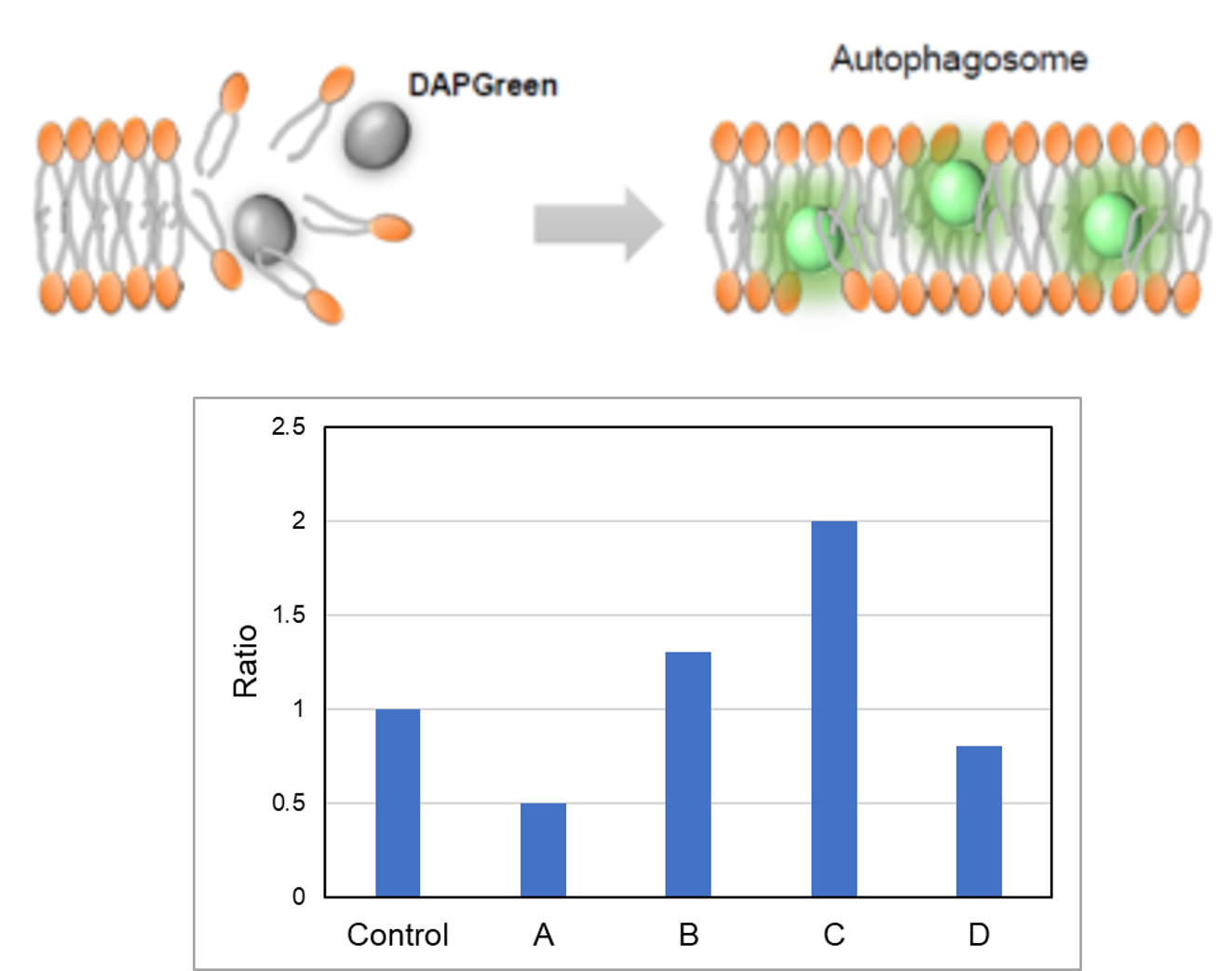
DALGreen / DAPGreen is incorporated into hydrophobic lipid bilayers due to its similar structure to membrane phospholipids such as phosphatidylethanolamine.
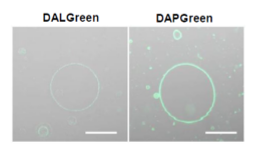
DALGreen and DAPGreen were each incorporated during liposome membrane formation and observed by confocal microscopy; DAPGreen showed strong fluorescence upon incorporation into the lipid bilayer, whereas weak fluorescence was observed for DALGreen. Scale bar: 20 μm
DAPGreen: fluorescence intensity increases in response to the hydrophobic field environment within the lipid bilayer (detects both autophagosomes and autolysosomes)
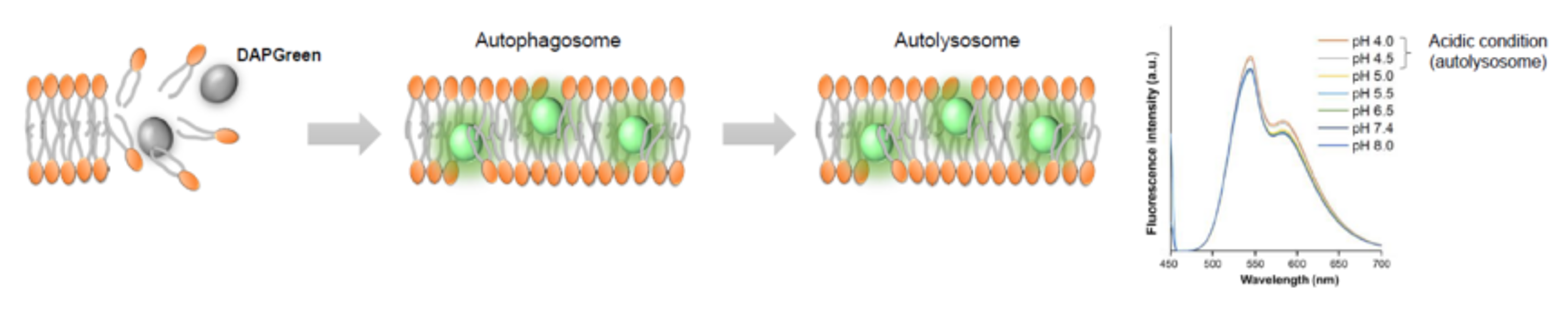
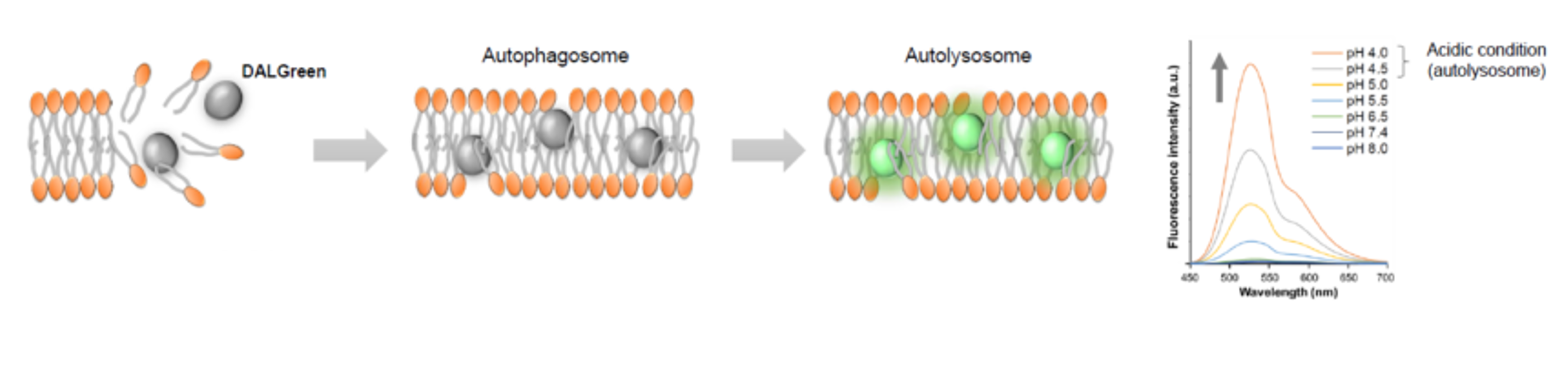
DALGreen : incorporated into lipid bilayers, fluorescence intensity increases in acidic environment (detects autolysosomes)
For detailed experimental results, including the specificity of autophagy, see the original paper here.
DAPGreen/DALGreen: H. Iwashita, et al., "Small fluorescent molecules for monitoring autophagic flux", FEBS Letters., 2018, 592, (4), 559–567.
DAPRed:H. Sakurai, et al, "Development of small fluorescent probes for the analysis of autophagy kinetics, iScience, 2023, 26, 107218.
Typical Examples of Article in Use
| Title | Discovery and Structure-Based Optimization of Novel Atg4B Inhibitors for the Treatment of Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Kudo, Y. et al., Journal of Medical Chemistry, 2022, 65(6) |
| Purpose | Evaluation of ATG4B inhibitors using autophagy activity as an indicator. |
|
Product/ |
DAPGreen/Microscope |
| Title | S-Nitrosylation of p62 Inhibits Autophagic Flux to Promote α-Synuclein Secretion and Spread in Parkinson's Disease and Lewy Body Dementia Oh, C. et al., Journal of Neuroscience, 2022, 41(14), 3011-3024 |
| Purpose | Confirmation that p62(C331A) knock-in mutant causes autophagy inhibition (decrease in autolysosomes). |
| Product/ Method |
DALGreen&DAPRed (Autophagic Flux Assay Kit)/Microscope |
| Title | Scd1 and monounsaturated lipids are required for autophagy and survival of adipocytes Mori, H. et al., Molecular Metabolism, 2024, 83, 101916 |
| Purpose | Confirmation that SCD1KO causes autophagy inhibition (decrease in autolysosomes). |
| Product/ Method |
DALGreen&DAPRed (Autophagic Flux Assay Kit)/Microscope |
Experimental Example: Analysis of autolysosome formation inhibition using Bafilomycin A1 by confocal fluorescence microscopy
DALGreen and DAPRed labeled HeLa cells were used to evaluate changes in autophagic flux induced by the lysosomal acidification inhibitor bafilomycin A1 (Baf. A1). Compared to starvation conditions, the fluorescence signals of DALGreen were decreased under inhibited conditions of autolysosome formation by the addition of Baf. A1. In contrast, the fluorescence signals of DAPRed were increased under the same conditions, indicating that Baf. A1 led to the accumulation of autophagosome.
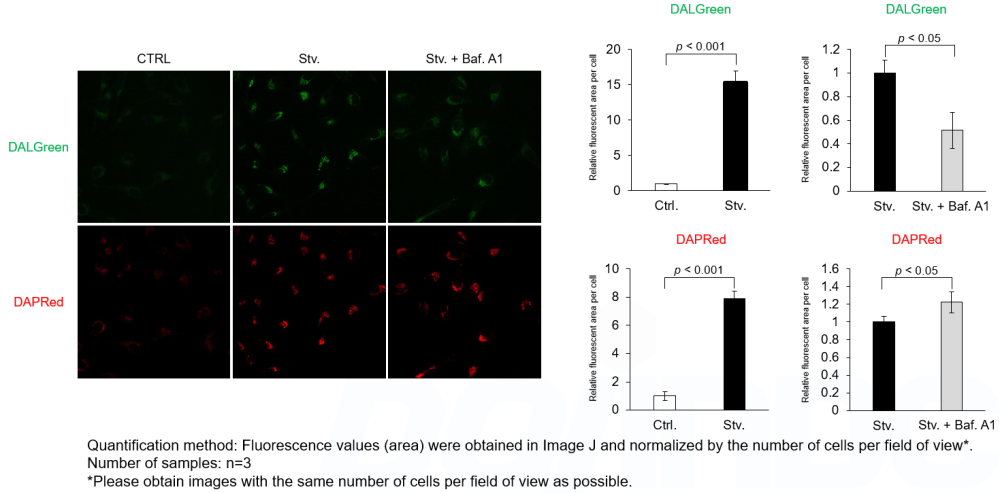
<Experimental Conditions>
CTRL: Normal condition, Stv.: Induction of autophagy, Stv. + Baf. A1: Inhibition of autolysosome formation
DALGreen filter set: 488 nm (Ex), 490–550 nm (Em)
DAPRed filter set: 561 nm (Ex), 565–700 nm (Em)
<Procedure>
1. HeLa cells were seeded (1.0 x 104 cells/well) on a μ-slide 8 well plate (ibidi) and cultured overnight at 37°C in an incubator equilibrated with 95% air and 5% CO2.
2. After washing twice with MEM containing 10% fetal bovine serum, 200 μl of DALGreen/DAPRed working solution (DALGreen: 1 µmol/l, DAPRed: 0.2 µmol/l) and the cells were incubated at 37°C for 30 minutes.
3. The supernatant was discarded, and the cells were washed twice with MEM containing 10% fetal bovine serum.
4. Samples were prepared under the following conditions.
• MEM containing 10% fetal bovine serum (200 µl) was added to the well, and the cells were incubated at 37 °C for 2 hours 20 minutes. (Control)
• Amino acid-free medium (FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., Catalogue code: 048-33575) (200 μl) was added to the well, and the cells were incubated at 37°C for 2 hours 20 minutes. (Starvation)
• Amino acid-free medium (200 μl) was added to the well, and the cells were incubated at 37°C for 2 hours. The supernatant was discarded, bafilomycin A1 working solution (10,000 times dilution, 200 μl), an inhibitor of lysosomal acidification, was added to the well, and the cells were incubated at 37°C for 20 minutes. (Inhibition of autolysosome formation)
5. The stained cells were observed under a confocal fluorescence microscope.
Experimental Example: Analysis of lysosomal protein degradation inhibition using E64d/Pepstatin A by confocal fluorescence microscopy
DALGreen and DAPRed labeled HeLa cells were used to evaluate changes in autophagic flux induced by the inhibitor of lysosome enzymes E64d/Pepstatin A (Pep A). Compared to starvation conditions, the fluorescence signals of DALGreen and DAPRed were increased due to autolysosome accumulation by the addition of E64d/Pep A.
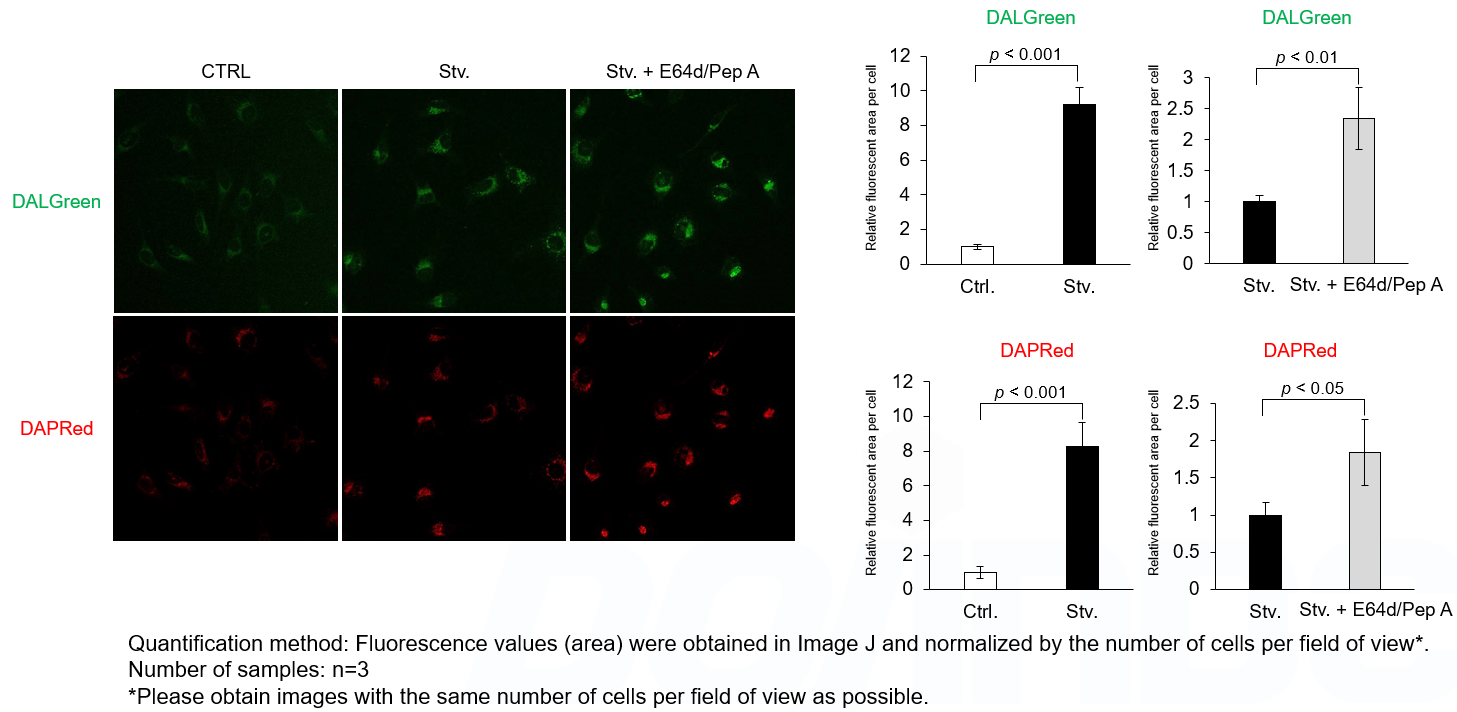
<Experimental Conditions>
CTRL: Normal condition, Stv.: Induction of autophagy, Stv. + E64d/Pep A: Inhibition of lysosomal protein degradation
DALGreen filter set: 488 nm (Ex), 490–550 nm (Em)
DAPRed filter set: 561 nm (Ex), 565–700 nm (Em)
<Procedure>
1. HeLa cells were seeded (1.0 x 104 cells/well) on a μ-slide 8 well plate (ibidi) and cultured overnight at 37 °C in an incubator equilibrated with 95% air and 5% CO2.
2. After washing twice with MEM containing 10% fetal bovine serum, 200 μl of DALGreen/DAPRed working solution (DALGreen: 1 µmol/l, DAPRed: 0.2 µmol/l) and the cells were incubated at 37°C for 30 minutes.
3. The supernatant was discarded, and the cells were washed twice with MEM containing 10% fetal bovine serum.
4. Samples were prepared under the following conditions.
• MEM containing 10% fetal bovine serum (200 µl) was added to the well, and the cells were incubated at 37°C for 2 hours. (Control)
• Amino acid-free medium (FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., Catalogue code: 048-33575) (200 μl) was added to the well, and the cells were incubated at 37°C for 2 hours. (Starvation)
• Amino acid-free medium containing E64d/Pep A (10 µg/ml each, 200 μl), an inhibitor of lysosomal protease, was added to the well, and the cells were incubated at 37°C for 2 hours. (Inhibition of lysosomal protein degradation)
5. The stained cells were observed under a confocal fluorescence microscope.
Experimental Example: Time-lapse imaging of autophagy with DALGreen
For more details, click application data
H. Iwashita, H. T. Sakurai, N. Nagahora, M. Ishiyama, K. Shioji, K. Sasamoto, K. Okuma, S. Shimizu, and Y. Ueno, “Small fluorescent molecules for monitoring autophagic flux“, FEBS Lett., 2018, 592, (4), 559–567.