| New Insights Reveal How Lipoproteins Protect Against Ferroptosis and EMCSs Initiate It Ferroptosis is intensively studied as a therapeutic target in cancer and a pathogenic mechanism in neurodegeneration. One study reveals an unexpected role for lipoproteins, showing that beyond serving as nutrient sources or substrates for peroxidation, they also deliver antioxidant lipids such as vitamin E that protect cancer cells from ferroptosis1. Another introduces ER–mitochondria contact sites (EMCSs) as a newly recognized hub of PUFA-containing phospholipid peroxidation2, highlighting an additional mechanism that can initiate ferroptosis. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
1. Glycosaminoglycan-mediated lipoprotein uptake protects cancer cells from ferroptosis (Nature, 2025) Related technique Lipid Peroxides Detection, Ferrous ion (Fe2+) Detection |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2. Endoplasmic reticulum–mitochondria contacts are prime hotspots of phospholipid peroxidation driving ferroptosis (Nature Cell Biology, 2025) Highlighted technique: To track the dynamics of lipid peroxides under ferroptosis-inducing conditions, cells were transfected with a fluorescently labeled ER marker and co-stained with mitochondrial and lipid peroxide probes. Time-lapse super-resolution live imaging with 3D rendering revealed that lipid peroxide signals first increased rapidly at EMCSs and subsequently redistributed to mitochondria. Furthermore, mitochondrial ROS measurements confirmed a marked increase following this redistribution. Related technique Lipid Peroxides Detection, Mitochondrial ROS Detection |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Related Techniques (click to open/close)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Application Note (click to open/close)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
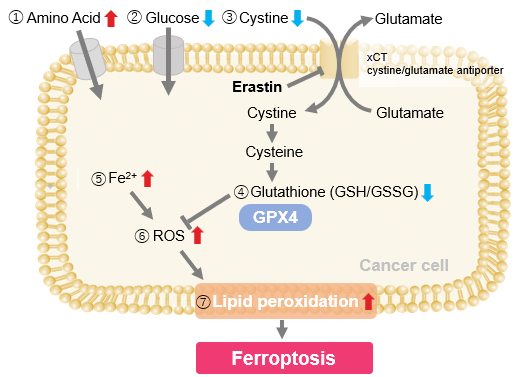
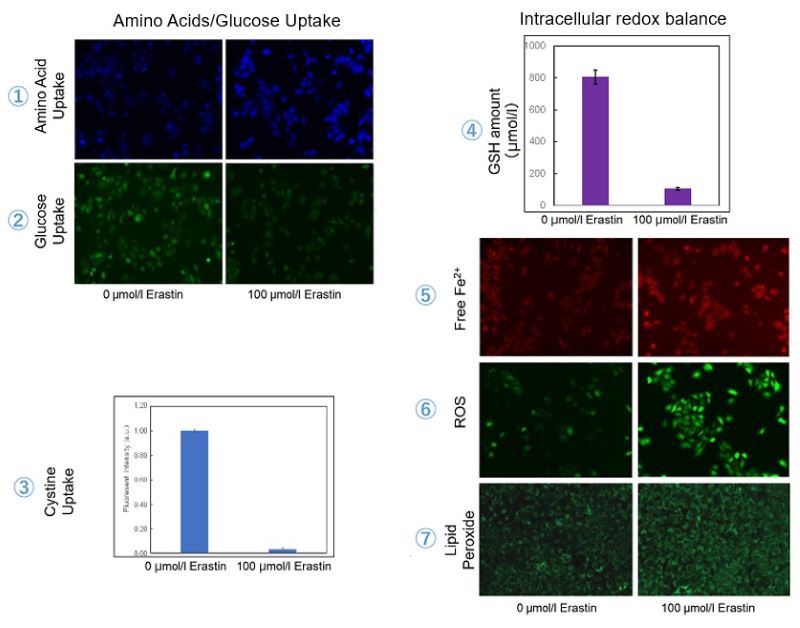
We investigated the transition of cellular metabolisms in A549 cells treated with erastin, a known ferroptosis inducer. Our results revealed the following. Results Cell Line: A549 |
||
|
Products in Use |
 |
||