Membrane Lipid Alterations Accelerate Cell Death [Mar. 11, 2025]
Previous Science Note
|
The lipid composition of cell membranes plays a critical role in regulating cell death by influencing membrane integrity, signaling pathways, and susceptibility to oxidative stress. This Science Note introduces the latest findings on lipid profile changes in cell and mitochondrial membranes as key factors in cell death processes such as apoptosis and ferroptosis. |
||||||||||||||||||
|
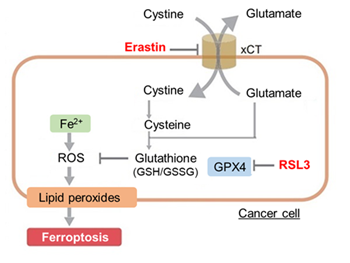
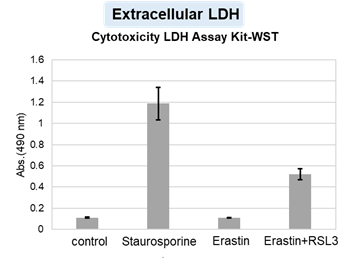
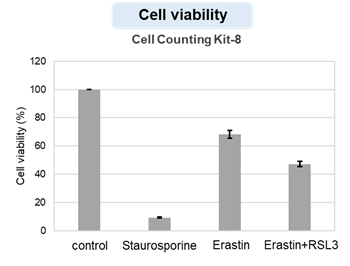
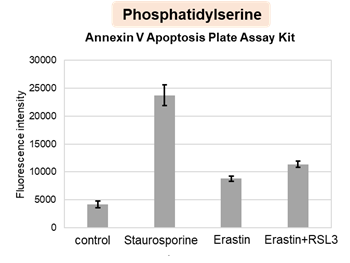
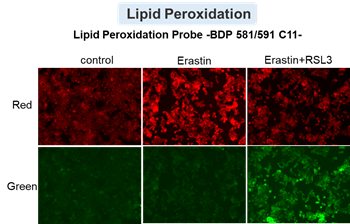
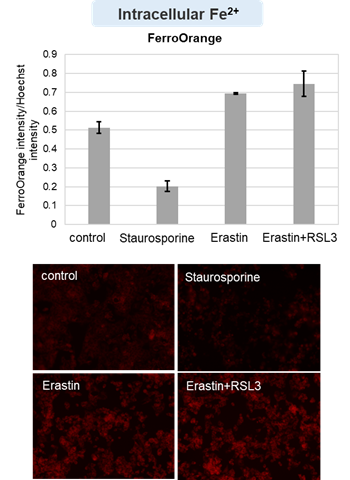
Cytotoxic stress-induced inhibition of receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) signaling not only induces cellular apoptosis but also increases the membrane PUFA ratio, thereby enhancing susceptibility to lipid peroxidation. Consequently, these cells become more susceptible to ferroptosis. Highlighted technique: Increased susceptibility of the cell membrane to lipid peroxidation increases the susceptibility to ferroptosis. The actual occurrence of ferroptosis can be assessed by quantifying intracellular iron levels, ROS, lipid peroxidation and other related factors. |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Bax promotes cell death by adsorbing to the outer mitochondrial membrane, extracting lipids and forming Bax/lipid clusters on the membrane surface, facilitating apoptotic pore formation. Highlighted technique: This study uses a biomimetic model of the mitochondrial outer membrane (MOM), as reported in several studies, to investigate the effect of Bax on membrane behavior. This model serves as a valuable tool for understanding how target factors influence MOM dynamics. |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Unsaturated lipids enrich near BAX/BAK during apoptosis, increasing BAX pore activity and promoting mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization, which is critical for apoptosis execution. Highlighted technique: The GUV assay is an in vitro technique for generating unilamellar vesicles and analyzing membrane properties. This study evaluates membrane permeability using fluorescent dyes and compares the transfer of dyes of different molecular sizes into the vesicles to assess membrane pore size. |
||||||||||||||||||
Related Techniques (click to open/close)
|
||||||||||||||||||
Application Note (click to open/close)
|
||||||||||||||||||