Previous Science Note
| Ferroptotic cells release signals that spread beyond themselves, inducing lipid peroxidation and death in neighbouring cells. This Science Note introduces recent advances in our understanding of how signals from ferroptotic cells spread and the molecular mechanisms underlying this process. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Ferroptosis spreads to neighboring cells via plasma membrane contacts Highlighted technique: In this study, the authors developed a novel model for ferroptosis induction by creating cells in which the lipid peroxide-detoxifying enzyme GPX4 can be selectively depleted by optogenetic activation. This system allowed the induction of ferroptosis in specific cells, allowing the observation of lipid peroxidation and the spread of ferroptosis to neighbouring cells. Related technique Lipid Peroxidation Detection, Intracellular Iron Detection |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Emergence of large-scale cell death through ferroptotic trigger waves Highlighted technique: The propagation of ferroptosis was analysed by dynamic observation using a combination of intracellular ROS staining and dead cell staining. Real-time time-lapse fluorescence microscopy revealed that ROS generation from ferroptotic cells preceded the wave-like spread of cell death. Related technique Highly Sensitive ROS Detection Dye, Long-Term ROS Detection Dye |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Microglial ferroptotic stress causes non-cell autonomous neuronal death Highlighted technique: In this study, ferroptosis inducers were applied to microglia, astrocytes or mixed glial cultures and the resulting conditioned media were added to neurons to assess lipid peroxidation and cell viability. Neuronal death was only observed with media from ferroptosis-treated mixed glial cultures, indicating that neurotoxicity requires interaction between multiple glial cell types. Related technique Lipid Peroxidation Assay, Cell Viability Assay |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Related Techniques (click to open/close)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Application Note (click to open/close)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
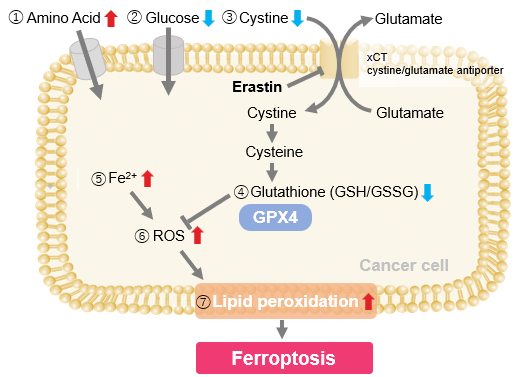
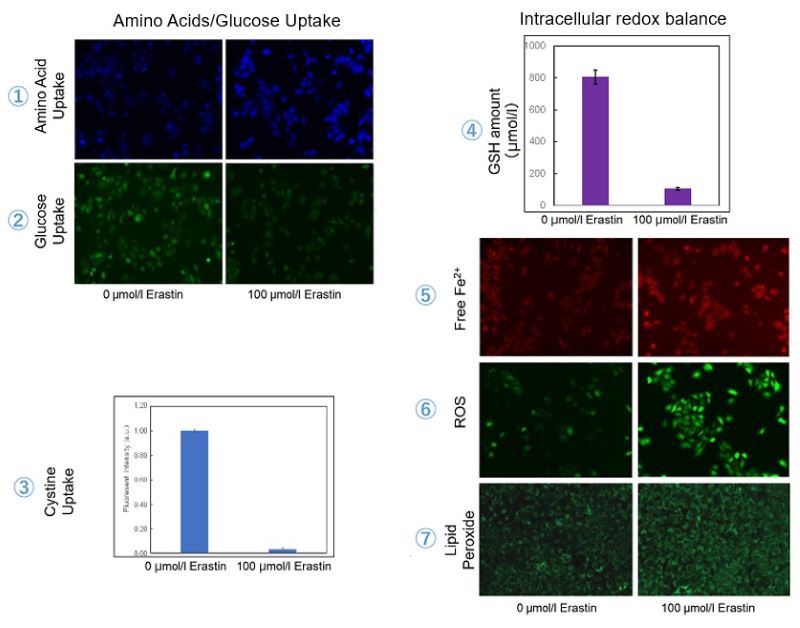
We investigated the transition of cellular metabolisms in A549 cells treated with erastin, a known ferroptosis inducer. Our results revealed the following. Results Cell Line: A549 |
|
|
Products in Use |
||