|
Recent research shows that autophagy inhibits protein aggregation and DNA lesions in cells, leading to cellular health and extended lifespan. Here are some of the papers that show some mechanisms and factors that control autophagy for cellular homeostasis.
Autophagy is a cellular process that removes damaged organelles and proteins to maintain cellular homeostasis and function. By reducing the accumulation of toxic aggregates and dysfunctional components, autophagy helps to prevent cellular stress and inflammation, key contributors to aging. Increased autophagic activity is associated with improved proteostasis, stress resistance and increased lifespan in several model organisms. Thus, autophagy is a critical mechanism linking cellular health to healthy aging and longevity.
|
-
The neurotrophic factor MANF regulates autophagy and lysosome function to promote proteostasis in Caenorhabditis elegans
Click here for the original article: Shane K. B. Taylor, et. al., PNAS, 2024.
Point of Interest
- Mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor 1 (MANF-1 regulates autophagy and lysosomal function via HLH-30/TFEB signaling to promote proteostasis and extend lifespan in C. elegans.
- MANF-1 localizes to lysosomes, modulates autophagic flux and reduces protein aggregation, thereby promoting neuronal survival and stress response.
- MANF is essential for cellular proteostasis, stress response and regulation of ageing through ER-lysosomal localisation and transcriptional signaling.
-
C16ORF70/MYTHO promotes healthy aging in C.elegans and prevents cellular senescence in mammals
Click here for the original article: Anais Franco-Romero, et. al., J Clin Invest., 2024.
Point of Interest
- MYTHO, which is conserved across species, promotes lifespan, health and stress resistance by initiating autophagy through the WIPI2-BCAS3 scaffold.
- MYTHO deletion shortens lifespan, reduces oxidative stress resistance and disrupts autophagy, highlighting its role in healthy aging.
- MYTHO is a transcriptionally regulated autophagy initiator essential for stress resistance and longevity in C. elegans and humans.
-
TEX264 drives selective autophagy of DNA lesions to promote DNA repair and cell survival
Click here for the original article: Pauline Lascaux, et. al., Cell, 2024.
Point of Interest
- Autophagy processes TOP1cc DNA lesions via lysosomes, enabling DNA repair and genome stability in vertebrates.
- The autophagy receptor TEX264 detects TOP1cc at replication forks and triggers p97-mediated lysosomal delivery through MRE11- and ATR-dependent pathways.
- The conserved role of selective autophagy in DNA repair supports cell survival and is clinically relevant.
|
|
Related Technique in This Topic
|
|
|
- Autophagy detection
- DAPRed (Autophagosome detection), DALGreen (Autolysosome detection)
|
|
|
- Mitochondrial superoxide detection
- MitoBright ROS Deep Red - Mitochondrial Superoxide Detection
|
- Mitophagy detection
- Mitophagy Detection Kit
|
- Mitochondrial membrane potential detection
- JC-1 MitoMPDetection Kit, MT-1 MitoMPDetection Kit
|
- Ready-to-use Kit for The First Time LLPS Research
- NEW LLPS Starter Kit
|
- Optimization of Target Protein Droplets
- NEW LLPS Forming Condition Screening Kit
|
- Glycolysis/Oxidative phosphorylation Assay
- Glycolysis/OXPHOS Assay Kit, Extracellular OCR Plate Assay Kit
|
- Apoptosis detection in multiple samples
- Annexin V Apoptosis Plate Assay Kit
|
- Cell proliferation/ cytotoxicity assay
- Cell Counting Kit-8 and Cytotoxicity LDH Assay Kit-WST
|
|
Related Applications
|
NAD+ Depletion and Autophagy-Lysosomal Pathway Response
-
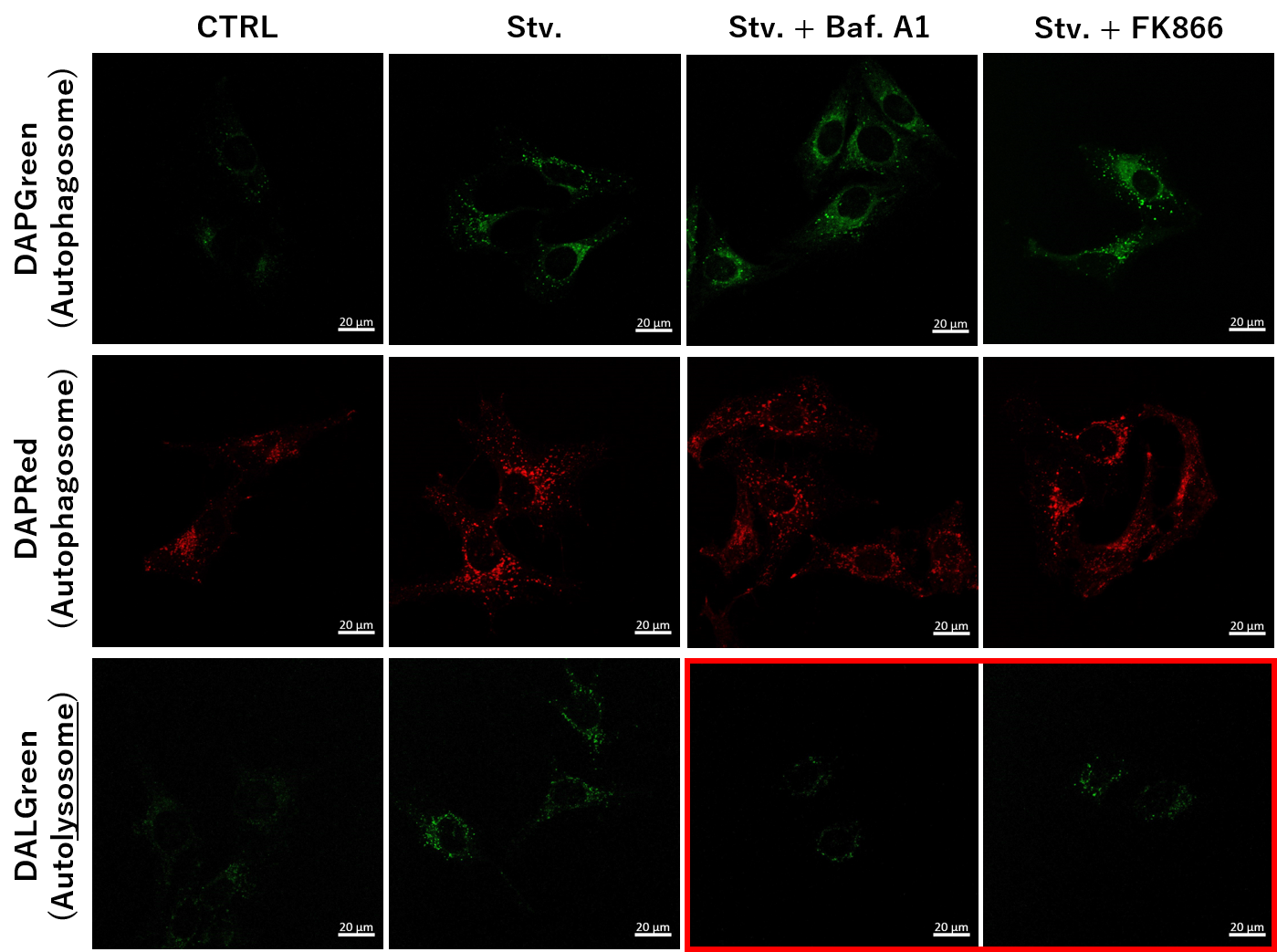
Nampt inhibitor, FK866 inhibits the progress of autophagosome to autolysosome by lysosomal deacidification. A recent finding shows that the dysfunctional condition of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) biosynthetic enzyme, Nampt induces lysosomal deacidification1). In this section, we tried to determine how NAD+ depletion-induced lysosomal deacidification affects the autophagy-lysosomal pathway. 1) Mikako Yagi, et. al., EMBO J., 40(8), e105268 (2021)
-
We next determined how FK866-induced lysosomal deacidification affects the autophagy-lysosomal pathway. After staining with DAPGreen/DAPRed (for detecting autophagosome), or DALGreen (for detecting autolysosome), HeLa cells were starved in HBSS incubation and then treated with FK866 or Bafilomycin A1. Under the starvation condition, the fluorescent signals from all dyes increased, indicating the proceeding autophagy-lysosomal pathway. On the other hand, only DALGreen's signals were decreased in FK866 and Bafilomycin A1 treated cells with starvation conditions. These results clearly suggested that FK866 inhibits the autophagy-lysosomal pathway by NAD+ depletion-induced lysosomal deacidification.
(Protocol)
HeLa cells (8 well ibidi) (MEM, FBS+)
↓
Single-stain with 2 umol/I DALGreen or
0.2 umol/I DAPGreen or
0.2 umol/I DAPRed
30 min, 37℃
↓
Wash x2 (MEM, FBS+)
↓
. Control (MEM, FBS+) for 2 h 20 min
· Starvation (HBSS) for 2 h 20 min
· Stv.2 h = 10 nM Bafilomycin A1 (HBSS) for 20 min
· Stv.2 h = 10 nM FK866 (HBSS) for 20 min
Observed by confocal microscopy (x40)
Products in Use
- Autophagic Flux Assay Kit
(combination kit of DAPRed / DALGreen)
- DAPGreen
|
Simultaneous Detection of Lysosomal and Mitochondrial Dysfunction
-
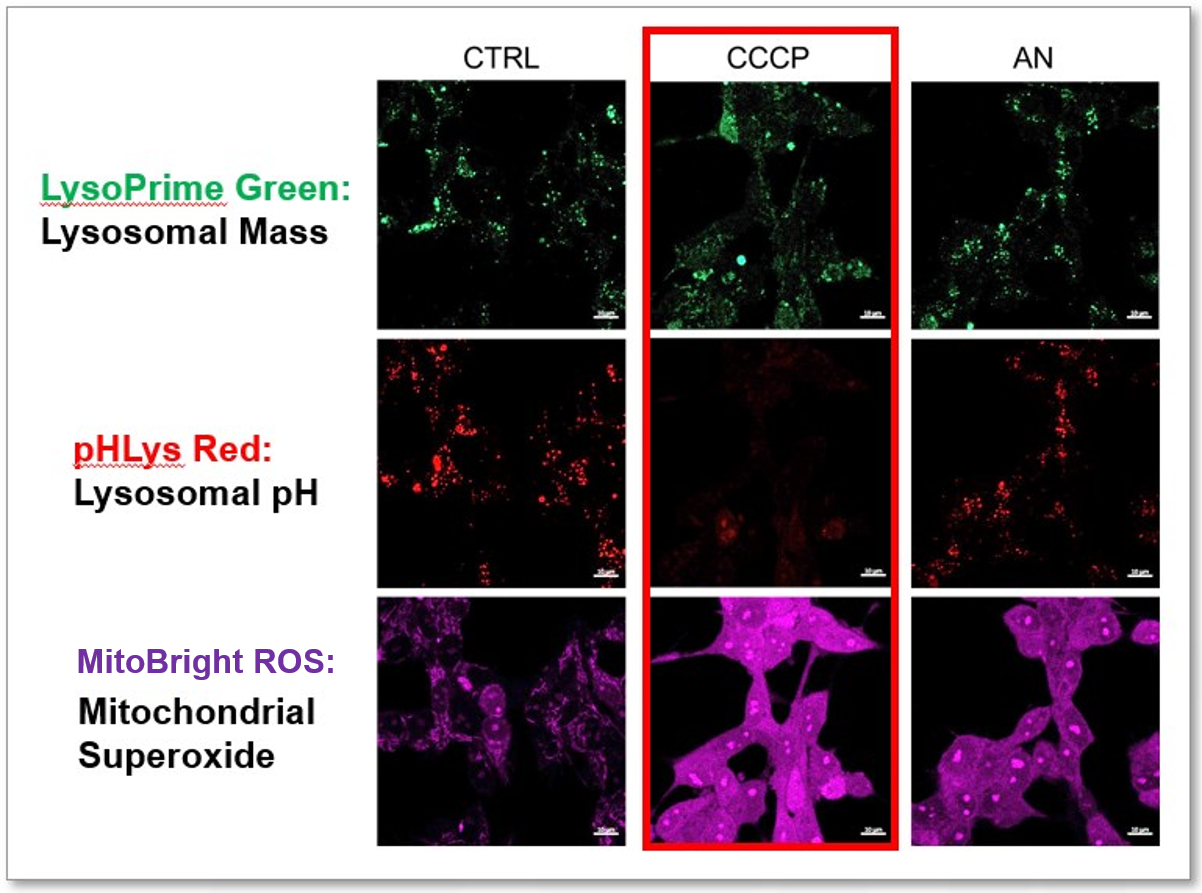
-
We tried the simultaneous detection of lysosomal and mitochondrial dysfunction in Hela cells treated with CCCP or Antimycin (AN). CCCP and AN are well-known inducers of mitochondrial ROS regarding loss of mitochondrial membrane potential. Recent research showed the result that CCCP induces not only mitochondrial ROS but also lysosomal neutralization. To detect mitochondrial ROS, HeLa cells were labeled by MitoBright ROS Deep Red - Mitochondrial Superoxide Detection, and the lysosomal mass and pH were detected separately with LysoPrime Green and pHLys Red. Co-staining with MitoBright ROS and Lysosomal dyes demonstrated that CCCP causes lysosomal neutralization and mitochondrial ROS induction at the same time.
Products in Use
- Lysosomal Acidic pH Detection Kit
(combination kit of LysoPrime Green / pHLys Red)
- MitoBright ROS Deep Red - Mitochondrial Superoxide Detection
|

















