| [Sep. 3, 2024] | Previous Science Note |
|
Endosomal proteins play a critical role in determining cell fate by regulating the trafficking and signaling of receptors and other membrane-bound molecules within cells. These proteins control the endocytosis, recycling, or degradation of signaling receptors, thereby influencing key pathways such as those governing differentiation, survival, and apoptosis. By modulating the duration and intensity of signaling cascades, endosomal proteins help determine whether a cell will proliferate, differentiate, or undergo programmed cell death. Dysregulation of these processes can lead to inappropriate cell fate decisions and contribute to diseases such as cancer and neurodegeneration. |
|
|
Related Techniques |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Related Applications |
Clear visualization of intracellular vesicular trafficking
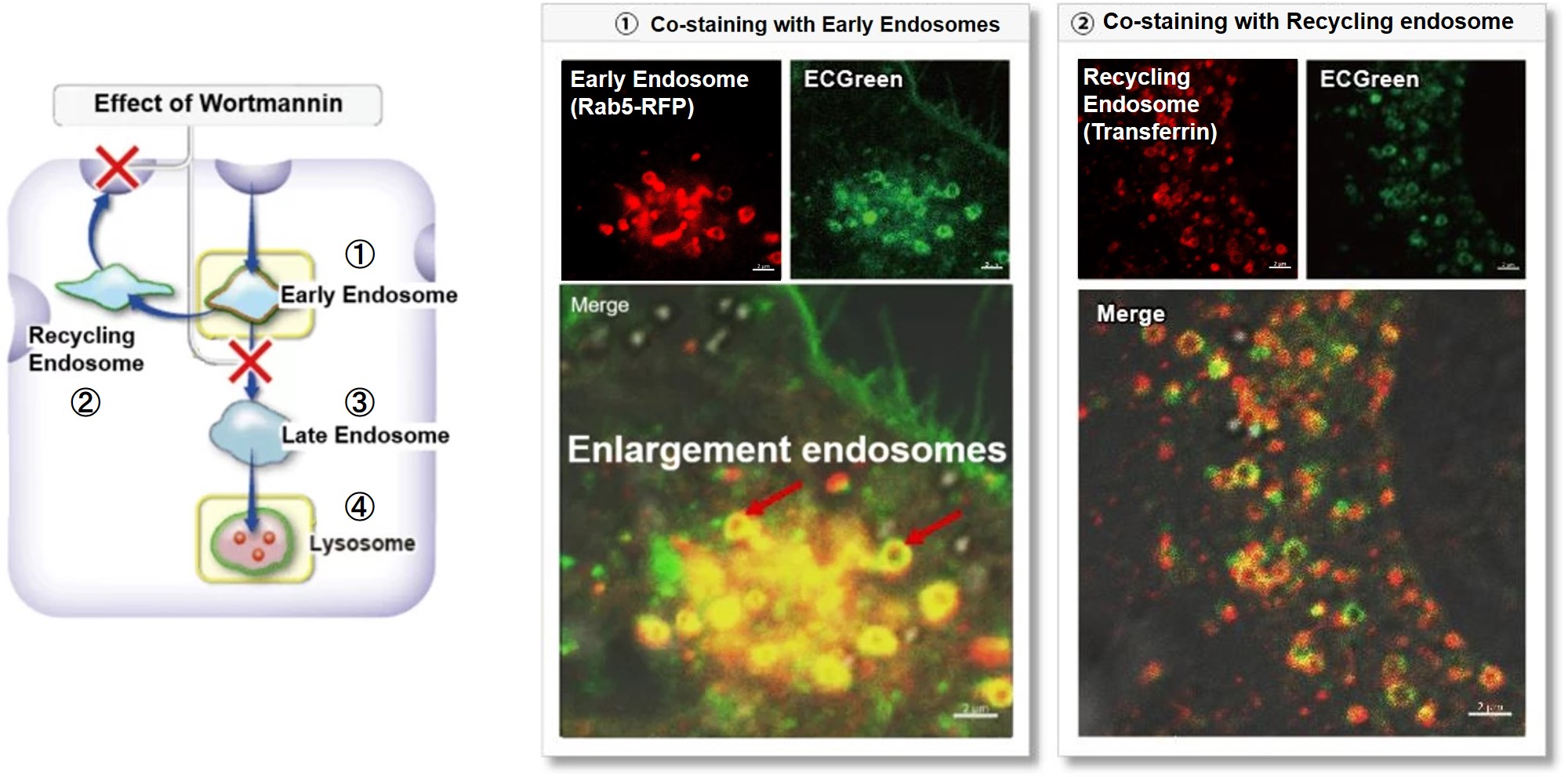
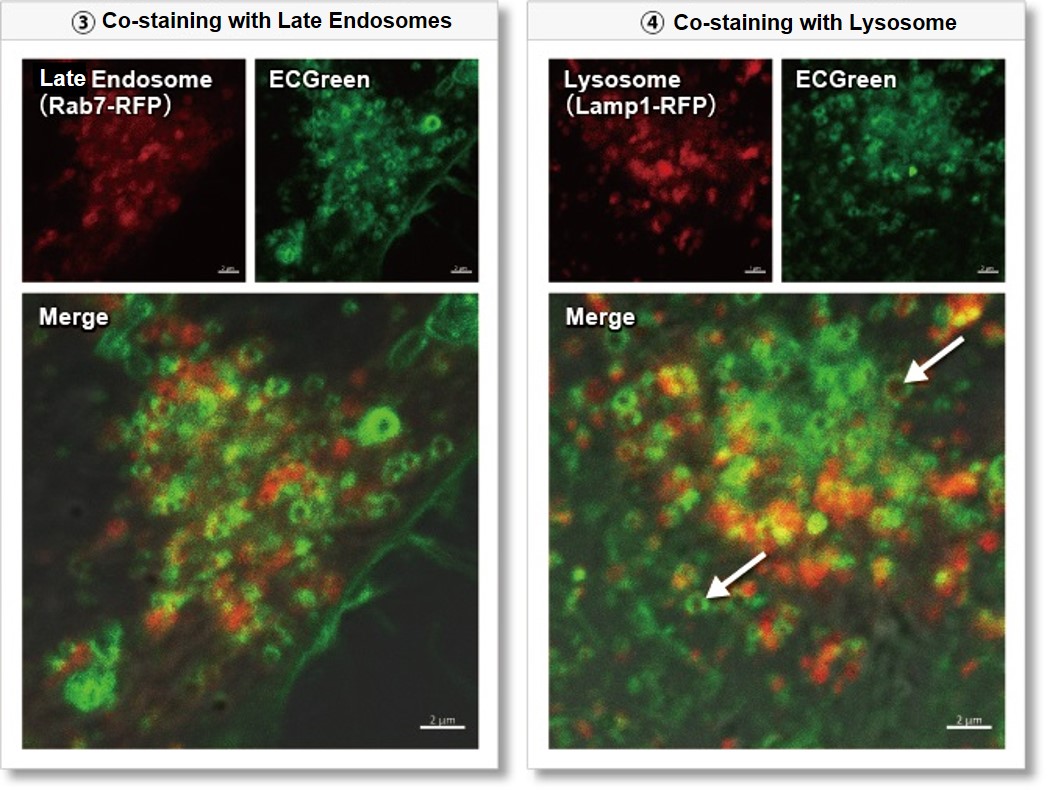
Wortmannin is known to inhibit endosomal recycling and lysosomal translocation, leading to endosomal enlargement. ①Eary endosome: Rab5-RFP (red) As a result, it was confirmed that ECGreen (green) co-localizes only with enlarged early endosomes and recycling endosomes (Fig. ① and ②), but not with late endosomes or Lysosomes (Fig. ③ and ④), supporting Wortmannin's effect. ECGreen can visualize changes in the intracellular vesicular trafficking system and endosome shape. Endosomes (ECGreen, green): Ex. 405 nm / Em. 500 – 560 nm [Experimental Procedure] |