General Information
It has been recognized that hydrogen sulfide (H2S) has an important role as a physiological active substance for vasodilation, cytoprotection, and modulation of insulin secretion. H2S is considered as a gaseous molecule such as NO and CO. However, around 80% of the total sulfide exists as hydrogen sulfide anion (HS-) under physiological condition, since the pKa is about 7.
Monobromobimane method is one of the most sensitive and reliable method for H2S detection. One molecule of H2S reacts with two molecules of monobromobimane to form a sulfide dibimane (Fig. 1). Sulfide dibimane can be separately analyzed from glutathione or cystein that reacted with monobromobimane by HPLC, and also sensitively detected because it emits fluorescence1), 2), 3).
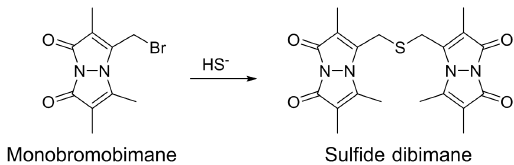
Fig. 1 Reaction mechanism of monobromobimane
Contents
| -SulfoBiotics- Sulfide dibimane | 10 nmol/tube x 5 |
- The pellet in the tube may be barely visible due to the small amount. Please handle it accordingly.
Storage Condition
Store at 0-5℃ and protect from light.
- Sulfide dibimane is sensitive to light. Store unused sulfide dibimane in the bag.
Use the sulfide dibimane solution within the same day.
Example of HPLC analysis
Pretreatment of sample
- Transfer 30 μl of sample into a tube containing 70 μl of 100 mmol/l Tris-HCl buffer (pH 9.5, 0.1 mmol/l DTPA).
- Add 50 μl of 10 mmol/l monobromobimane acetonitrile solution.
- Incubate for 30 minutes.
- Add 50 μl of 200 mmol/l 5-sulfosalicylic acid.
- Use the supernatant as a sample.
- For the details of the monobromobimane method, refer Methods Enzymol., 2015, 554, 315).
Quantitative analysis of the hydrogen sulfide
- Add 100 μl of acetonitrile to the 10 nmol of Sulfide dibimane and dissolve it by pipetting to prepare 0.1 mmol/l Sulfide dibimane stock solution.
- Dilute the 0.1 mmol/l Sulfide dibimane stock solution with acetonitrile to prepare serially diluted solutions.
- Inject 5 μl of the each serially diluted solutions (from step7) into HPLC and preparate calibration curve (Fig. 2).
- Analyze the sample by HPLC (Fig.3) and calculate the area level of Sulfide dibimane.
- Calculate the concentration of HS- in the sample by the calibration curve.
- Sulfide dibimane solution is sensitive to light. Protect the solution from light and use it within the same day.
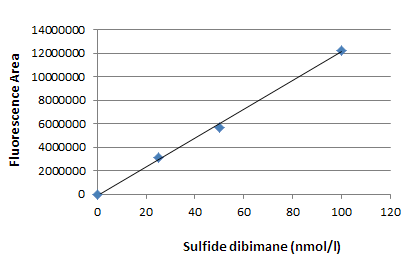
Fig. 2 Example of calibration curve
-
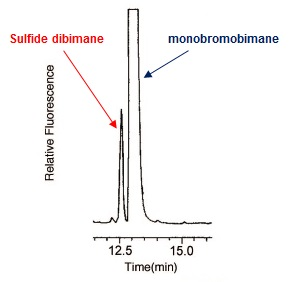
<HPLC conditions>
Column: Inertsil ODS-3Mobile Phase: A) 0.1% TFA/H2O, B) 0.1% TFA/Acetonitrile (TFA: trifluoroacetic acid)
B conc.: 5% to 35% (0 to 5 min.), 35% to 55% (5 to 16 min.),55% to 70% (16 to 23 min.)Detection: Fluorescence (Ex: 390 nm, Em: 475 nm) Flow Rate: 1 ml/min Column Temp: 40°C Fig. 3 Example of HPLC analysis
References
- G. L. Newton, R. Dorian and R. C. Fahey, Anal. Biochem., 1981, 114, 383.
- E. A. Wintner, T. L. Deckwerth, W. Langston, A. Bengtsson, D. Leviten, P. Hill, M. A. Insko, R. Dumpit, E. Vanden Ekart, C. F. Toombs and C. Szabo, Br. J. Pharmacology, 2010, 160, 941.
- X. Shen, C. B. Pattillo, S. Pardue, S. C. Bir, R. Wang and C. G. Kevil, Free Radic. Biol. Med., 2011, 50, 1021.
Frequently Asked Questions / Reference
SB15: -SulfoBiotics- Sulfide dibimane
Revised Apr., 05, 2024


 Hidden sections will not be printed.
Hidden sections will not be printed.

