Notice
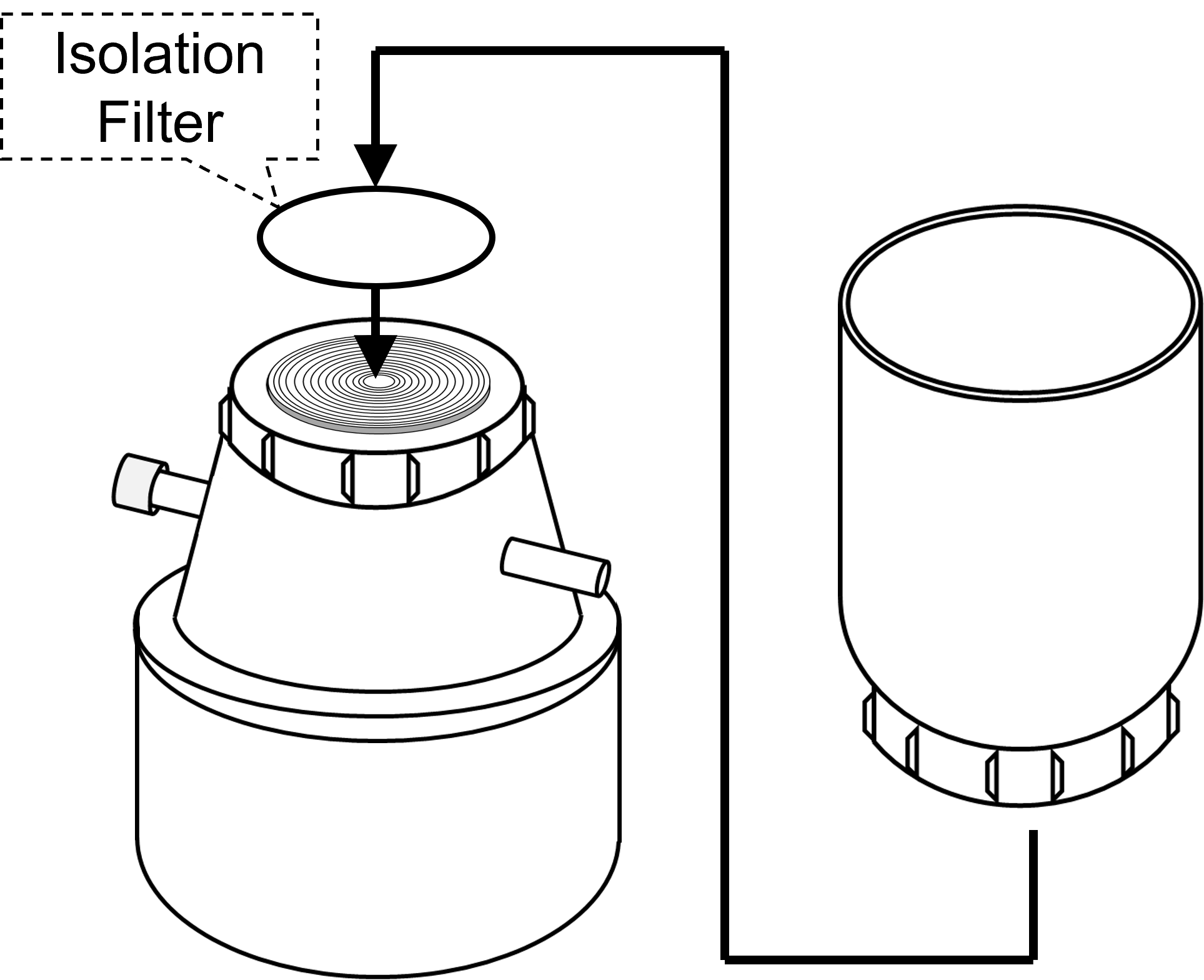
- EX10/11 with 'NEW FILTER sticker' employs a new version of the Isolation Filter (Figure 1). The following is the manual for this kit.
- Please check 'Required Equipment and Materials', 'General Protocol' and the 'User Guide Video' before using the product since the attachment of Isolaiotion Filter has been changed.
- We have confirmed there is no difference in performance between the new version filter and the previous.
| EX10 | EX11 |
|
|
 |
| Figure1. NEW FILTER sticker | |
General Information
Exosomes, a form of secreted extracellular vesicles, contain various proteins and nucleic acids; therefore, exosomes have various effects on recipient cells1). Recently, there have been many reports related to exosomes related, for example, metastasis and malignant progression of cancer, therapeutic research, and diagnostic research. Many methods have been developed for the purification of exosomes for research use. Of these, the main method is ultracentrifugation (UC). However, UC requires complicated operations and a long time to collect exosomes.
Dojindo’s ExoIsolator Exosome Isolation Kit can collect exosomes from cell supernatants with a recovery rate equivalent to that of UC. Unlike UC, ExoIsolator Exosome Isolation Kit requires only the filtration procedure, exosomes are obtained quickly without any complicated operations.
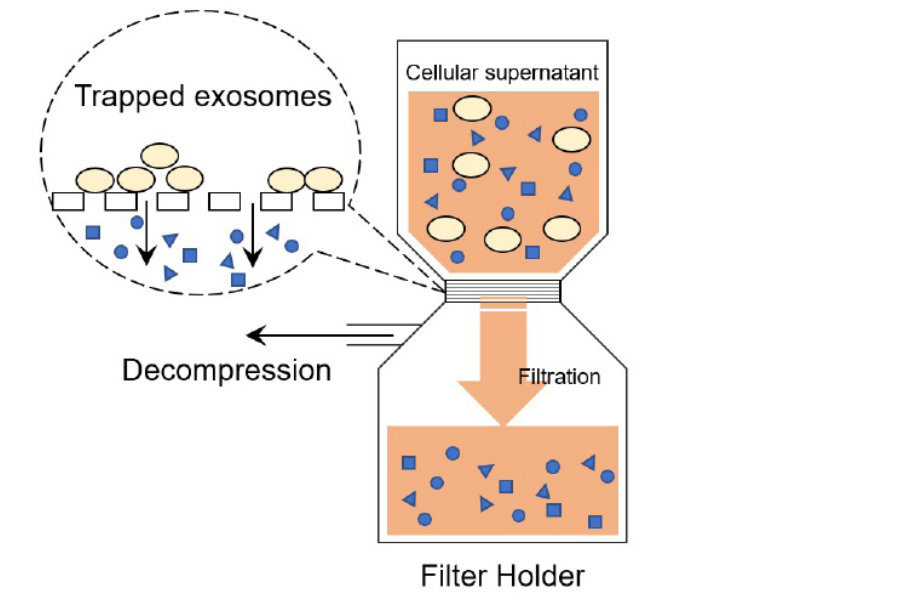
Figure 2. Principle of exosomes purification
(Patent pending)
Kit Contents
-
EX10 : ExoIsolater Exosome Isolation Kit Filter Holder x 1 Isolation Filter x 3 Tweezers x 1
-
EX11 : ExoIsolater Isolation Filter Isolation Filter x 10
Storage Condition
Store at room temperature
Required Equipment and Materials
- Aspirator
- Prepare an aspirator as commonly used for cell experiments. Recommended aspiration pressure for use is −25 kPa or lower.
- 0.22 μm filters
- The 0.22 μm filter is used for pre-filtration of the cell supernatant to remove cellular fragments and cell debris.
- Micropipettes
- 1.5 ml microtubes
- Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS)
- A container such as a petri dish (a 10 cm dish or a larger container).
- To use the Isolation Filter without causing damage, it is necessary to soak the filter before setting it onto the Filter Holder.
- For confirmation of the handling of the Isolation Filter, please refer to step 4-9 in the 'General Protocol'.
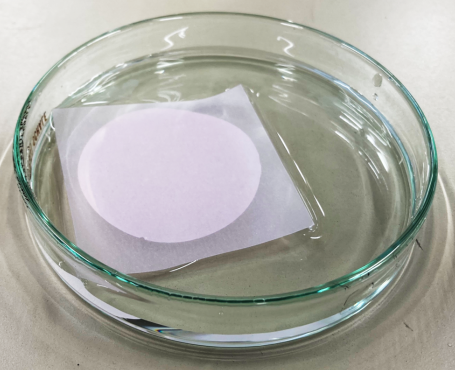 Figure 3. How to soak the Isolaiton Filter (a 10 cm dish). |
Precaution
- The new version of the Isolation Filter is reversible.
- Please make sure the step 4-9 in “General Protocol” below and “Operation Video” on our web site for setting the Isolation Filter on the Filter Holder.
- The Filter Holder should be washed and autoclaved before using. The Filter Holder is not sterilized.
- The Filter Holder is autoclavable and can be used repeatedly. The Isolation Filter is single-use only. If there are not enough Isolation Filters, please purchase the ExoIsolator Isolation Filter (EX11), which contains 10 Isolation Filters.
- Be careful to handle the Isolation Filter because it is very thin and fragile.
- The recommended sample volume is 25 ml. Approximately 5-15 minutes is required for filtration of 25 ml sample.
- When the sample volume is more than 25 ml, the time required for filtration will be longer.
- Filtration of exosome-rich supernatant may cause filter clogging. Divide the supernatant and serve them for filtration individually.
General Protocol
1. Preparation
-
Step 1
Prepare cell supernatant for the experiment.
-
Step 2

Pass the cell supernatant through a 0.22 μm sterile filter to prepare the pre-filtered sample.
- Prefiltrating is necessary for removing impurities such as cells or their residues from the sample.
-
Step 3
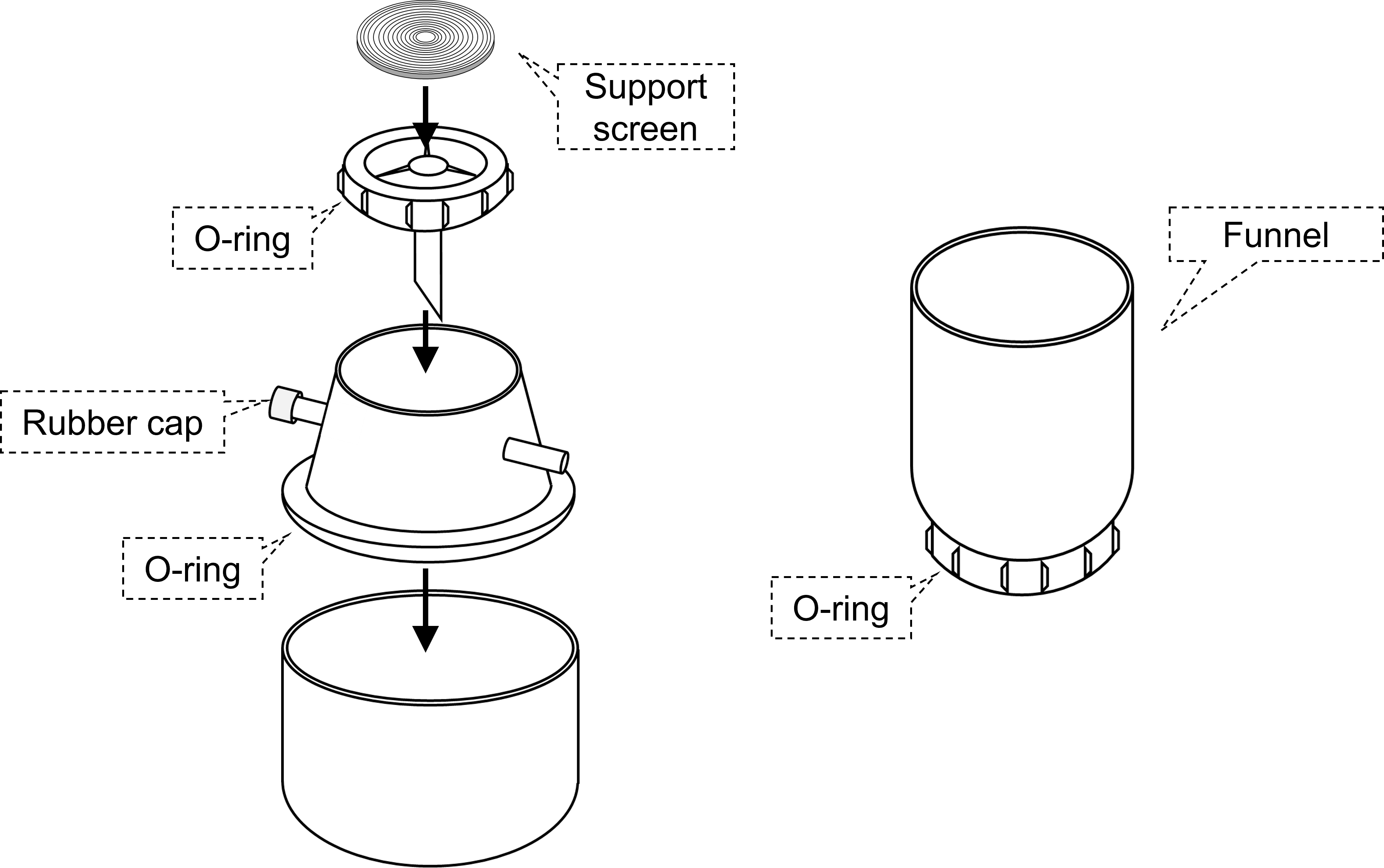
Filter HolderAssemble Filter Holder without the funnel.
- Three silicon O-rings are included in the ExoIsolator. Settle silicon O-ring correctly in the groove of the Filter Holder to improve the airtightness.
2.Setting Isolation Filter onto the Filter Holder
- Please refer to the User Guide video for detailed information.
-
Step 4
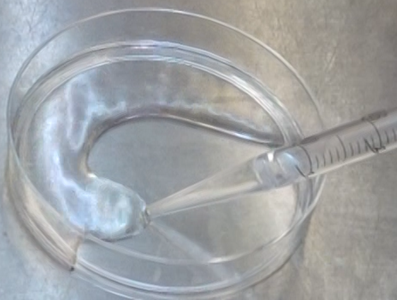
Pour PBS (or distilled water) into a petri dish (e.g., a 10 cm petri dish) and spread it over the entire surface of the dish (for a 10 cm petri dish, use approximately 10 ml).
-
Step 5

Take off only one of two red sheets holding the Isolation Filter.
For steps 6-7, we have provided two alternative methods. Please choose your preffered method.
1. Method to avoid direct touch with the filter
2. Method for not immersing the red sheet in the liquid
-
1. Method to avoid direct touch with the filter
-
Step 6
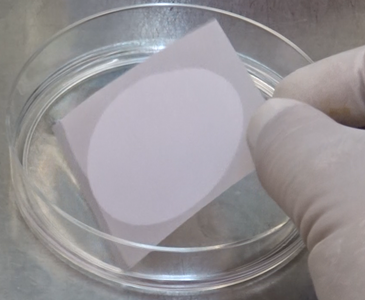
Soak the filter by turning the red sheet upside down on the PBS (or distilled water).
- The red sheet naturally detaches from the Isolation Filter in PBS (or distilled water) since it repels moisture.
-
Step 7

Remove only the detached red sheet from the dish.
-
-
2. Method for not immersing the red sheet in the liquid
-
Step 6
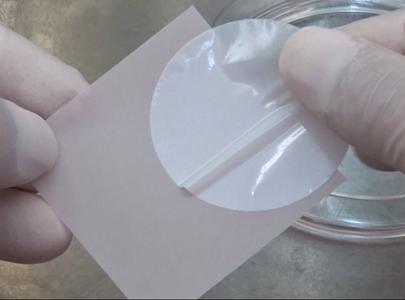
Prepare clean gloves without particles or contaminants.
Slide the Isolation Filter carefully not to tear it with your fingers and take off it from the red sheet.- Please do not use the tweezers provided in the kit.
If you remove the Isolation Filter from the red sheet using tweezers, there is a risk of tearing the Isolation Filter.
- Please do not use the tweezers provided in the kit.
-
Step 7

Soak it with PBS (or distilled water).
-
-
Step 8
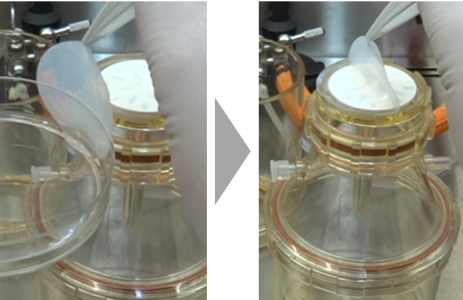
Carefully take the Isolation Filter out from the dish with tweezers and put it on the support screen.
-
Step 9

Press the funnel of the Filter Holder against the Isolation Filter, turn it slowly and place it on the main body.
Notice
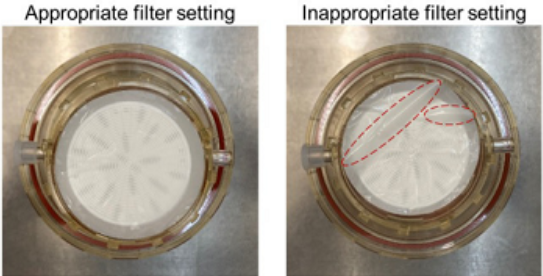 Make sure there are no wrinkles on the surface of the filter. |
3. Purificaition of exosomes
-
Step 10

Pour 4 ml PBS onto the Isolation Filter and aspirate for wetting the Isolation Filter.
-
Step 11

Add the pre-filtered sample onto the Isolation Filter and aspirate.
- The recommended sample volume is 25 ml.
- If the concentration of exosomes or proteins in the sample is large, it may cause filter clogged and the amount of filterated sample may be reduced.
- If the concentration of exosomes or proteins in the sample is small, the amount of filterated sample may be increased.
-
Step 12

Add 2 ml PBS onto the Isolation Filter and aspirate for washing. Repeat this step three times.
-
Step 13

Flush the filtered exosomes on the surface of the Isolation Filter with 250 μl PBS to collect it.
-
Step 14

Collect the exosome suspended 250 μl PBS by using a pipet.
-
Step 15

Add the collected exosomes suspended PBS to flush the Isolation Filter again.
Repeat flushing and collecting process (step 13-14) for 20 times.
-
Step 16
Transfer the collected exosome solution into a 1.5 ml microtube.
Repeat step 13–16 once again (total amount of recovery: 500 μl).
- User Guide Video is available on our website.
- To increase the concentration of the exosomes, decrease the volume of PBS used in step 13-14. Be aware that reducing PBS volume may result in lower recovery of exosomes.
- Make sure all surface of the Isolation Filter being flushed to collect the exosomes in high recovery rate.
Experimental example
Isolation of exosomes from HEK293S cell supernatant using ExoIsolator
- HEK293S cells suspended in 30 ml serum free medium at 5×105 cells/ml were placed in a 125 ml baffled Erlenmeyer flask. The cells were shaken at 155 rpm at 37°C for 2 days in a 5% CO2 incubator.
- After centrifuging at 1,500 rpm for 5 min, the cell supernatant was transferred to a 50 ml conical tube and stored at 4℃.
- The collected cells were resuspended in 30 ml of fresh serum free medium and cultured for another 2 days in the same conditions.
- After centrifuging at 1,500 rpm for 5 min, the cell supernatant was transferred to a 50 ml conical tube and stored at 4℃.
- The cell supernatants collected in steps 2–4 were mixed and passed through a 0.22 μm filter to prepare the prefiltered cell supernatant.
- The Isolation Filter was put on the support screen and the funnel was settled on the Isolation Filter.
- PBS (4 ml) was poured onto the Isolation Filter and aspirated.
- After aspiration, 25 ml of pre-filtered cell supernatant was poured onto the Isolation Filter.
- After aspiration, 2 ml of PBS was poured onto the Isolation Filter and aspirated. This operation was repeated three times.
- After aspiration, the Isolation Filter was flushed repeatedly with 250 μl PBS using a micropipette and the suspension was collected by pipetting.
- The PBS containing the exosomes was transferred to a 1.5 ml microtube.
- Steps 10–11 were repeated.
- The PBS containing exosomes were collected as 500 μl of total volume and were examined by nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) and western blotting.
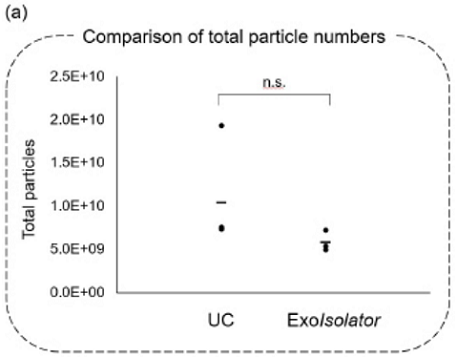
Comparison of exosome purity collected by UC and ExoIsolator
[Purification of exosomes by UC]
- The cell supernatant from HEK293S cells was passed through a 0.22 μm filter to prepare the pre-filtered cell supernatant.
- The pre-filtered cell supernatant (25 ml) was transferred to a centrifuge tube and centrifuged at 100,000 × g for 2 hours (himac CP80NX, Hitachi).
- After decantation, the pellet was then suspended in 6 ml PBS and centrifuged at 100,000 × g for 2 hours.
- After decantation, the pellet was then suspended in 100 μl PBS.
- The PBS containing the exosomes was transferred to a 1.5 ml microtube.
- The centrifuge tube was washed with 100 μl PBS. PBS used for washing was transferred to the 1.5 ml microtube. This step was repeated three times. (total volume:300 µl )
- The PBS containing the exosomes was centrifuged at 10,000 × g for 5 min. The supernatant was transferred to a new 1.5 ml microtube.
[Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)]
Particle number of purified exosomes were measured using Nanosight NS300 (Quantum Design; camera level 13; detect threshold 5).
[Western blotting]
- Purified exosomes were mixed with sample buffer without dithiothreitol and boiled at 95°C for 5 min.
- Samples were separated by SDS-PAGE (SuperSep Ace, 10-20%, 13well; Wako) and transferred to PVDF membranes (Trans-Blot Turbo Transfer System Transfer Pack; Bio-Rad).
- Following antibodies were used for detection of CD9, CD63, and CD81.
Primary antibody Secondary antibody CD9 Monoclonal rabbit anti-CD9 antibody
(diluted 1:1000; cat. no. ab236630; abcam)Polyclonal goat anti-rabbit antibody conjugated with
HRP (diluted 1:2000; cat. no. ab97051; abcam)CD63 Monoclonal mouse anti-CD63 antibody
(diluted 1:1000; cat. no. MEX002-3; MBL)Polyclonal goat anti-mouse antibody conjugated with
HRP (diluted 1:2000; cat. no. ab205719; abcam)CD81 Monoclonal mouse anti-CD81 antibody
(diluted 1:500; cat. no. MEX003-3; MBL)Polyclonal goat anti-mouse antibody conjugated with
HRP (diluted 1:2000; cat. no. ab205719; abcam) - The membranes were treated with SuperSignal West Pico PLUS Chemiluminescent Substrate (Thermo Fisher Scientific).
- The protein bands were detected using a Syngene Pxi (Syngene).
Figure 4. Exosomes collected by UC or using the ExoIsolator Exosome Isolation Kit
were evaluated using (a) NTA and (b) western blotting.
References
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V. S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020, 367(6478).
Frequently Asked Questions / Reference
EX10: ExoIsolator Exosome Isolation Kit / ExoIsolator Isolation Filter
Revised Jan., 31, 2024


 Hidden sections will not be printed.
Hidden sections will not be printed.