Cell Cycle Assay Solution Deep Red
Cell Cycle Measurement
- Can be used with a 633 nm laser
- No RNase treatment necessary!
-
Product codeC548 Cell Cycle Assay Solution Deep Red
| Unit size | Price | Item Code |
|---|---|---|
| 50 tests | $159.00 | C548-10 |
| 50 tests | Cell Cycle Assay Solution Deep Red | 250 μl×1 |
|---|
Product Description
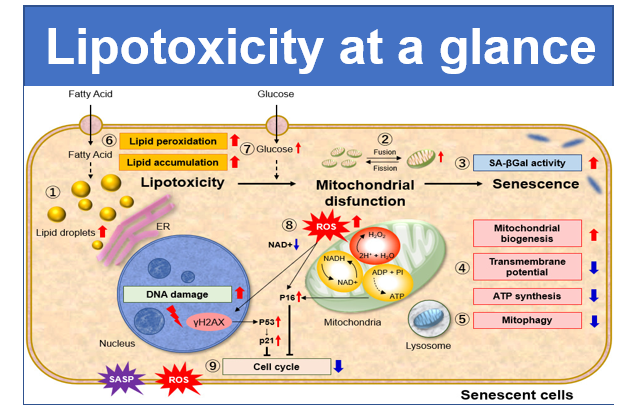
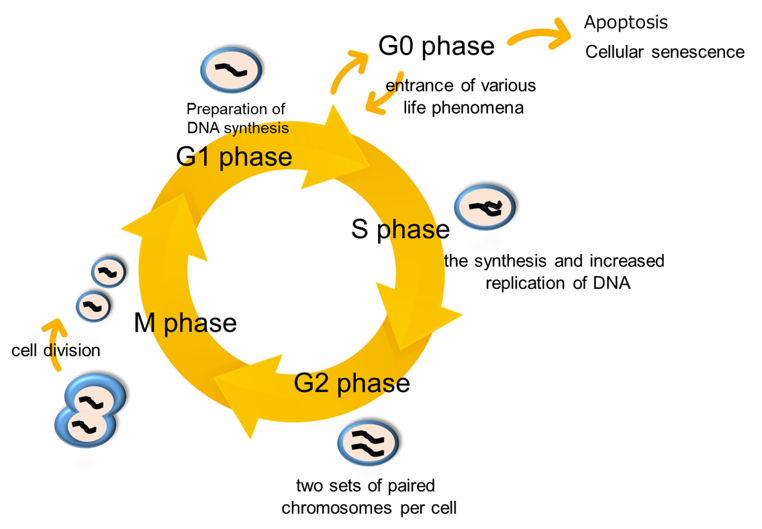
The control system of the cell cycle is closely linked to cell proliferation. Cell division in which one cell produces two daughter cells occurs as part of the cell cycle. The cell cycle can be analyzed by measuring the cells stained for DNA using flow cytometry, followed by analysis of the proportion of stained nuclei in cell cycle phase. The cell cycle is classified into two major phases: interphase and the mitotic (M) phase. Interphase is composed of G1 phase (preparation for DNA synthesis which occurs prior to cell division), S phase (DNA synthesis and replication), and G2 phase (a single cell with duplicated chromosomes). M phase involves mitosis and cytokinesis. Cell cycle progression is regulated by cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases. To determine the action of anticancer drugs and others, it is important to analyze the mechanism of cell-cycle checkpoint.
Manual
Technical info
Propidium iodide (PI) is generally used for cell cycle analysis using flow cytometry. Compared to this analysis method, the Cell Cycle Assay Solution Deep Red has good membrane permeability and uses the dye with high specificity for DNA, which makes it possible to analyze the cell cycle just by adding the reagent to a cell suspension. Additionally, a 633 nm laser is available in the Cell Cycle Assay Solution Deep Red, allowing you to concurrently use a highly versatile 488 nm laser.
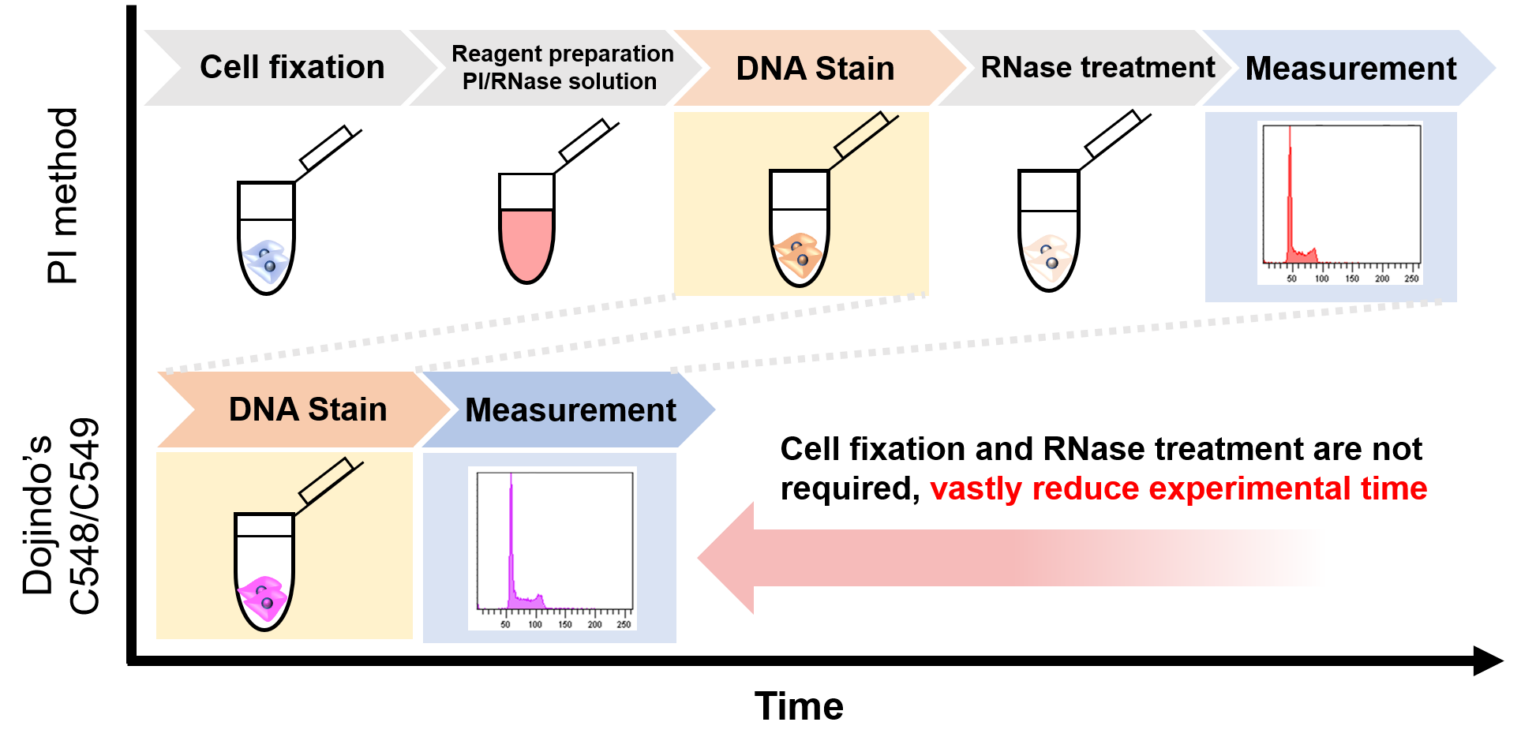
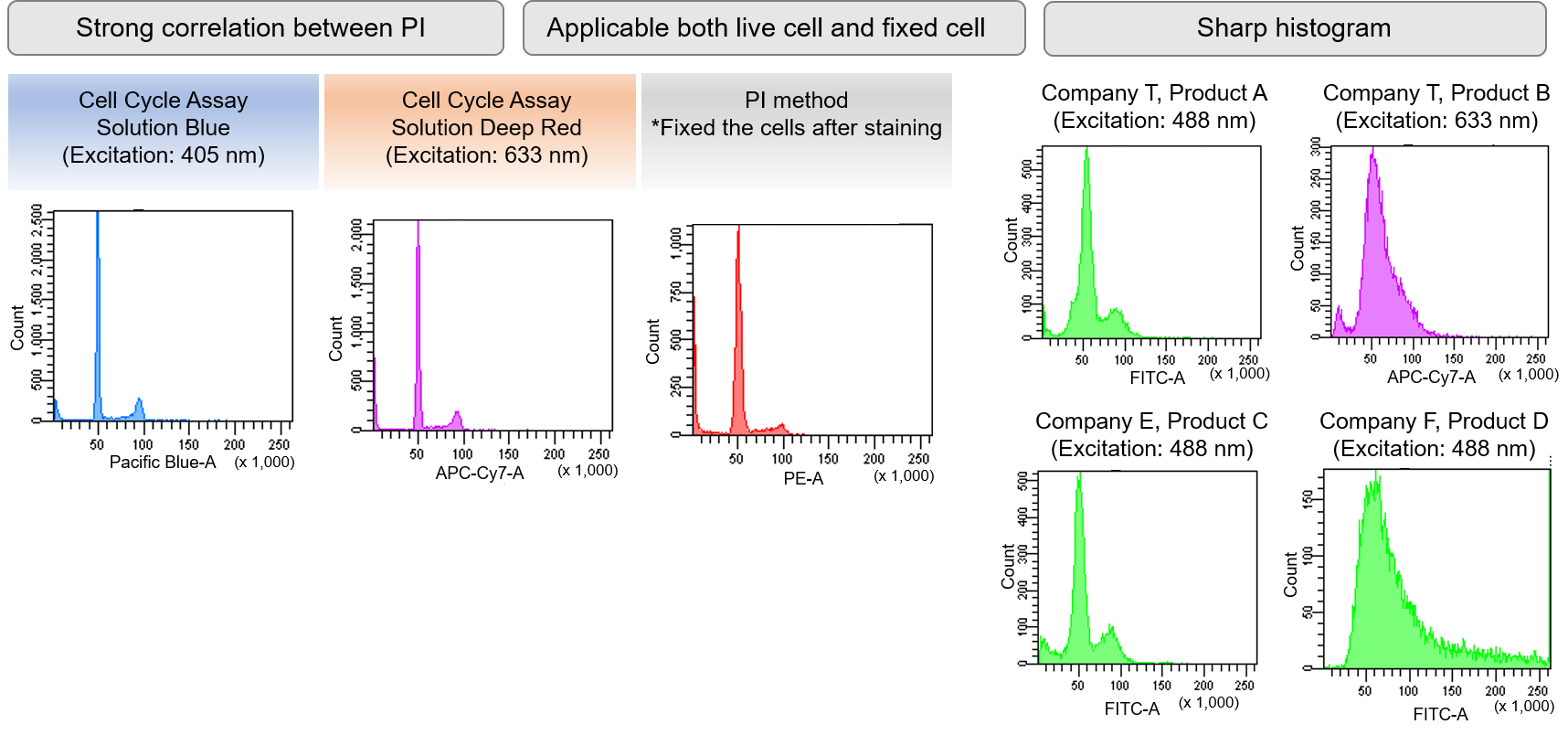
Clearly Identify Cell Cycle Stages
Live CHO cells stained by the Cell Cycle Assay Solution Blue and Deep Red were measured by flow cytometry. Similar experiments were performed using the existing reagent for cell cycle analysis and PI staining a widely used staining technique. As a result, results obtained by the Cell Cycle Assay Solution were equivalent to PI staining results (shown below). Compared to four different products, our product obtained a sharp histogram peak in live cells.
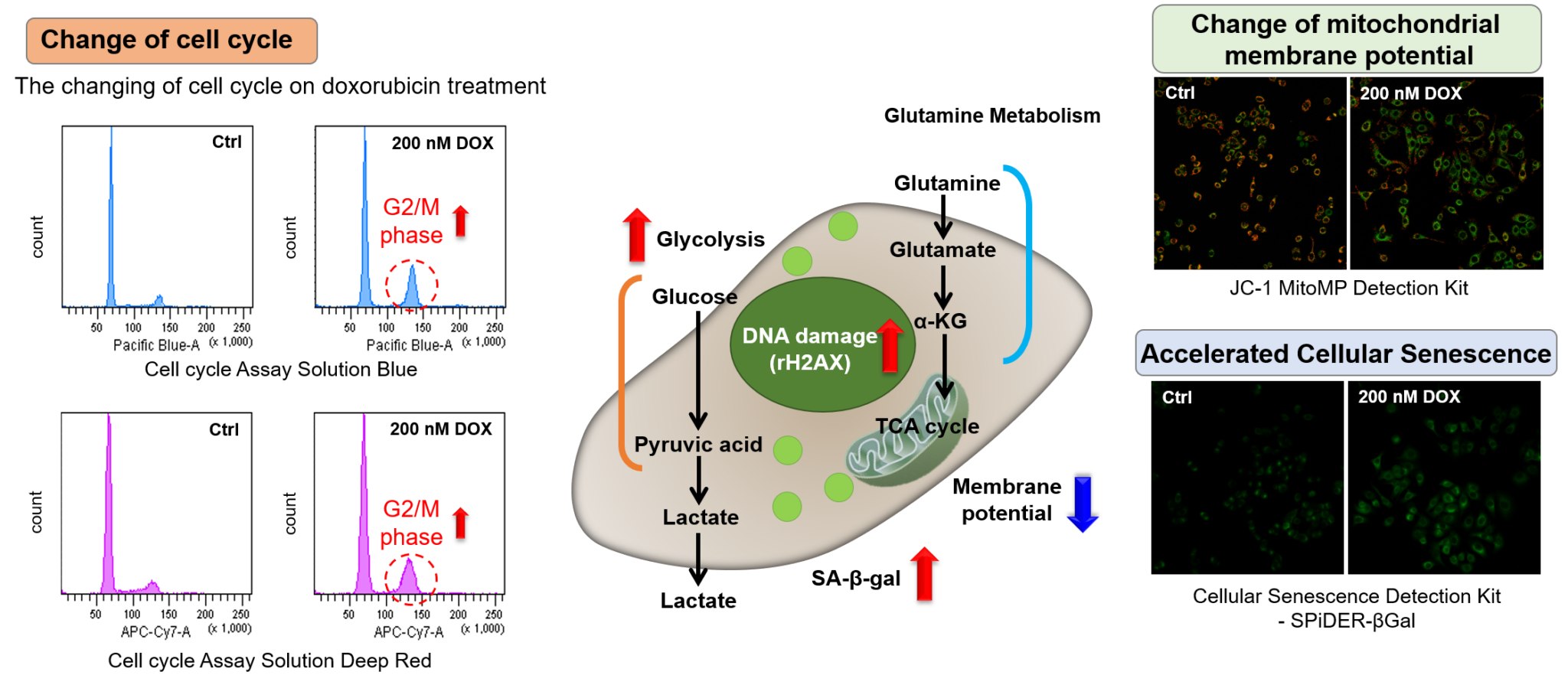
Measurement Example
Doxorubicin (DOX) acts to inhibit cell proliferation during G2/M phases of the cell cycle and induces cellular senescence. After adding DOX to A549 cells, higher histogram peaks for the G2/M phase (Cell Cycle Assay Solution Blue and Deep Red), induced cellular senescence (Cellular Senescence Detection Kit – SPiDER-βGal), and differences in mitochondrial membrane potential (JC-1 MitoMP Detection Kit) were observed compared to before.
Supplementary information on technology and products used
-
Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Detection
JC-1 MitoMP Detection Kit
-
Senescence Cell Detection
Cellular Senescence Detection Kit - SPiDER-βGal
References
| Reference No. | Sample | Cite |
|---|---|---|
| 1) | Cells (HCAECs) |
N. Sasaki, Y. Itakura and M. Toyoda, "Rapamycin promotes endothelial-mesenchymal transition during stress-induced premature senescence through the activation of autophagy”, Cell Commun. Signal, 2020, 18(1), 43 |
| 2) | Cells (ARPE-19) |
T. Yamazaki, H. Suzuki, S. Yamada, K. Ohshio, M. Sugamata, T. Yamada and Y. Morita, "Lactobacillus paracasei KW3110 Suppresses Inflammatory Stress-Induced Premature Cellular Senescence of Human Retinal Pigment Epithelium Cells and Reduces Ocular Disorders in Healthy Humans”, Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(14), 5091 |
| 3) | Cells (MIA PaCa-2) |
N. Sasaki, F. Gomi, F. Hasegawa, K. Hirano, M. Fujiwara, M. Toyoda and T. Ishiwata, "Characterization of the metastatic potential of the floating cell component of MIA PaCa-2, a human pancreatic cancer cell line”, Biochem. biophys. res. commun, 2020, 522(4), 881-888 |
Q & A
-
Q
Can I use both floating cells and adherent cells?
-
A
Yes, this kit can be used for both floating cells and adherent cells.
-
Q
Is it necessary to fix cells?
-
A
No, this kit can be used for both unfixed and fixed cells.
-
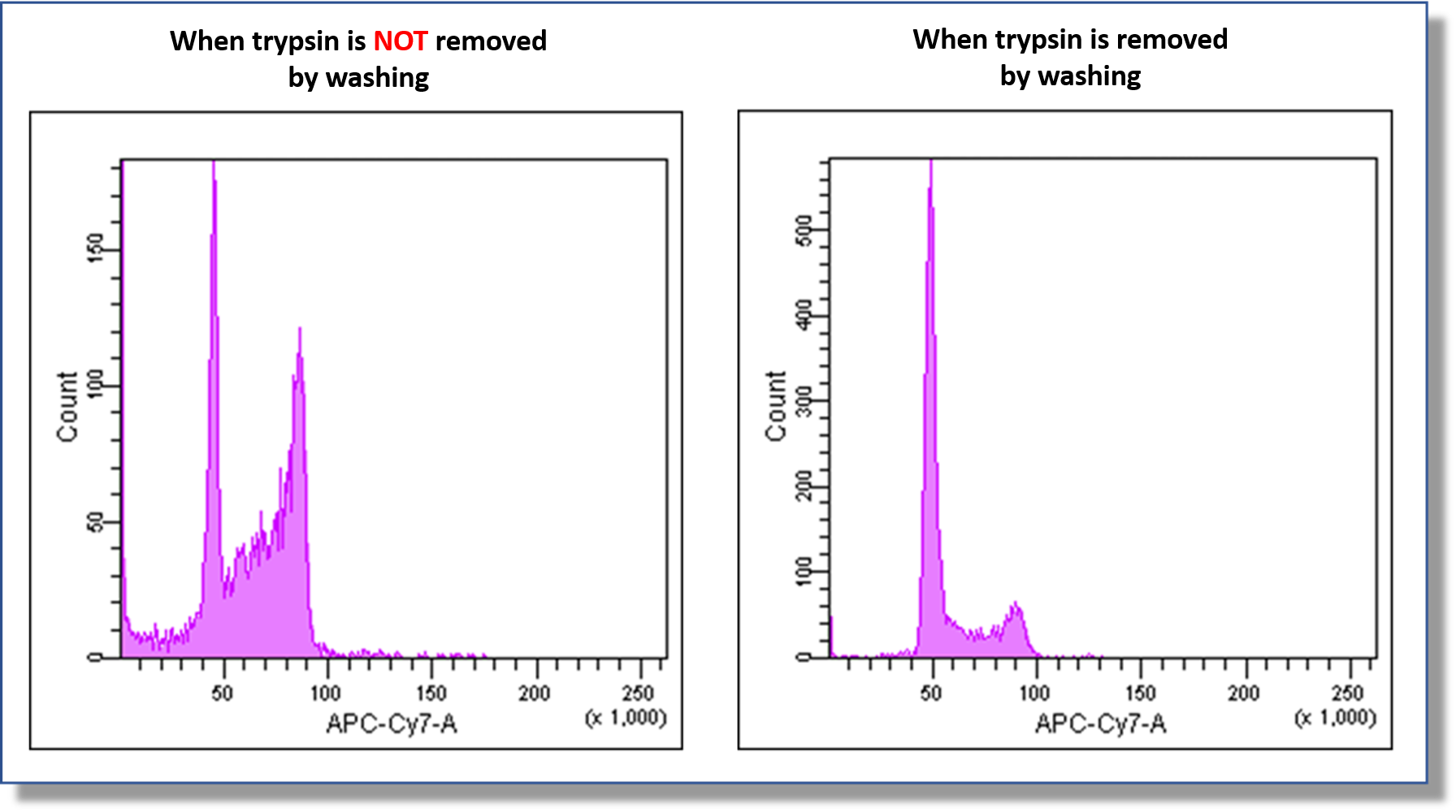
Q
Does trypsin affect the measurement?
-
A
Any residual trypsin will affect the measurement.
After recovery of cells with trypsin, be sure to wash the cells before staining according to the protocol.An example of an experiment confirming the effect of trypsin is shown below.
-
Q
Can immunostaining of cell surface antigens and Cell Cycle Assay Solution be co-stained?
-
A
No, co-staining is not compatible because the additives in the Cell Cycle Assay Solution affect the immunodetection system.
-
Q
When fixed cells are stored for measurement, should staining be done before or after storage?
-
A
Both can work well. We have experience with staining under the following conditions.
When each stained sample was measured by flow cytometry before and after storing fixed cells, there was no change in the results.・Fixed cells were refrigerated (4°C) for 1 week and stained according to the instruction manual.
・Fixed cells were stained according to the instruction manual, and the cells were kept refrigerated (4°C) for 1 week.Storing cells by freezing is not recommended due to the possibility of precipitation of insoluble matter.
-
Q
After staining with Cell Cycle Assay Soluton, can I wash the cells to remove excess reagent?
-
A
Washing after staining is not recommended.
The centrifugation step after washing may result in histograms that are not appropriate for cell cycle analysis.
-
Q
What should be care when performing flow cytometry?
-
A
When performing flow cytometry, measurements must be performed under optimal conditions.
The following are actual examples of measurement failures reported by our customers.(1) The filter does not match the measurement conditions.
For example, if a filter used in the Propidium Iodide (PI) method, which is commonly used for cell cycle measurement in flow cytometers, is used, a good histogram cannot be obtained regardless of the voltage setting.Please use the following filters for your measurement.

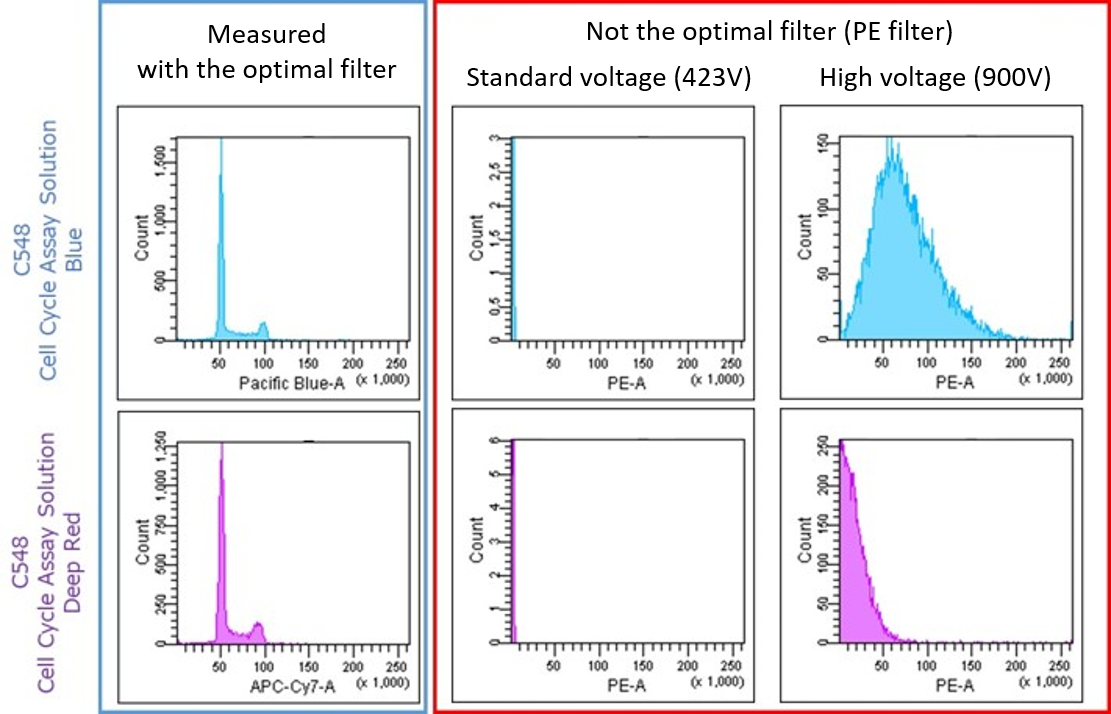
(2) The measurement voltage is not appropriate.
For example, if the flow cytometer voltage is too high (or too low), a good histogram cannot be obtained.
Adjust the measurement voltage to a voltage at which the G0/G1, S-phase, and G2/M-phases are clear in the histogram.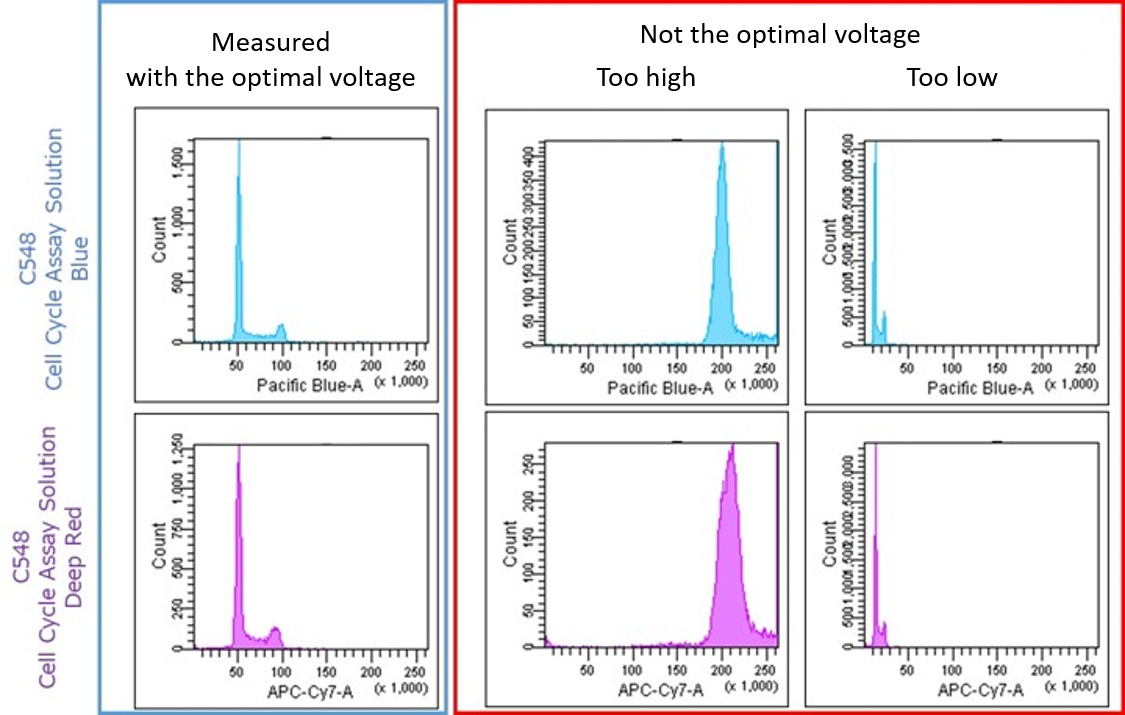
(3) Cells are not gated properly.
For example, if gating is improper during analysis, a good histogram cannot be obtained.
Make sure to gate the entire cell at the time of analysis.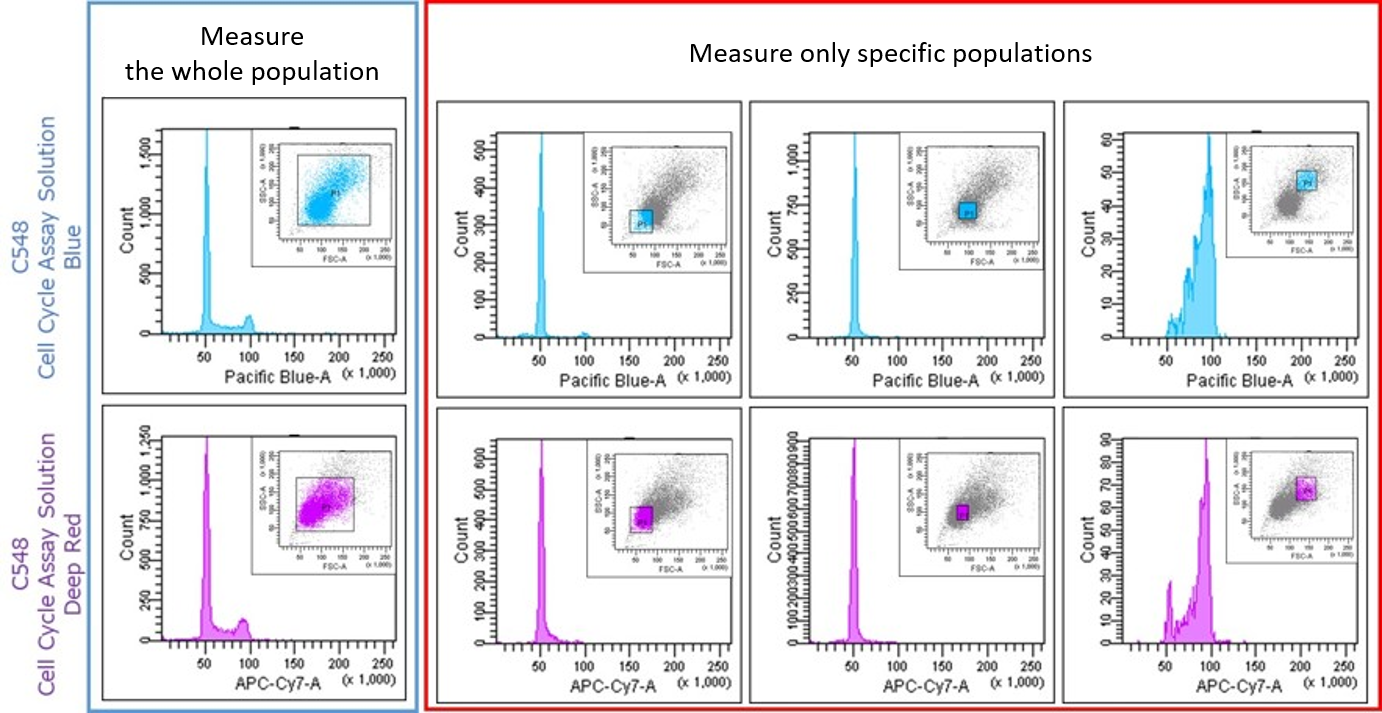
-
Q
I found agglomerates after adding this reagent. What should I do?
-
A
For some cells, aggregates as shown below may be observed when the number of cells is high.
In such cases, reduce the number of cells (guideline: 0.25-1x105 cells/ml), add this reagent, and perform the assay immediately.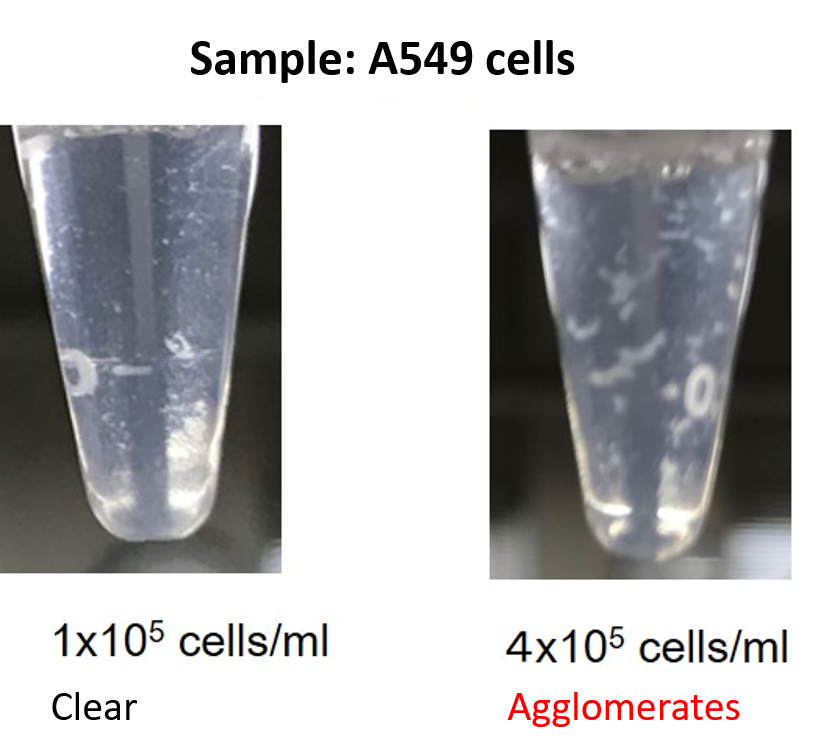
Handling and storage condition
| -20°C, Protect from light | |
|
Danger / harmful symbol mark |
  
|
|---|---|