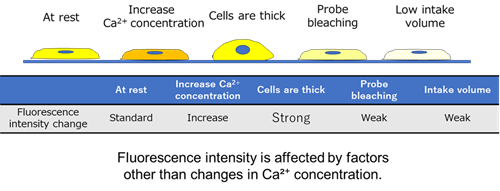
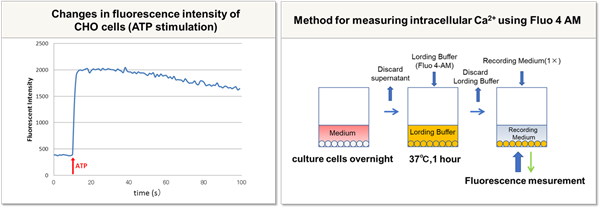
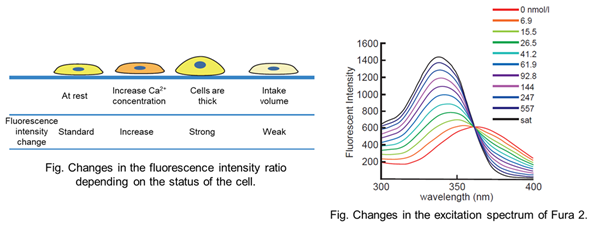
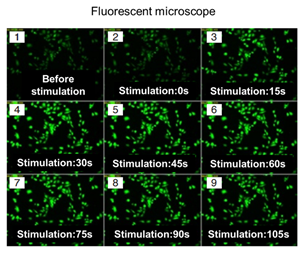
|
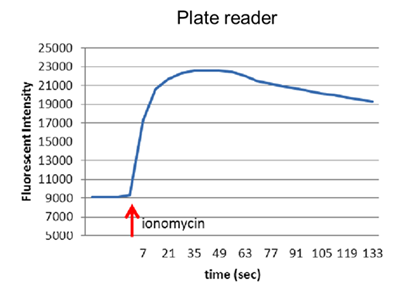
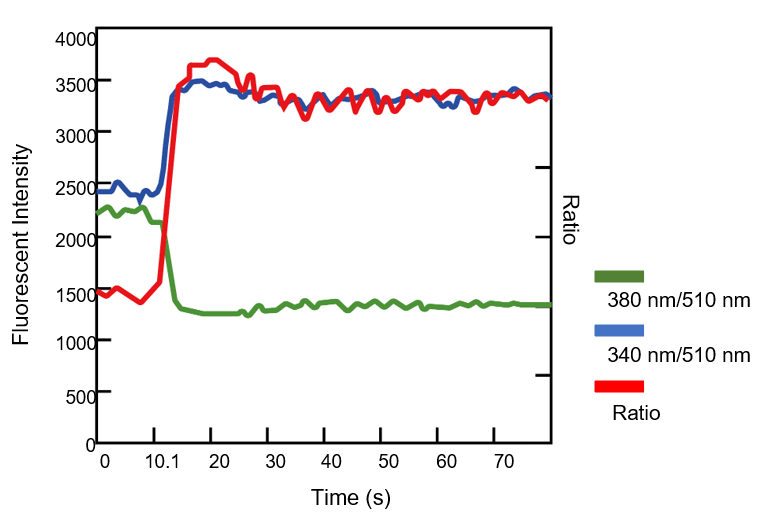
Annexin A5 (AnxA5) is a phospholipid-binding protein and a central regulator of intracellular Ca²⁺ homeostasis. In this study, we demonstrate that AnxA5 regulates mitochondrial Ca²⁺ flux and controls the permeability of the VDAC1 channel in the outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM) under physiological and apoptotic conditions.
F. E. Oflaz, A. I. Bondarenko, M. Trenker, M. Waldeck-Weiermair, B. Gottschalk, E. Bernhart, Z. Koshenov, S. Radulović, R. Rost, Martin Hirtl , Johannes Pilic, Aditya Karunanithi Nivedita, A. Sagintayev, G. Leitinger, B. Brachvogel, S. Summerauer, V. Shoshan-Barmatz, R. Malli and W. F. Graier, Annexin A5 controls VDAC1-dependent mitochondrial Ca2+ homeostasis and determines cellular susceptibility to apoptosis, EMBO J, 2025, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s44318-025-00454-9
|