MitoComplex-I Activity Assay Kit
MitoComplex-I Activity Assay Kit
- Measurement of Complex I activity in fractionated mitochondria
- Simple procedure by adding the included reagents only
-
Product codeMT18 MitoComplex-I Activity Assay Kit
| Unit size | Price | Item Code |
|---|---|---|
| 100 tests | $380.00 | MT18-10 |
[Notice]
This product is intended for fractionated mitochondria.
Before measurement, mitochondria must be fractionated using a kit such as the IntactMito Fractionation Kit for Tissue (Product Code: MT17-10).
| 100 tests | ・Assay Buffer ・Assay Reagent ・Coenzyme ・Ubiquinone |
25ml ×1 ×1 ×1 ×1 |
|---|
Mitochondrial Complex I Activity Assay
The mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes I–IV each play distinct roles in electron transfer, contributing to cellular energy metabolism and redox regulation. Among them, Complex I (NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase) serves as the entry point for electron transfer and is recognized as a major source of reactive oxygen species (ROS) within mitochondria.
Fluctuations in Complex I activity are directly linked to oxidative stress responses and the induction of cell death pathways, particularly necroptosis and ferroptosis, thereby playing a central role in disease pathogenesis. Furthermore, inhibition of Complex I reduces CoQH₂ (ubiquinol) levels, which accelerates lipid peroxidation and triggers ferroptosis, suggesting a potential mechanism for promoting selective cancer cell death.
References:
R. Deng et al., Cell Death Dis. 2025, 16, 254.
F. Basit et al., Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2716.
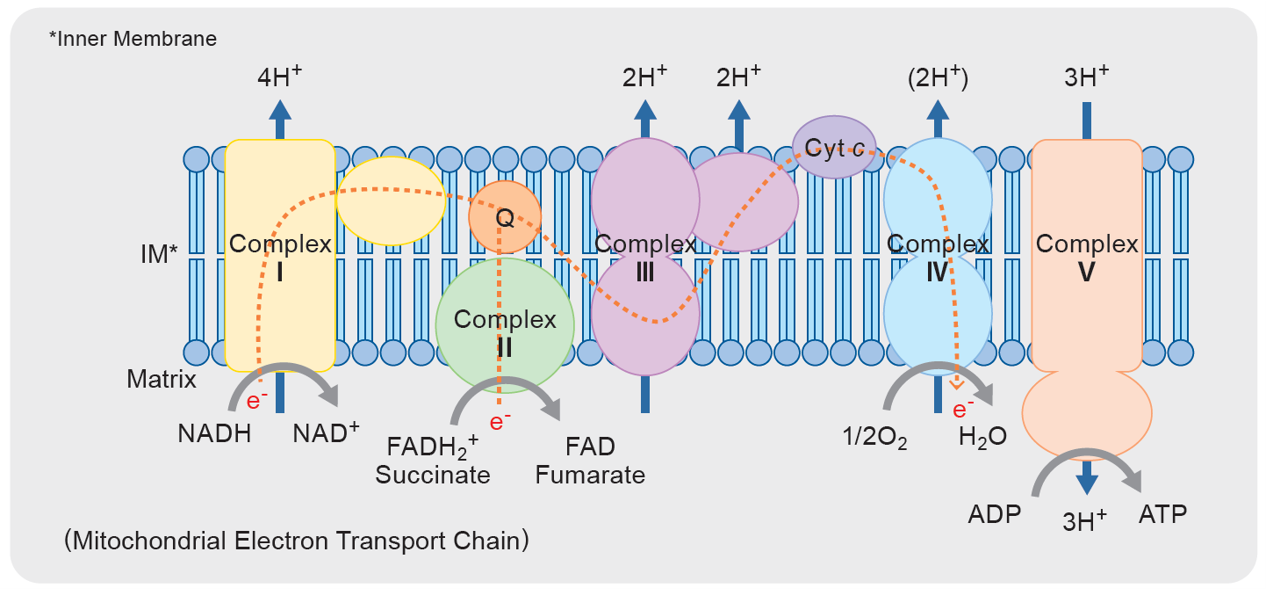
Mitochondrial electron transport chain
Main Roles of Mitochondrial Respiratory Chain Complexes I–V and Associated Diseases
| Complex (Name) | Main Role | Characteristics | Associated Diseases / Pathologies | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I (NADH: Ubiquinone Oxidoreductase) |
Electron transfer from NADH to CoQ (ubiquinone) | Primary source of ROS production; involved in supercomplex formation | Parkinson’s disease Cancer, ischemic injury Induction of ferroptosis |
|
| II (Succinate Dehydrogenase) |
Electron transfer from succinate to CoQ | Low ROS production; linked to the TCA cycle | Leigh Syndrome Mitochondrial Disease |
|
| III (Cytochrome bc₁ Complex) |
Electron transfer from CoQH₂ to cytochrome c | Participates in supercomplex formation and ROS regulation | Inflammatory Diseases, Immune Disorders Microglial Dysfunction |
|
| IV (Cytochrome c Oxidase) |
Transfer of electrons to oxygen to produce water | Final electron acceptor; directly coupled to ATP production; oxygen-dependen | Alzheimer’s Disease Parkinson’s Disease |
|
| V (ATP Synthase) |
ATP synthesis utilizing the proton gradient | Contains a membrane-embedded F₀ domain and a rotary F₁ domain; rotation of F₀ driven by proton flow transmits energy to F₁ for ATP synthesis | Complex V Deficiency: NARP, MILS, Neonatal Mitochondrial Encephalopathy, etc. |
Products Related to Mitochondrial Activity Evaluation
| Product Name | Target | Detection Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Extracellular OCR Plate Assay Kit | Extracellular Oxygen Concentration | Plate Reader Ex: 500 nm / Em: 650 nm |
| JC-1 MitoMP Detection Kit | Mitochondrial Membrane Potential | Fluorescence Microscope, FCM, Plate Reader Green:Ex 488 nm / Em 500-550 nm Red:Ex 561 nm / Em 560-610 nm |
| ATP Assay Kit-Luminescence | ATP | Plate Reader Luminescence |
| IntactMito Fractionation Kit for Tissue | ※Tissue Mitochondrial Fractionation | - |
Manual
Technical info
Principle
Complex I functions by accepting electrons from NADH and transferring them to ubiquinone (Coenzyme Q) within the cell. This electron transfer reaction is coupled with the pumping of protons from the mitochondrial matrix (inner side) to the intermembrane space (outer side), contributing to the formation of the membrane potential required for ATP synthesis.
IIn this kit, fractionated mitochondria are supplemented with NADH and ubiquinone included in the reagents, allowing electron transfer via Complex I. During this process, NADH is oxidized to NAD⁺. By measuring the change in absorbance at 340 nm (corresponding to the rate of NADH decrease), the activity of Complex I can be evaluated.
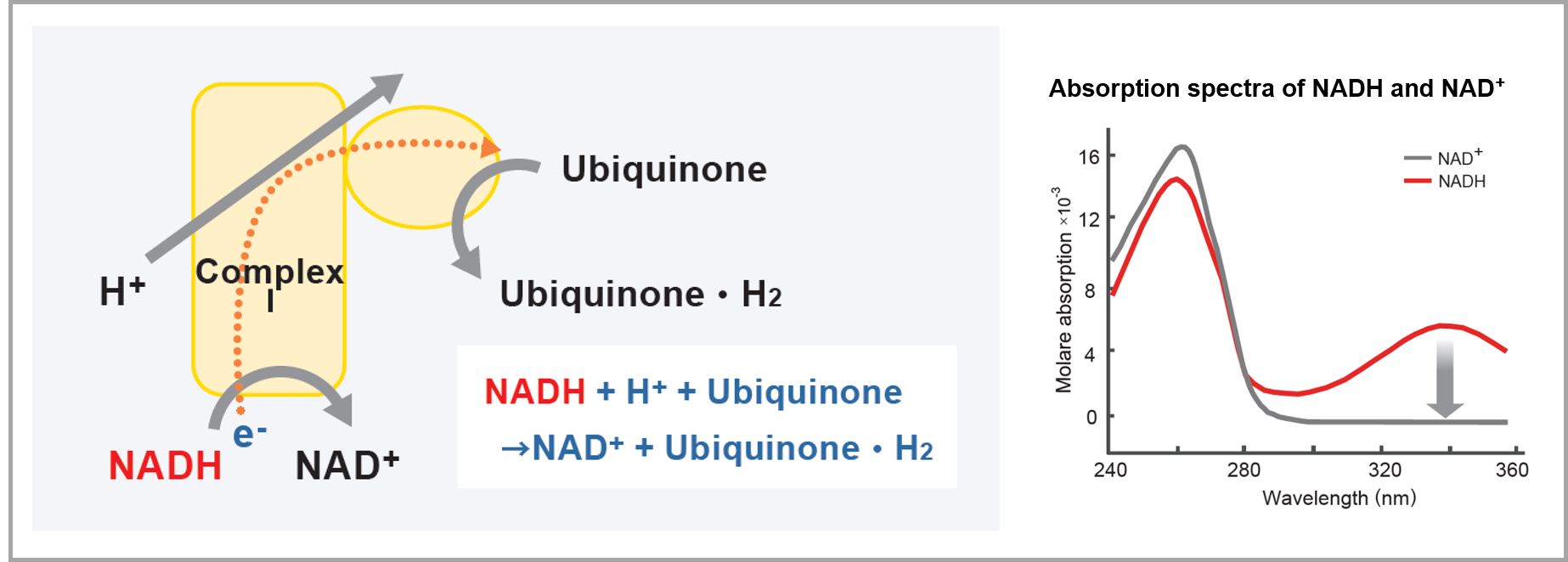
Procedure
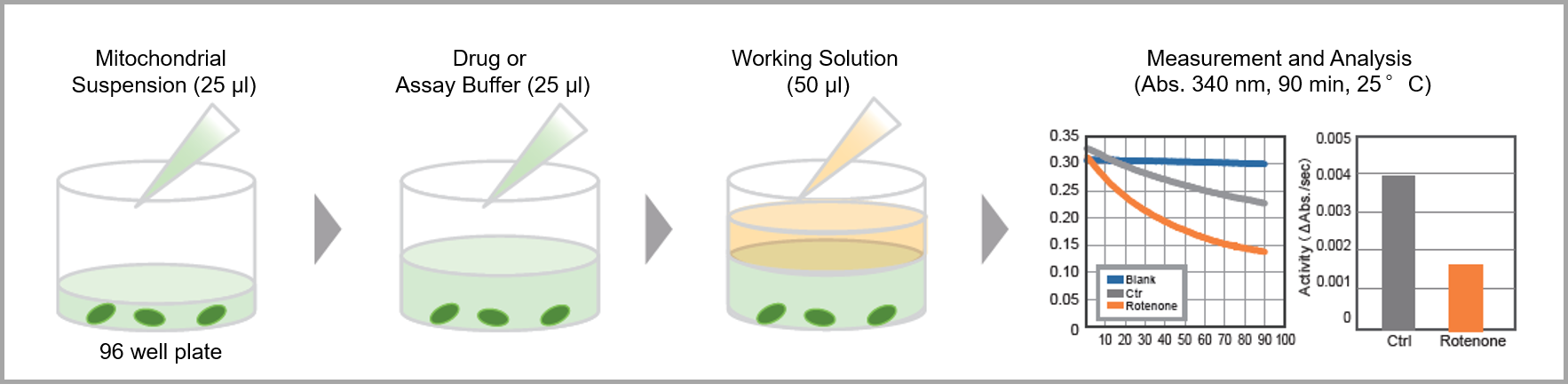
Measurement can be performed easily by simply adding the reagents included in the kit.
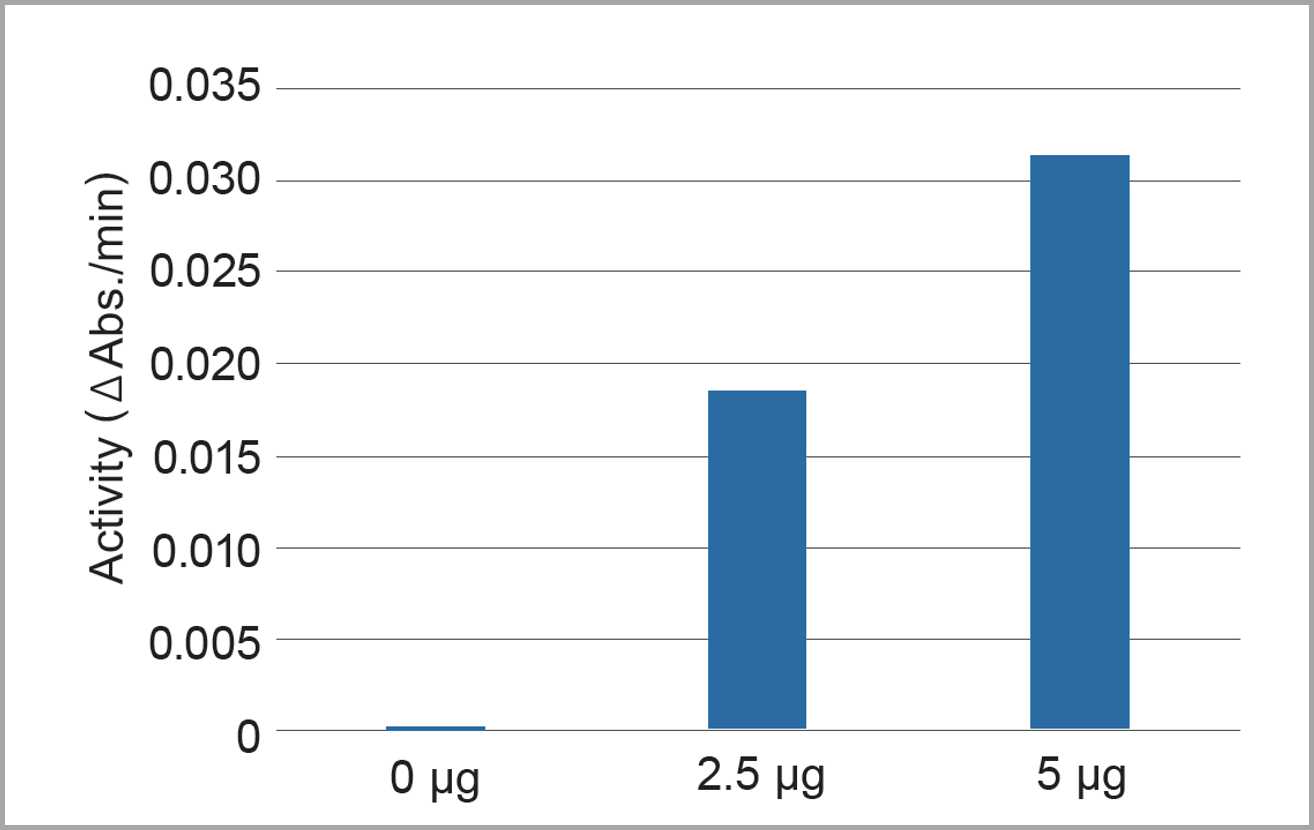
Activity Evaluation According to Mitochondrial Amount
Using this kit, Complex I activity was measured in fractionated mitochondria at 0 µg, 2.5 µg, and 5 µg. The results confirmed that Complex I activity values are proportional to the amount of mitochondria.
Sample: Mitochondria Derived from Bovine Heart
Complex I activity was calculated based on the rate of change in absorbance from 0 to 6.5 minutes.
Complex I-Specific Measurement
Using mitochondria derived from bovine heart (5 µg/well), Complex I activity was measured with this kit in the presence of mitochondrial complex inhibitors and a depolarizing agent.
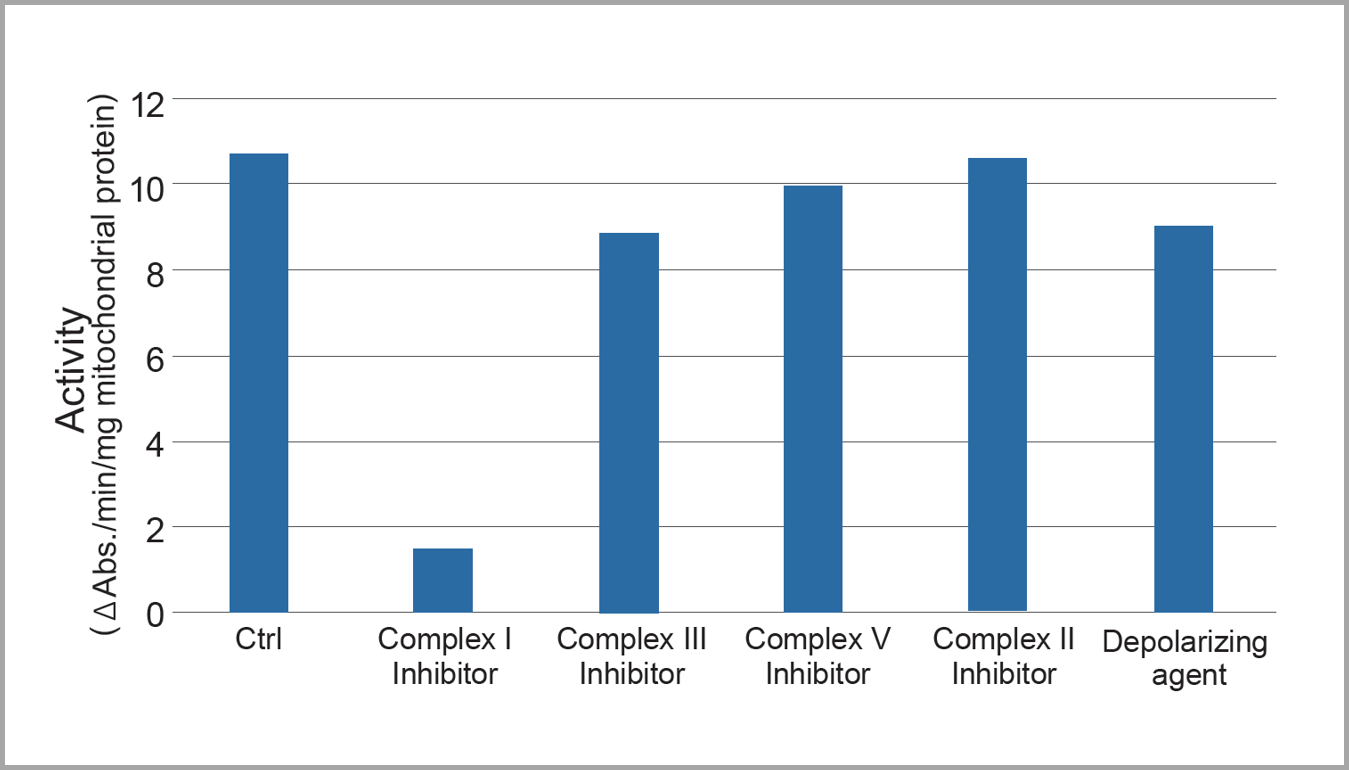
Sample:Mitochondria Derived from Bovine Heart
Drug Treatment Conditions:
• Complex I inhibitor: 0.5 µmol/L Rotenone
• Complex II inhibitor: 0.5 mmol/L TTFA
• Complex III inhibitor: 0.5 µmol/L Antimycin
• Complex V inhibitor: 0.5 µmol/L Oligomycin
• Depolarizing agent: 0.5 µmol/L FCCP
Analysis: Enzyme activities were calculated based on the rate of change in absorbance from 0 to 3.5 minutes.
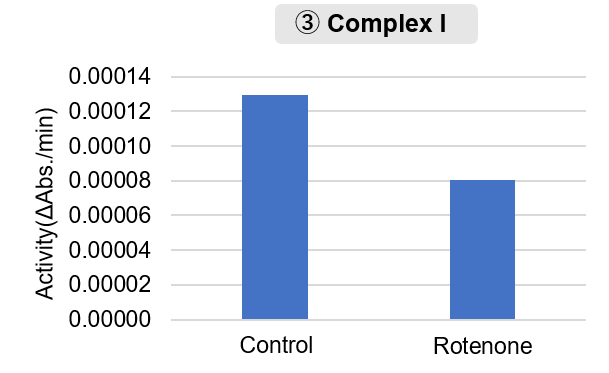
Experimental Example: Measurement of Mitochondrial Activity Fractionated from Mouse Brain
Mitochondria were fractionated from mouse brain tissue using this kit, and oxygen consumption rate (OCR), mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), and Complex I activity were measured.
The results showed that the addition of succinate, a substrate that activates Complex II of the electron transport chain, increased both OCR and MMP. In contrast, FCCP treatment reduced MMP, indicating that intact mitochondria were successfully fractionated.
Furthermore, in the Complex I activity assay, a decrease in activity was observed following treatment with rotenone, a Complex I inhibitor.
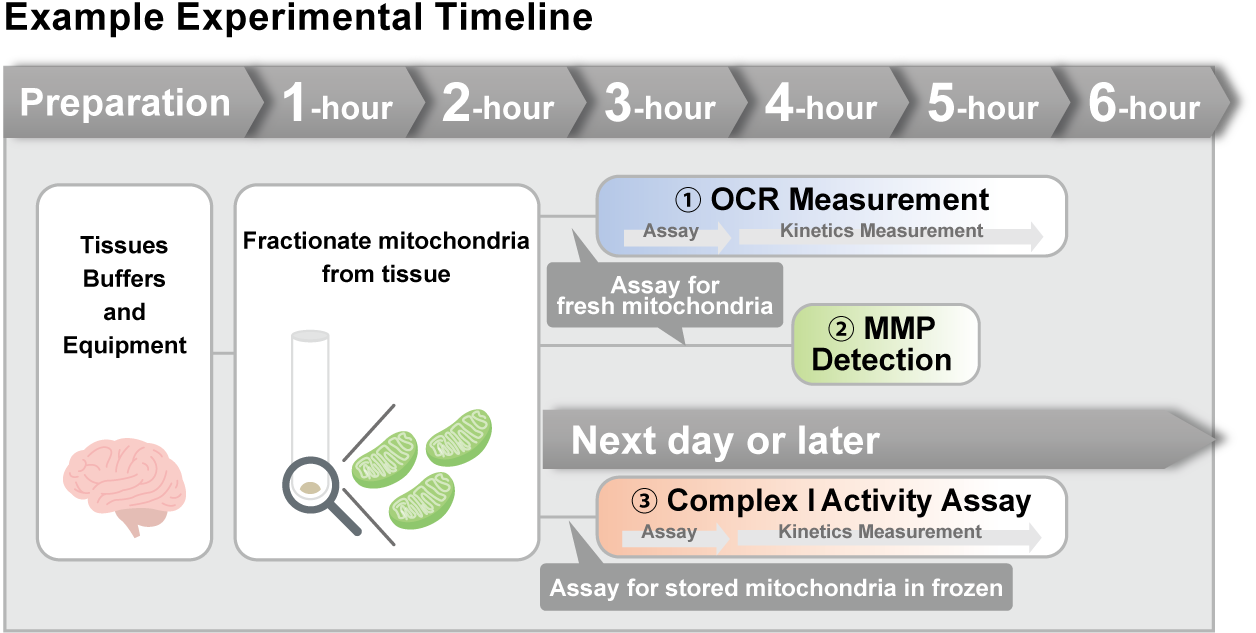
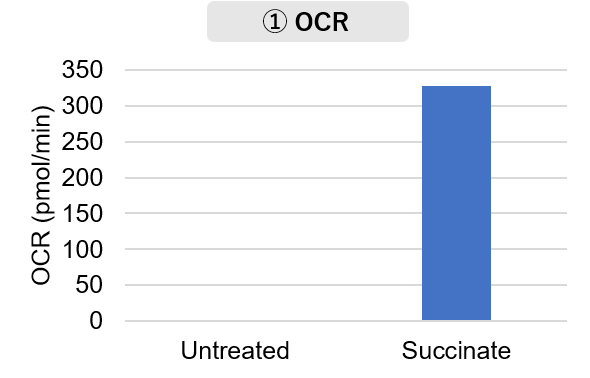
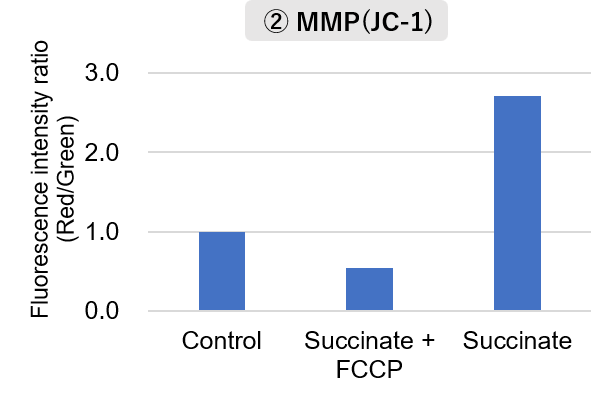
<Experimental Conditions>
OCR Measurement
Amount of mitochondria: 50 μg/well (as protein levels)
Succinate: 10 mmol/l
MMP Detection
Amount of mitochondria: 50 μg/well (as protein levels)
Succinate: 10 mmol/l, FCCP: 4 μmol/l
Complex I Activity Assay
Amount of mitochondria: 20 μg/well (as protein levels)
Rotenone: 10 μmol/l
<Product used>
Mitochondrial Fractionation: IntactMito Fractionation Kit for Tissue (Code: MT17)
OCR measurement: Extracellular OCR Plate Assay Kit (Code: E297)
MMP detection: JC-1 MitoMP Detection Kit (Code: MT09)
Complex I activity assay: MitoComplex- I Activity Assay Kit (Code: MT18)
Q & A
-
Q
Can Complex I activity in cells be measured directly without the need for mitochondrial fractionation?
-
A
Complex I activity cannot be measured directly in intact cells.
Measurement of Complex I activity is based on a reaction principle using NADH as a reference. However, because endogenous NADH is present within cells, background interference makes accurate measurement difficult.
-
Q
Does frozen storage affect the measurement values?
-
A
Yes, it does. We fractionated mitochondria from mouse brain tissue and compared Complex I activity between samples measured immediately after fractionation and samples frozen for one day. The frozen samples showed clearer S/N ratios.
Based on these results, we recommend using mitochondria that have been frozen for at least overnight.

<Experimental Conditions>
Rotenone : 10 μmol/l
-
Q
How long can fractionated mitochondria be stored frozen?
-
A
We recommend using mitochondria that have been frozen for at least overnight. However, because Complex I activity gradually decreases during frozen storage, we advise performing the assay as soon as possible after freezing.
In our internal testing, we successfully detected rotenone-induced changes using fractionated mitochondria derived from mouse brain tissue that had been stored at −20°C for one month.
-
Q
How can I quantify the sample (fractionated mitochondria)?
-
A
We have experience performing protein concentration quantification using the BCA method. When using the IntactMito Fractionation Kit for Tissue (MT17-10), note that the Stabilization Buffer contains protein. Therefore, when determining protein concentration, measure a blank using Stabilization Buffer alone and subtract its value from the sample measurement.
Handling and storage condition
| 0-5°C, Protect from light, Nitrogen substitution, Protect from moisture |











