General Information
Mitochondria are one of the cytoplasmic organelles that play a crucial role in cells such as production of energy for cell viability. Recently, Mitophagy appears to be related to Alzheimer and Parkinson disease induced by the accumulationof depolarized mitochondria. Mitophagy serves as a specific elimination system that dysfunctional mitochondria caused by oxidative stress and DNA damage are sequestered into autophagosome, fused to lysosome anddegraded by digestion.
This kit is composed of Mtphagy Dye, reagent for detection of mitophagy, and Lyso Dye. Mtphagy Dye accumulates in intact mitochondria, is immobilized on it with chemical bond and exhibits a weak fluorescence from the influence of surrounding condition. When Mitophagy is induced, the damaged mitochondria fuse to lysosome and then Mtphagy Dye emits a high fluorescence. To confirm the fusion of Mtphagy Dye–labeled mitochondria and lysosome, Lyso Dye included in this kit can be used.
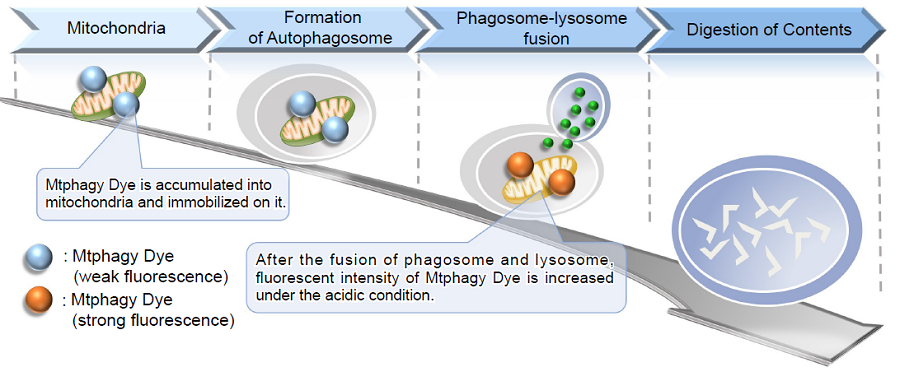
Fig. 1 The mechanism of mitophagy detection with Mtphagy Dye
Kit Contents
| Mtphagy Dye | 5 μg x 1 |
| Lyso Dye | 30 μg x 1 |
Storage Condition
Store at 0-5°C and protect from light.
Required Equipment and Materials
- Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO)
- Hanks’ HEPES buffer or serum-free medium
- Micropipettes
Preparation of Solutions
Preparation of 100 μmol/l Mtphagy Dye DMSO stock solution
Add 50 μl of DMSO to a tube of Mtphagy Dye (5 μg) and dissolve it with pipetting.
- Store reconstituted DMSO solution at -20°C. The reconstituted solution is stable at -20°C for 1 month.
Preparation of 1 mmol/l Lyso Dye DMSO stock solution
Add 55 μl of DMSO to a tube of Lyso Dye (30 μg) and dissolve it with pipetting.
- Store reconstituted DMSO solution at -20°C. The reconstituted solution is stable at -20°C for 1 month.
Preparation of 100 nmol/l Mtphagy Dye working solution
Dilute the 100 μmol/l Mtphagy Dye DMSO stock solution with Hanks’ HEPES buffer or serum-free medium to prepare
100 nmol/l Mtphagy working solution.
- Use Hanks’ HEPES buffer or serum-free medium to the dilution because serum in medium is interference with Mtphagy Dye.
Preparation of 1 μmol/l Lyso Dye working solution
Dilute the 1 mmol/l Lyso Dye DMSO stock solution with Hanks’ HEPES buffer or serum-free medium to prepare
1 μmol/l Lyso Dye working solution.
- Use Hanks’ HEPES buffer or serum-free medium to the dilution because serum in medium is interference with Lyso Dye.
Supplemental Information
Excitation and emission spectra of Mtphagy Dye and Lyso Dye
- Mtphagy Dye
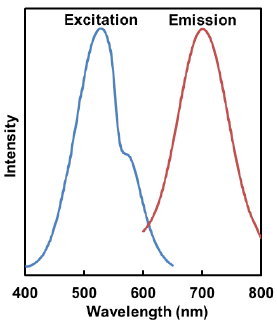
λex:530 nm
λem:700 nm<Recommended Filter>
Ex:500-560 nm
Em:670-730 nm
- Lyso Dye
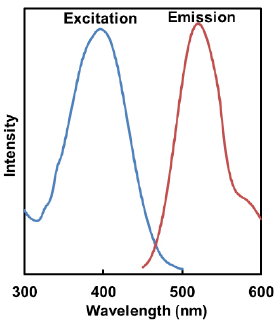
λex:398 nm
λem:525 nm<Recommended Filter>
Ex:350-450 nm
Em:500-560 nm
General Protocol
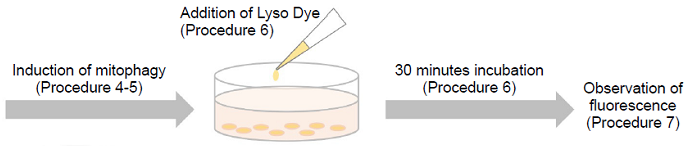
- Mtphagy Dye can not be applied to the fixed cells. If the cells are fixed before staining, Mtphagy Dye is unable to accumulate in mitochondria. In addition, the fixation after Mtphagy Dye staining is not recommended because lysosome merged phagosome is not maintained under the acidic condition and consequently the fluorescent intensity of Mtphagy Dye is not increased.
Mitophagy detection
- Prepare cells on dish for assay.
- Discard the culture medium and wash the cells with Hanks’ HEPES buffer or serum-free medium twice.
- Add an appropriate volume of 100 nmol/l Mtphagy Dye working solution and then incubate at 37oC for 30 minutes.
- Discard the supernatant and wash the cells with Hanks’ HEPES buffer or serum-free medium twice.
- Add medium containing mitophagy-inducing agent and incubate at 37oC for appropriate time. Confirm the mitophagy
phenomenon on a fluorescence microscope. - To observe the co-localization of Mtphagy Dye and lysosome, incubate at 37oC for 30 minutes with 1 μmol/l Lyso
Dye working solution. - Discard the supernatant, wash the cells with Hanks’ HEPES buffer or serum-free medium twice and observe on a
fluorescence microscope.
Experimental Example
Induction of mitophagy by carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenyl hydrazone (CCCP) as a mitochondrial-uncoupling reagent with Parkin expressed HeLa cells
- HeLa cells were seeded on μ-slide 8 well (Ibidi) and cultured at 37°C overnight in a 5%-CO2 incubator.
- The cells were transfected with Parkin plasmid vector by HilyMax transfection reagent (Dojindo, Code#:H357), and incubated at 37°C overnight.
- The Parkin expressed HeLa cells were washed with Hanks’ HEPES buffer twice and then incubated at 37°C for 30 minutes with 250 μl of 100 nmol/l Mtphagy Dye working solution containing 100 nmol/l MitoBright Deep Red (Dojindo, Code#:MT08).
- After the washing of the cells with Hanks’ HEPES buffer twice, the culture medium containing10 μmol/l CCCP was added to the well.
- After 24 hours incubation, mitophagy was observed by a fluorescence microscopy.
- After removing the supernatant, 250 μl of 1 μmol/l Lyso Dye working solution were added to the cells and incubated at 37°C for 30 minutes.
- The cells were washed with Hanks’ HEPES buffer twice and then co-localization of Mtphagy, Lyso Dye and MitoBright Deep Red was observed by confocal fluorescence microscopy.
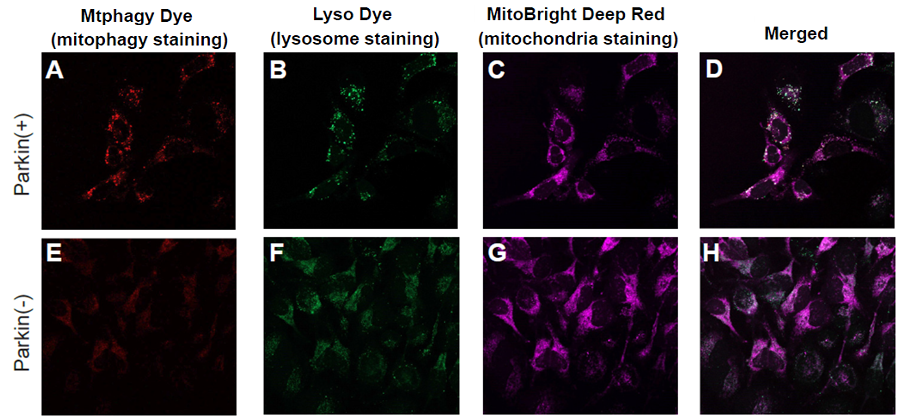
Fig. 2 Observation of mitophagy using Parkin expressed HeLa cells (upper panel) and normal HeLa cells (lower)
-
A, E) Fluorescent images of Mtphagy Dye;
B, F) Fluorescent images of Lyso Dye;
C, G) Fluorescent images of MitoBright Deep Red;
D, H) Co-localized fluorescent images of Mtphagy, Lyso Dye and MitoBright Deep Red;
-
- Mtphagy Dye: 561 nm (Ex)、LP 650 nm (Em)
- Lyso Dye: 488 nm (Ex)、502-554 nm (Em)
- MitoBright Deep Red: 640 nm (Ex)、656-700 nm (Em)
Frequently Asked Questions / Reference
MD01: Mitophagy Detection Kit
Revised Aug., 30, 2023


 Hidden sections will not be printed.
Hidden sections will not be printed.