General Information
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) is one of the key elements responsible for vasopressor action. ACE converts angiotensin-I to angiotensin-ll, a potent vasopressor, in the rennin-angiotensin system and contributes to increasing blood pressure by inactivating bradykinin, a strong antihypertensive peptide. Recently, various functional foods have received attention because of their inhibitory activity toward ACE.
ACE activity is conventionally determined by UV measurement of the hippuric acid produced from the synthetic substrate Hyppuryl-His-Leu. However, the assay process is complicated and requires organic solvent. In this kit, a safe and straightforward modified method has been developed.
The colorimetric detection system in the ACE Kit-WST determines the amount of 3-hydroxybutyric acid (3HB) generated from 3-hydroxybutyryl-Gly-Gly-Gly by ACE. The kit is designed for 96-well microplate assays and is suitable for multiple sample measurements. No organic solvent extraction is required. The ACE Kit - WST assay is safe, simple, and provides highly reproducible data.
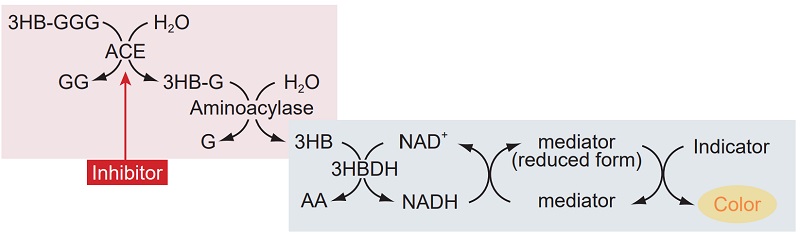
Figure 1 Principle of the ACE inhibition assay using ACE Kit - WST
Contents of the Kit
| 50 tests | 100 tests | |
| Substrate buffer | 1 ml × 1 | 1 ml × 2 |
| Enzyme A | × 1 | × 2 |
| Enzyme B | × 1 | × 2 |
| Enzyme C | × 1 | × 2 |
| Coenzyme | × 1 | × 2 |
| Indicator solution | 5 ml × 1 | 5 ml × 2 |
Storage Precaution
Store the kit at 0-5 °C. The kit is stable for 6 months.
- Several kit components are in glass vials. Please handle with care.
- Multiple measurements (triplicates of each sample) are recommended to obtain accurate data.
- If the water solubility of the sample is low, use dimethylsulfoxide or ethanol to dissolve. Then, dilute the solution with an appropriate buffer. The final concentration of organic solvent should be <1%.
- If the sample solution is acidic, adjust the pH to ≥5 before use for measurement.
- Ascorbic acid may interfere with the assay. The concentration of ascorbic acid in the sample solution should be <0.01% w/v. If the sample solution contains insoluble materials, remove it by centrifugation or filtration before use for measurement.
Required Equipment and Materials
- Microplate reader (450 nm filter)
- 96-well microplate
- 2-20 μl, 20-200 μl, and 100-1000 μl pipettes
- Incubator
- Multi-channel pipette
- Disposable syringes (1 ml)
Preparation of Working Solutions
Enzyme working solution:
Dissolve Enzyme B in 2 ml of deionized water to prepare Enzyme B solution. Then add 1.5 ml of Enzyme B solution to Enzyme A to prepare Enzyme working solution.
- Enzyme A and B vials are capped under vacuum pressure. Add deionized water or solution through the rubber septum with a syringe, and then remove the septum.
- The Enzyme working solution is stable at -20 °C for 2 weeks or in a refrigerator for 3 days.
Indicator working solution:
Dissolve Enzyme C and Coenzyme in 3 ml of deionized water each. Add 2.8 ml of Enzyme C solution and 2.8 ml of Coenzyme solution to Indicator solution to prepare Indicator working solution.
- Enzyme C and Coenzyme vials are capped under vacuum pressure. Add deionized water through the rubber septum with a syringe, and then remove the septum.
- The Indicator working solution is stable at -20 °C for 2 weeks or in a refrigerator for 3 days.
Selection of Protocol
- Protocol 1
-
Confirmation of the presence or absence of ACE inhibition
Fourteen samples (50-test kit) or 28 samples (100-test kit) can be measured in triplicate. Please refer to the procedure on page 2.
- Protocol 2
-
Determination of IC50
Two samples (50-test kit) or four samples (100-test kit) can be measured in triplicate. Please refer to the procedure on page 4.
Protocol 1
Confirmation of the presence or absence of ACE inhibition
Preparation of Sample Solution
Prepare 100 μl of each sample.
- If the sample volume is <100 μl, please dilute the sample.
- If the sample is colored, prepare 150 μl of each sample.
General Procedure for the Assay
Colorless sample
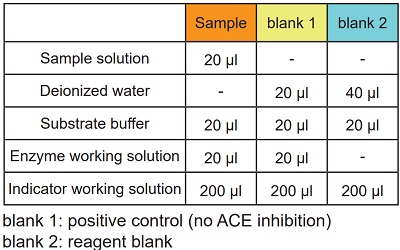
See Table 1 and Figure 2
- Add 20 μl of sample solution to each sample well.
- Add 20 μl of deionized water to each blank 1 well and 40 μl to each blank 2 well.
- Add 20 μl of Substrate buffer to each well.
- Add 20 μl of Enzyme working solution to each sample well and blank 1 well.
- Enzyme working solution is easy to remain on the well wall. Please tap the plate to ensure that all solutions have been mixed completely.
- Since the enzymatic reaction starts immediately after adding the Enzyme working solution, use a multi-channel pipette to minimize the well-to-well time lag.
- Incubate at 37 °C for 1 h.
- Add 200 μl of Indicator working solution to each well.
- Incubate at room temperature for 10 min.
- Read the absorbance at 450 nm using a microplate reader.
-
Table 1 Amount of sample and reagent needed for each well.
-
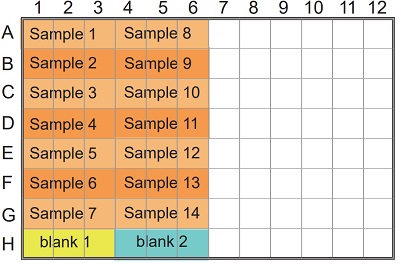
Figure 2 Example of arrangement on a 96-well microplate.
Confirmation of the presence or absence of ACE inhibition
-
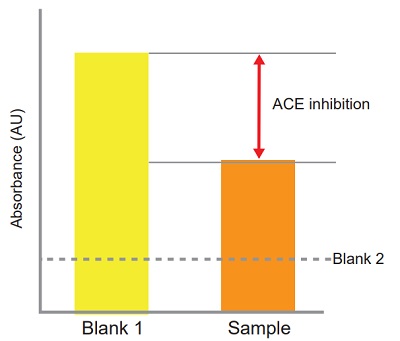
ACE inhibition can be calculated from the equation:
ACE inhibition (%) =
[(Ablank 1 - Asample)/(Ablank 1 - Ablank 2)] × 100
-
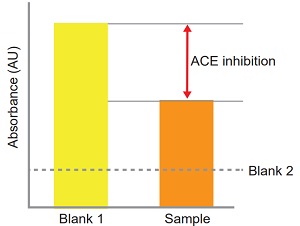
Figure 3 Confirmation of the presence or absence of ACE inhibition.
Colored sample
See Table 2 and Figure 4
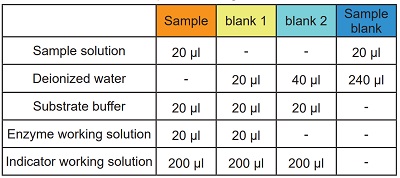
- Add 20 μl of sample solution to each sample well and sample blank well.
- Add 20 μl of deionized water to each blank 1 well, 40 μl to each blank 2 well and 240 ul to each sample blank well.
- Add 20 μl of Substrate buffer to each sample well, blank 1 well and blank 2 well.
- Add 20 μl of Enzyme working solution to each sample well and blank 1 well.
- Enzyme working solution is easy to remain on the well wall. Please tap the plate to ensure that all solutions have been mixed completely.
- Since the enzymatic reaction starts immediately after adding the Enzyme working solution, use a multi-channel pipette to minimize the well-to-well time lag.
- Incubate at 37 °C for 1 h.
- Add 200 μl of Indicator working solution to each sample well, blank 1 well and blank 2 well.
- Incubate at room temperature for 10 min.
- Read the absorbance at 450 m using a microplate reader.
-
Table 2 Amount of sample and reagent needed for each well.
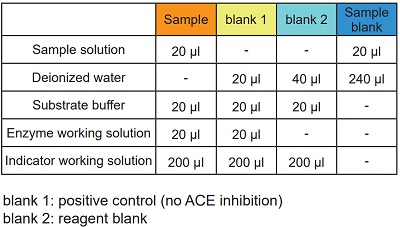
-
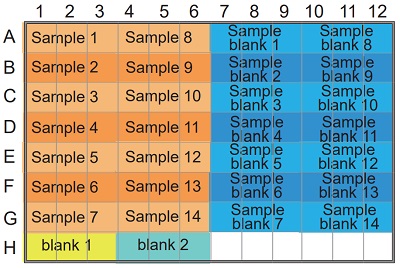
Figure 4 Example of arrangement on a 96-well microplate.
Confirmation of the presence or absence of ACE inhibition
-
ACE inhibition can be calculated from the equation:
ACE inhibition (%) =
[{Ablank 1 - (Asample - Asample blank)}/(Ablank 1 - Ablank 2)] × 100
-
4 Example of arrangement on a 96-well microplate.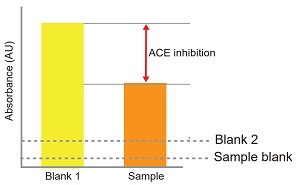
Figure 5 Confirmation of the presence or absence of ACE inhibition
Protocol 2
Determination of IC50
Preparation of Sample Solution
Dilute sample solution with deionized water.
Dilutions: 1 (no dilution), 1/5, 1/52, 1/53, 1/54, 1/55, 1/56
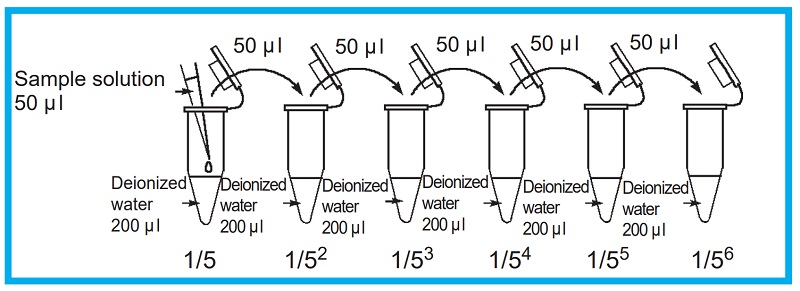
Figure 6 Prepatation of sample solution
General Procedure for the Assay
Colorless sample
See Table 3 and Figure
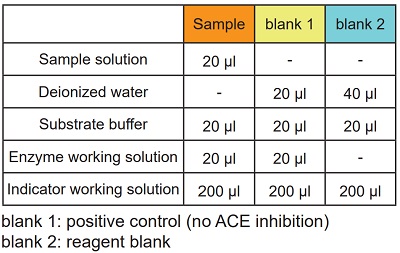
- Add 20 μl of sample solution to each sample well.
- Add 20 μl of deionized water to each blank 1 well and 40 μl to each blank 2 well.
- Add 20 μl of Substrate buffer to each well.
- Add 20 μl of Enzyme working solution to each sample well and blank 1 well.
- Enzyme working solution is easy to remain on the well wall. Please tap the plate to ensure that all solutions have been mixed completely.
- Since the enzymatic reaction starts immediately after adding the Enzyme working solution, use a multi-channel pipette to minimize the well-to-well time lag.
- Incubate at 37 °C for 1 h.
- Add 200 μl of Indicator working solution to each well.
- Incubate at room temperature for 10 min.
- Read the absorbance at 450 nm using a microplate reader.
- ACE inhibition can be calculated from the equation:
ACE inhibition (%) = [(Ablank 1 - Asample)/(Ablank 1 - Ablank 2)] × 100
-
Table 3 Amount of sample and reagent needed for each well.
-
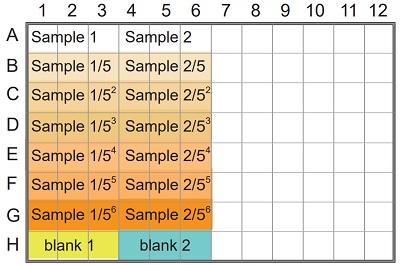
Figure 7 Example of arrangement on a 96-well microplate.
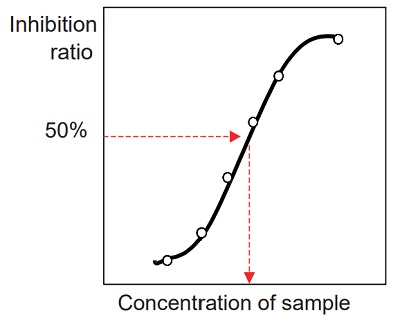
Determination of IC50 (50% inhibitory concentration)
-
- Prepare an inhibition curve using sample concentration for the x-axis and percentage inhibition of ACE for the y-axis. A typical inhibition curve is shown in Figure 8.
- Determine the concentration of the sample solution that gives
- 50% ACE inhibition as indicated in Figure 8.
- Because the total volume of the inhibition assay is 60 ul (first step of the assay), the original sample is diluted 3 times in the reaction. Therefore, the actual concentration of the sample at 50% inhibition is one-third of the concentration determined from the inhibition curve.
-
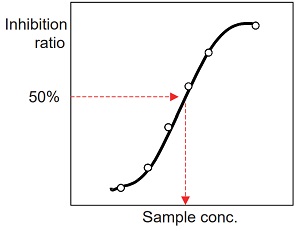
Figure 8 Inhibition curve
Colored sample
See Table 4 and Figure 9
- Add 20 μl of sample solution to each sample well and sample blank well.
- Add 20 μl of deionized water to each blank 1 well, 40 μl to each blank 2 well and 240 μl to each sample blank well.
- Add 20 μl of Substrate buffer to each sample well, blank 1 well and blank 2 well.
- Add 20 μl of Enzyme working solution to each sample well and blank 1 well.
- Enzyme working solution is easy to remain on the wellywall. Please tap the plate to ensure that all solutions have been mixed completely.
- Since the enzymatic reaction starts immediately after adding the Enzyme working solution, use a multi-channel pipette to minimize the well-to-well time lag.
- Incubate at 37 °C for 1 h.
- Add 200 μl of Indicator working solution to each sample well, blank 1 well and blank 2 well.
- Incubate at room temperature for 10 min.
- Read the absorbance at 450 nm using a microplate reader.
- ACE inhibition can be calculated from the equation:
ACE inhibition (%) = [{Ablank 1 - (Asample - Asample blank)}/(Ablank 1 - Ablank 2)] × 100
-
Table 4 Amount of sample and reagent needed for each well.
-
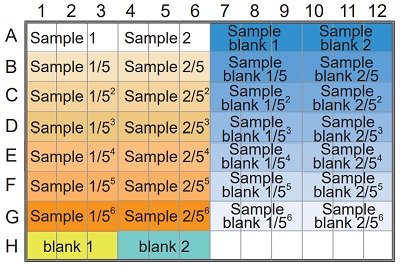
Figure 9 Example of arrangement on a 96-well microplate.
Determination of IC50 (50% inhibitory concentration)
-
- Prepare an inhibition curve using sample concentration for the x-axis and percentage inhibition of ACE for the y-axis. A typical inhibition curve is shown in Figure 10.
- Determine the concentration of the sample solution that gives 50% ACE inhibition as indicated in Figure 10.
- Because the total volgme of the inhibition assay is 60 ml (first step of the assay), the original sample is diluted 3 times in the reaction. Therefore, the actual concentration of the sample at 50% inhibition is one-third of the concentration determined from the inhibition curve.
-
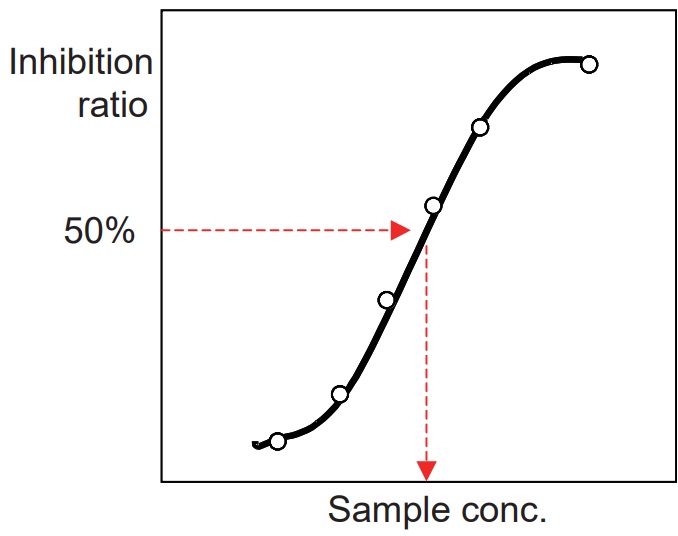
Figure 10 Inhibition curve
References
- Le Hoang Lam, T. Shimamura, K. Sakaguchi, K. Noguchi, M. Ishiyama, Y. Fujimura and H. Ukeda, Anal. Biochem., 2007, 364, 104.
- Le Hoang Lam, T. Shimamura, S. Manabe, M. Ishiyama and H. Ukeda, Anal. Sci., 2008, 24, 1057.
Frequently Asked Questions / Reference
A502: ACE Kit - WST
Revised Dec., 08, 2023


 Hidden sections will not be printed.
Hidden sections will not be printed.