General Information
Glutathione (GSH) is the most abundant thiol(SH) compound in animal tissues, plant tissues, bacteria and yeast. GSH plays many different roles such as protection against reactive oxygen species and maintenance of protein SH groups. During these reactions, GSH is converted into glutathione disulfide (GSSG: oxidized form of GSH). Since GSSG is enzymatically reduced by glutathione reductase, GSH is the dominant form in organisms.
DTNB (5,5’-Dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid)) and glutathione (GSH) react to generate 5-mercapto-2-nitrobenzoic acid and glutathione disulfide (GSSG). Since 5-mercapto-2-nitrobenzoic acid is a yellow colored product, GSH concentration in a sample solution can be determined by the measurement at 412 nm absorbance. GSH is generated from GSSG by glutathione reductase, and reacts with DTNB again to produce 5-mercapto-2-nitrobenzoic acid. Therfore, this recycling reaction improves the sensitivity of total glutathione detection (Fig. 1).
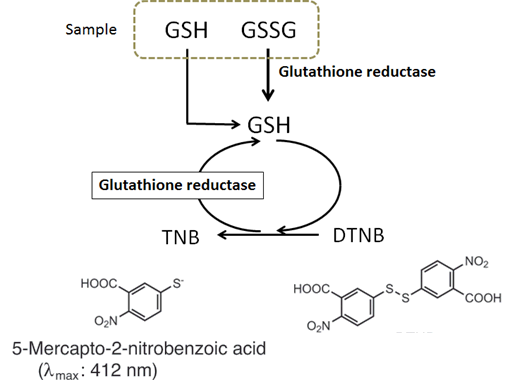
Fig. 1. Principle of Total Glutathione Quantification Kit
Kit Contents
| Substrate(DTNB) | x 2 |
| Enzyme Solution | 50 μl x 1 |
| Coenzyme | x 2 |
| Buffer Solution | 50 ml x 1 |
| Standard GSH | x 1 |
Storage Condition
Store the kit at 0-5°C. Substrate working solution, Coenzyme working solution and GSH standard solution can be stored at -20°C for 2 months. Enzyme working solution is stable for 2 months at 4°C (Do not freeze).
Required Equipment and Materials
- Microplate reader (with 405 nm filter or 415 nm filter)
- 96-well microplate
- 20 μl, 200 μl and multi-channel pipettes
- Incubator (37°C)
- 5-Sulfosalicylic acid (SSA)
Precaution
- Use the reagents in the kit after the reagents temperatures are equilibrated to the room temperature.
- Triplicate measurements per sample is recommended to obtain accurate data.
- Since the colorimetric reaction starts immediately after the addition of Substrate working solution to a well, use a multichannel pipette to avoid the reaction time lag of each well.
- If the concentration range of total glutathione in a sample is not known, prepare multiple-diluted sample solutions.
- This kit contains glass vials with an aluminium cap. Please handle carefully.
Preparation of Sample Solution
General preparation methods are available at www.dojindo.com by searching "T419".
Preparation of Solutions
Substrate working solution
Add 1.2 ml of Buffer solution to one vial of Substrate, and dissolve.
- Store the remaining solution at -20oC (stable at -20oC for 2 months).
Enzyme working solution
Mix Enzyme solution using pipette. Take out 20 μl of Enzyme solution, and mix it with 4 ml of Buffer solution.
- Store the remaining solution at 4oC (stable at 4oC for 2 months).
Coenzyme working solution
Add 1.2 ml of ddH2O to the Coenzyme vial, and dissolve.
- The Coenzyme vial is decompressed; carefully open the cap or use a syringe to add ddH2O.
- Store the remaining solution at -20oC (stable at -20oC for 2 months).
GSH standard solutions
- Add 2 ml of 0.5% SSA to the Standard GSH vial, and dissolve to prepare 200 μmol/l GSH standard solution.
- The Standard GSH vial is decompressed; carefully open the cap or use a syringe to add SSA.
- Store the remaining solution at -20oC (stable at -20oC for 2 months).
-
- Dilute 100 μl of 200 μmol/l GSH standard solution by serial dilution with 100 μl of 0.5% SSA in plastic tubes as indicated in Fig. 2.
- GSH standard solutions: 100 μmol/l, 50 μmol/l, 25 μmol/l, 12.5 μmol/l, 6.25 μmol/l, 3.13 μmol/l, 1.56 μmol/l and 0 μmol/l.
- Use up the solution within one day.
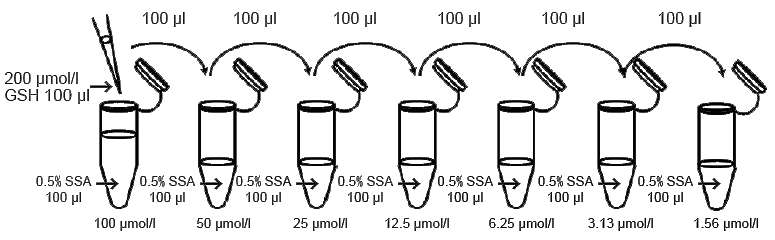
Fig. 2 Preparation of GSH standard solutions.
General Protocol
- To each well, add 20 μl of Coenzyme working solution, 120 μl of Buffer solution and 20 μl of Enzyme working solution.
- Incubate the plate at 37oC for 5 minutes.
- Add 20 μl of either one of the GSH standard solutions or the sample solutions.
- Adjust the concentration of SSA in the sample solution to 0.5-1% with ddH2O before the assay. High concentrations of SSA
( >1%) interfere with the assay. See Fig. 3 for a plate diagram of the solution arrangement.
- Adjust the concentration of SSA in the sample solution to 0.5-1% with ddH2O before the assay. High concentrations of SSA
- Incubate the plate at 37oC for 10 minutes.
- Add 20 μl of Substrate working solution, and incubate the plate at room temperature for 10 minutes.
- Read the absorbance at 405 nm or 415 nm using a microplate reader.
- Determine concentrations of GSH in the sample solutions using a calibration curve.
- Since the colorimetric reaction is stable and the O.D. increases linearly over 30 minutes, GSH concentration can be determined by using kinetic or pseudo-end point (no stopping reaction, quick measurement of the O.D. at certain time points between 5 and 10 minutes.) methods.
- Typical calibration curves prepared using the kinetic method and the pseudo-end point method are indicated in Fig. 4 and 5, respectively.
- If the expected concentration of total glutathione in the sample is 25 μmol/l or lower, the GSH standard solution can be further diluted from 25 μmol/l by following the procedure above and then incubate at room temperature for 20-30 minutes after adding Substrate working solution.
-
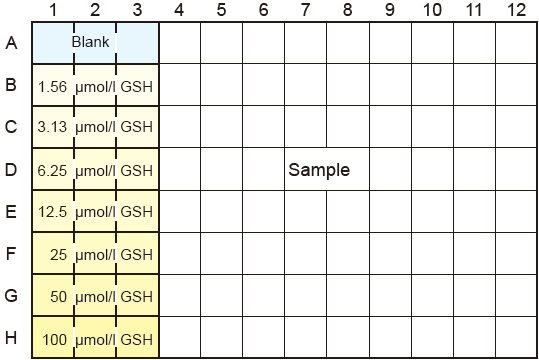
Fig.3 Plate Diagram: an example of the GSH standard solution and sample solution arrangement to be measured in triplicate (up to 24 samples can be determined in one plate).
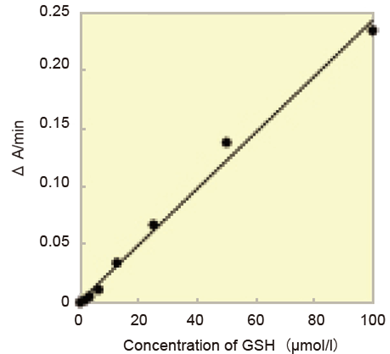
Fig. 4 Calibration curve prepared using kinetic method.
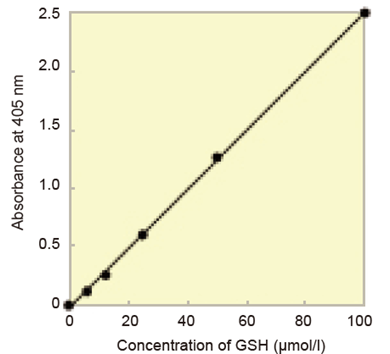
Fig. 5 Calibration curve prepared using pseudo-end point method.
Calculation of total glutathione (GSH and GSSG) concentration
Determine the total glutathione concentration a) in a sample solution using the following equations.
Pseudo-end point method:
Total glutathione = (O.D.sample – O.D.blank) / slope
Kinetic method:
Total glutathione = (Slope c)sample – Slope c)blank) / slope b)
a) Since the values obtained by these equations are the amount of total glutathione in treated sample solutions, further calculations are necessary if the actual concentrations of glutathione in cells or tissues need to be determined.
b) slope of the calibration curve.
c) slope of the kinetic reaction.
Interference
Reducing agents such as ascorbic acid, β-mercaptoethanol, dithiothreitol (DTT) and cysteine, or thiol reactive compounds such as maleimide compounds, interfere with the glutathione assay. Therefore, SH compounds, reducing agents and SH reactive materials should be avoided during the sample preparation.
References
- G. L. Ellman, Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 1959, 82, 70.
- O. W. Griffith, Anal. Biochem., 1980, 106, 207.
- M. E. Anderson, Methods in Enzymol., 1985, 113, 548.
- M. A. Baker, G. J. Cerniglia, and A. Zaman, Anal. Biochem., 1990, 190, 360.
- C. Vandeputte, I. Guizon, I. Genestie-Denis, B. Vannier and G. Lorenzon, Cell Biol. Toxicol., 1994, 10, 415.
Frequently Asked Questions / Reference
T419: Total Glutathione Quantification Kit
Revised Nov., 28, 2023


 Hidden sections will not be printed.
Hidden sections will not be printed.

