|
Discovery of New Transcriptional Programs Restoring Lysosomes Suggests New Therapeutic Opportunities |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
1. A lysosomal surveillance response to stress extends healthspan (Nature Cell Biology, 2025) Summary: Researchers found that silencing vacuolar H+-ATPase subunits in the intestine of C. elegans creates a stress that activates the lysosomal surveillance response (LySR), governed by the GATA transcription factor ELT-2, to boost lysosomal activity and clear protein aggregates. This mechanism enhances lysosomal function, extends lifespan, and suggests that activating the newly identified LySR pathway could be a strategy to treat lysosome-related diseases and promote healthy aging. Highlighted technique: To examine how silencing v-ATPase subunits affects lysosomal function, the authors used two approaches in living C. elegans. They applied a fluorescent probe that labels lysosomes and a pH-sensitive lysosomal reporter to monitor changes in acidification, and these assays demonstrated that LySR activation boosts lysosomal activity. Related technique Lysosome Detection, Lysosomal Acidic pH Detection |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Summary: STING, long recognized as a cytosolic DNA sensor that initiates immune responses, is now shown to have a distinct role in maintaining lysosomal homeostasis. This study reveals that lysosomal dysfunction activates a STING–TFEB pathway, in which STING’s proton channel function triggers TFEB-driven expression of lysosomal and autophagy genes, thereby facilitating lysosomal repair and highlighting new therapeutic avenues for lysosomal storage disorders and neurodegenerative diseases. Highlighted technique: To evaluate lysosomal damage and repair, researchers used LLOME to rupture lysosomal membranes. When lysosomes were damaged, cytosolic Galectin-3 bound to the exposed glycans and was visualized as fluorescent puncta with antibodies, allowing the appearance and disappearance of these puncta over time to reveal the repair process. Related technique Lysosomal Function, Autophagic Flux Assay |
||||||||||||||||||||||
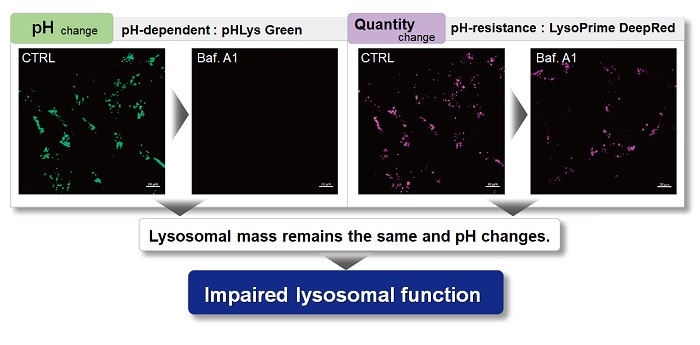
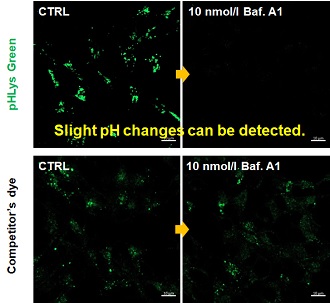
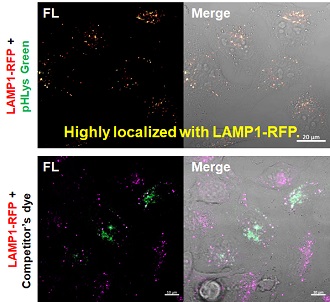
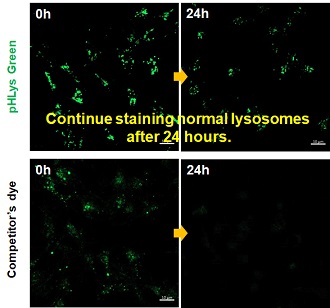
Application Note
> Accurate Measurement for Lysosomal pH changes
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
All Related Techniques
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
New Lysosome Restoration Pathways for Disease and Aging [Aug. 27, 2025]
Digital Brochure and other information
Curious about other Dojindo products? Discover more with our digital brochure! : Cell Function Analysis
 |
 |
Stay informed and connect with us on our LinkedIn page!