|
Autophagy is a cellular process in which intracellular components are degraded and recycled. It is broadly categorized into macroautophagy, which involves the formation of autophagosomes, and microautophagy, where lysosomes directly engulf target materials without autophagosome intermediates1. While mitophagy is typically mediated by macroautophagy, recent studies have uncovered a microautophagy-like mechanism by which lysosomes selectively remove damaged portions of mitochondria rather than the entire organelle2. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
1. Autophagy genes in biology and disease (Nature Reviews Genetics, 2024) Related techniques Autophagic Flux Detection |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2. Lysosomes drive the piecemeal removal of mitochondrial inner membrane (Nature, 2024) Highlighted technique: This study uses a combination of super-resolution microscopy, live-cell imaging, and specific fluorescent probes and proteins to visualize and track in real time the dynamic process of IMM protruding through the OMM and their subsequent uptake by lysosomes. Related techniques Lysosomal Function Analysis, Mitophagy detection |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
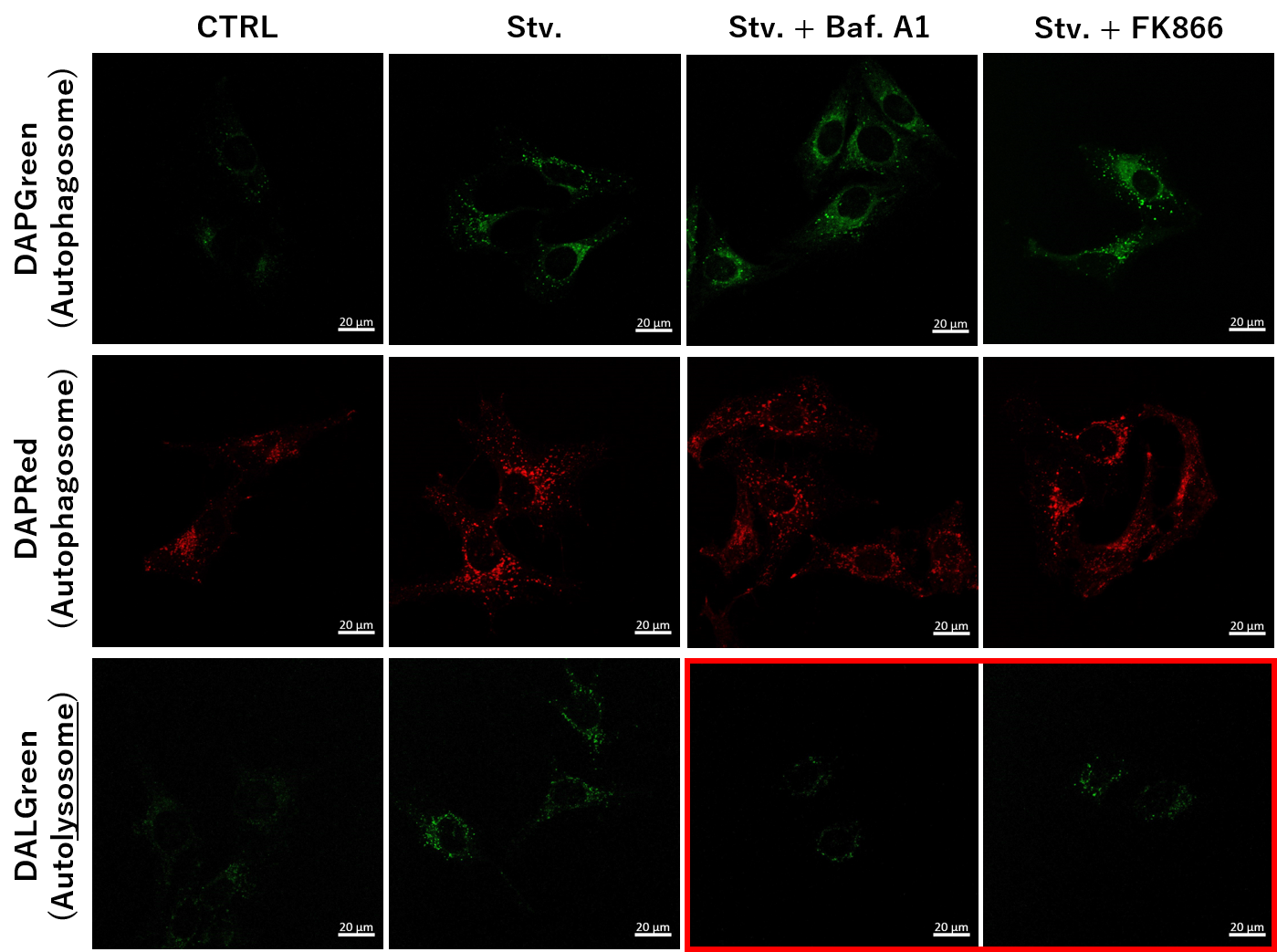
Application Note I > NAD+ Depletion and Autophagy-Lysosomal Pathway Response
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
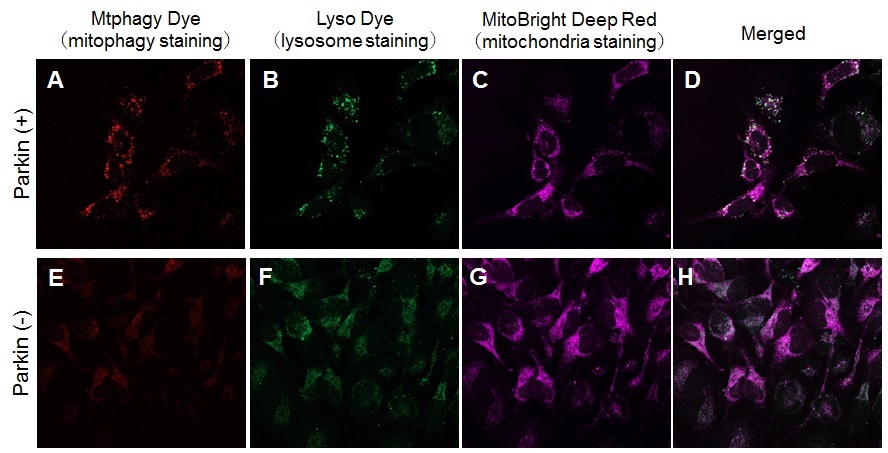
Application Note II > Induction of Mitophagy in Parkin Expressed HeLa cells
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Previous Science Note | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Related Techniques
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||