|
Ferroptosis is a form of programmed cell death characterized by the accumulation of lipid peroxides to lethal levels and is distinct from other forms of cell death such as apoptosis or necrosis. In cancer, ferroptosis can act as a double-edged sword: on the one hand, inducing ferroptosis in cancer cells may be a promising therapeutic strategy, as many cancers are resistant to traditional forms of cell death such as apoptosis. On the other hand, cancer cells can develop resistance to ferroptosis, which contributes to therapy resistance and tumor progression. Understanding and manipulating the pathways that regulate ferroptosis in cancer cells holds the potential for developing novel cancer treatments and overcoming resistance to existing therapies.
|
-
Targeted activation of ferroptosis in colorectal cancer via LGR4 targeting overcomes acquired drug resistance
Click here for the original article: Hao Zheng, et. al., Nature Cancer, 2024.
Point of Interest
- Chemoresistant cancer-derived organoids exhibited increased expression of LGR4 and activation of the Wnt signaling pathway.
- Inhibition of LGR4-Wnt signaling sensitized drug-induced ferroptosis.
- LGR4-dependent Wnt signaling upregulated SLC7A11, a key inhibitor of ferroptosis, leading to drug resistance.
-
7-Dehydrocholesterol is an endogenous suppressor of ferroptosis
Click here for the original article: Florencio Porto Freitas et. al., Nature, 2024.
Point of Interest
- High concentrations of 7-DHC are cytotoxic to developing neurons by promoting lipid peroxidation.
- On the other hand, 7-DHC accumulation confers a prosurvival function in cancer cells.
- 7-DHC effectively protects (phospho)lipids from autoxidation and subsequent fragmentation due to its superior reactivity with peroxyl radicals.
- Accumulation of 7-DHC induces a shift to a ferroptosis-resistant state in tumors.
-
Sensitization of cancer cells to ferroptosis coincident with cell cycle arrest
Click here for the original article:Jason Rodencal et. al., Cell Chemical Biology, 2023.
Point of Interest
- Stabilization of p53 and inhibition of CDK4/6 enhance ferroptosis induced by GPX4 inhibitors.
- Stabilization of p53 and inhibition of CDK4/6 decrease the expression of MBOAT1 and EMP2.
- Loss of EMP2 increases cell sensitivity to GPX4 inhibitors by altering lipid metabolism.
- An orally bioavailable GPX4 inhibitor shows in vivo activity.
|
|
Related Techniques
|
- Intracellular / mitochondrial ferrous ion (Fe2+) detection
- FerroOrange(intracellular), Mito-FerroGreen(mitochondrial)
|
- NAD(H) and NADP(H) redox couples assay
- NAD/NADH and NADP/NADPH Assay Kit
|
|
|
- Lipid Peroxidation Assay
- Lipid Peroxidation Probe -BDP 581/591 C11-
|
- Total ROS detection
- Highly sensitive DCFH-DA or Photo-oxidation Resistant DCFH-DA
|
- Glutathione Quantification
- GSSG/GSH Quantification Kit
|
- Cystine Uptake detection
- Cystine Uptake Assay Kit
|
- MDA detection
- MDA Assay Kit
|
- Glycolysis/Oxidative phosphorylation Assay
-
- Glycolysis/OXPHOS Assay Kit
-
|
- Apoptosis detection in multiple samples
-
- Annexin V Apoptosis Plate Assay Kit
-
|
|
Related Applications
|
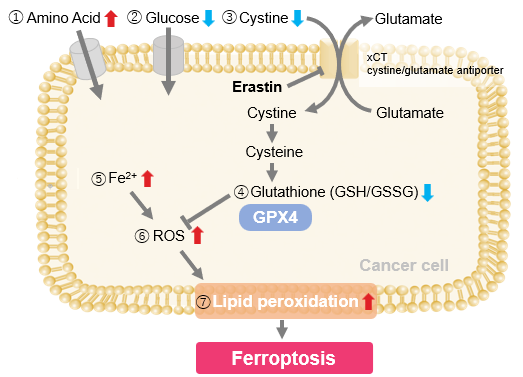
Erastin-Induced Ferroptosis: Evaluating Intracellular Uptake and Redox Balance
We investigated the transition of cellular metabolisms in A549 cells treated with erastin, a known ferroptosis inducer. Our results revealed the following.
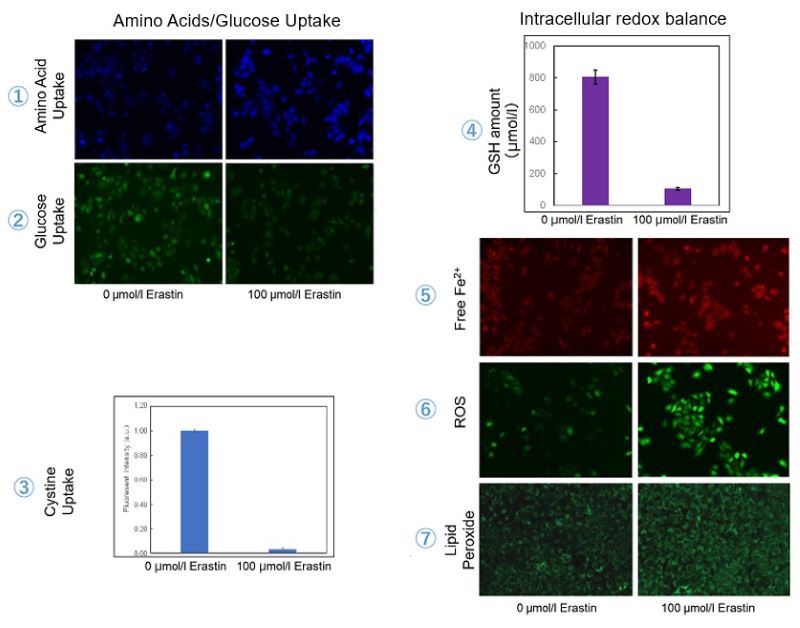
- The inhibition of cystine uptake by erastin led to a depletion of cysteine, which in turn increased the compensatory uptake of other amino acids.
- Glucose uptake, which typically promotes ferroptosis*, was found to decrease upon erastin treatment, suggesting a potential cellular self-defense mechanism.
- The depletion of cysteine resulted in a decrease in glutathione levels and an increase in Fe2+, ROS, and lipid peroxides, all of which are recognized markers of ferroptosis.
Cell Line: A549
Incubation Conditions: 100 μmol/l Erastin/MEM, 37℃, 3h
*Reference: Xinxin Song, et al., Cell Reports, (2021)
Products in Use
|

















