|
Cell death, once thought to follow distinct and irreversible routes, is now understood to involve overlapping and even reversible processes. Recent studies reveal new dimensions of how cells coordinate or recover from death signals, expanding the concept of programmed cell death. One study defines PANoptosis, a coordinated form of cell death in which apoptosis, pyroptosis, and necroptosis act together through the PANoptosome, linking inflammation and immune regulation in cancer. Another reports an NF-κB–dependent programmed cell revival after sublethal exposure to cell death–inducing agents, adding a reversible layer to cell-fate control. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
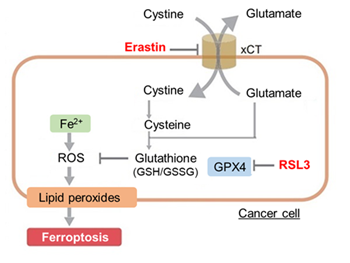
PANoptosis in cancer: bridging molecular mechanisms to therapeutic innovations (Cell Mol Immunol., 2025) Review Article Summary: PANoptosis is a newly characterized form of programmed cell death in which apoptosis, pyroptosis, and necroptosis operate together through the assembly of an inducible multiprotein scaffold known as the PANoptosome. This review focuses on cancer, describing the interplay among these death pathways and highlighting the defining characteristics and assembly mechanisms of PANoptosis. It also discusses functional roles in tumor initiation and progression, and its link to immune responses within the tumor microenvironment. Furthermore, the review explores the therapeutic implications of PANoptosis, including the potential of targeting this pathway in cancer therapy. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
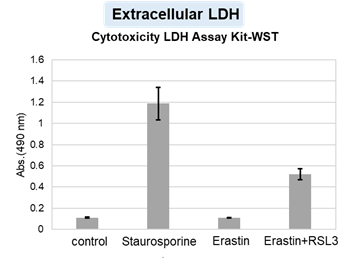
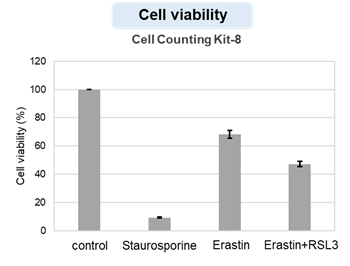
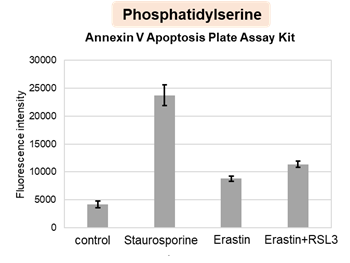
Summary: This study reveals that exposure to the cell death-inducing agent (LLOMe) triggers a previously unrecognized programmed cell regeneration, where cells avoid death, open chromatin, activate developmental and inflammatory genes, and rebuild to restore tissue repair. NF-κB is essential, defining a conserved self-healing pathway and a promising therapeutic target for regenerative medicine. Highlighted technique: This study used flow cytometry and live cell confocal imaging to monitor cellular dynamics during the transition from death to recovery. Annexin V/PI staining, mitochondrial membrane potential (JC-1), lysosomal probe, and organelle markers such as TOM20 and Rab7 were used to monitor cell state and organelle integrity. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
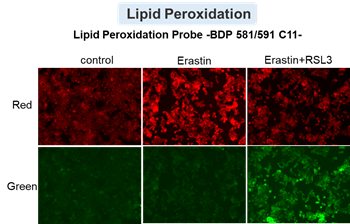
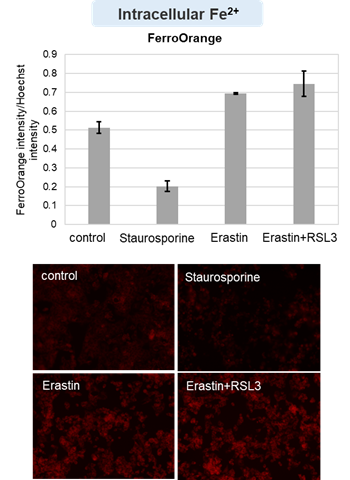
Cell Death Indicators (click to open/close)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Application Note (click to open/close)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||