General Information
Glutamine, a α-ketoglutarate source that is an intermediate of the TCA cycle, is an important substance involved in energy production and synthesis of nucleic acids and other amino acids. In cancer cells, glutaminolysis, the metabolic pathway for supplying α-ketoglutarate using glutamine as a substrate, is upregulated. A previous study suggested that glutaminolysis contributes to scavenging of reactive oxygen species and reduction of oxidized glutathione1).
Glutamine Assay Kit-WST enables quantitation of glutamine as a substrate in energy metabolism. This kit has been optimized to quantify glutamine in cell culture supernatants as well as intracellular glutamine by measuring absorbance in a colorimetric WST reaction. This kit is formatted for 96-well microplates and the assay has a detection limit of 5 μmol/l glutamine.
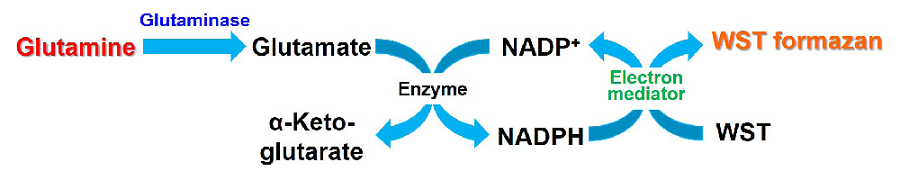
Figure 1. Principle of Glutamine Assay Kit-WST
Kit Contents
| Dye Mixture | x 1 |
| Glutamine Standard (Red cap) | x 1 |
| Enzyme (Green cap) | x 1 |
| Glutaminase(Yellow cap) | 20 μl x 1 |
| Reconstitution Buffer (White cap) | 750 μl x 1 |
| Reaction Buffer | 5 ml x 1 |
| Assay Buffer | 7.5 ml x 1 |
| Lysis Buffer | 25 ml x 1 |
| Filtration Tube | x 12 |
- Use the filtration tube for quantifying intracellular glutamine. Twelve tubes correspond to 12 test samples. For additional samples, commercially available filtration tubes (e.g., Nanosep Centrifugal Devices (10K)([OD010C33], PALL)) are recommended.
Storage Conditions
Store at 0-5 °C
Required Equipment and Materials
- Microplate reader (450 nm filter)
- Incubator (37 °C)
- 100-1000 μl, 20-200 μl, 2-20 μl micropipettes
- Conical tube
- 96-well microplate
- 20-200 μl multichannel pipette
- Phosphate buffered saline (PBS)
Precautions
- Equilibrate reagents to room temperature prior to use.
- Centrifuge the tube with Glutamine Standard (red cap), Enzyme (green cap) and Glutaminase (yellow cap) briefly before opening to remove all content from walls of the tube and inside the cap.
- Pipette the Glutaminase before use to ensure the Enzyme is homogenous.
- Analyzing samples and standards in triplicate is recommended for accuracy.
- Use a multichannel pipette to dispense the working solution and to minimize time lags in pipetting, because the enzymatic reaction is initiated immediately upon its addition.
- Prepare samples at different dilutions to determine the most suitable concentration, ranging from 0 to 0.5 mmol/l glutamine.
- Dye Mixture is stored in a glass bottle with an aluminum cap. Handle with caution, and wear gloves.
- The kit has been designed for analyzing cell culture supernatants and intracellular glutamine. To measure intracellular glutamine, prepare cell lysates and glutamine standards in a Lysis Buffer. Use cell lysates deproteinized with the Filtration Tube.
Preparation of Solutions
Preparation of Dye Mixture stock solution
Add the entire volume of Reconstitution Buffer to the Dye Mixture vial and dissolve contents completely.
- Transfer the resulting Dye Mixture stock solution to the vial from the Reconstitution Buffer and store at 0-5 °C, protected from light.
- The Dye Mixture stock solution is stable for 2 months under these conditions.
Preparation of Enzyme stock solution
Add 120 μl PBS to the Enzyme tube and dissolve by pipetting.
- Centrifuge the tube briefly each time before opening to remove all content from the tube wall or inside the cap.
- The Enzyme stock solution should be maintained in an ice bath during use.
- The Enzyme stock solution is stable for 2 months when stored at 0-5 °C.
Preparation of Glutamine Standard stock solution (10 mmol/l)
Add 300 μl double-deionized H2O (ddH2O) to the Glutamine Standard tube and dissolve by pipetting.
- Centrifuge the tube briefly each time before opening to remove all content from the tube wall or inside the cap.
- The Glutamine Standard stock solution should be maintained in an ice bath during use.
- The Glutamine Standard stock solution is stable for 2 months when stored at 0-5 °C.
Preparation of Glutaminase solution
Dilute Glutaminase with Reaction Buffer.
- Refer to Table 1.
| for 24 well | for 48 well | for 96 well | |
| Reaction Buffer | 550 μl | 1100 μl | 2200 μl |
| Glutaminase | 2.5 μl | 5 μl | 10 μl |
Preparation of working solution
- Add the Dye Mixture stock solution to a conical tube and dilute with the Assay Buffer.
- Add the Enzyme stock solution to the solution prepared in the step (1).
- Refer to Table 2.
- The working solution is light-sensitive. Prepare it immediately prior to use and protect it from light by covering the tube with aluminum foil. Prepare the working solution fresh each day and use immediately after preparation.
| for 24 well | for 48 well | for 96 well | |
| Dye Mixture stock solution | 175 μl | 350 μl | 700 μl |
| Assay Buffer | 1575 μl | 3150 μl | 6300 μl |
| Enzyme stock solution | 24.5 μl | 49 μl | 98 μl |
General Protocol
1. Total test sample needed for assay
Prepare a test sample to be assayed. Please note that a minimum of 240 μl of sample (e.g., supernatant, lysate) is needed for each test sample (See Figure 2).
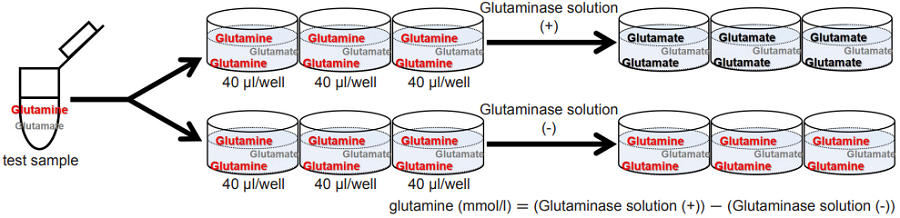
Figure 2. Method for glutamine detection
- Sample preparation (supernatant) -
Dilute cell culture supernatants (test samples) as follows.
- Prepare samples at different dilutions to determine the most suitable concentration. Glutamine concentrations should range from 0 to 0.5 mmol/l. Use ddH2O for dilutions.
- Sample preparation (cell lysate) -
- Prepare a cell suspension (5-10×105 cells) in a 1.5 ml microtube.
- Centrifuge at 300×g for 5 minutes and remove the supernatant.
- Add 500 μl PBS and resuspend the pellet by pipetting; centrifuge at 300×g for 5 minutes and remove the supernatant.
- Add 400 μl Lysis Buffer and lyse the cells by pipetting; centrifuge at 12,000×g for 5 minutes.
- Transfer 350 μl supernatant to a Filtration Tube and centrifuge at 12,000×g for 10 minutes.
- Extend the centrifugation time if the filtrate volume is less than 240 μl.
- Use the sample solution from Step 5. (test samples) for measuring.
- Prepare samples at different dilutions to determine the most suitable concentration. Glutamine concentrations should range from 0 to 0.5 mmol/l. Use Lysis Buffer for dilutions.
2. Preparation of glutamine standard solution
Mix 50 μl Glutamine Standard stock solution (10 mmol/l) and 950 μl ddH2O in a microtube to prepare a 0.5 mmol/l glutamine standard solution. Serially dilute the solution with ddH2O to prepare 0.5, 0.25, 0.125, 0.0625, 0.0313, 0.0157, 0.00785, and 0 mmol/l (Figure 3).
- To measure intracellular glutamine concentration, use Lysis Buffer to prepare the glutamine standard solution instead of ddH2O.
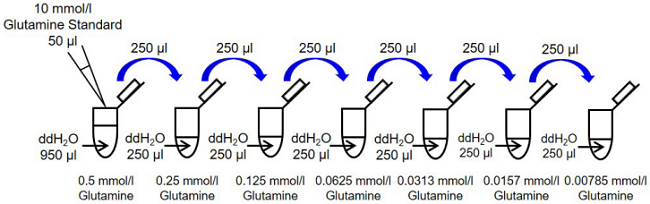
Figure 3. Preparation of glutamine standard solutions
3. Measurements
- Add 40 μl glutamine standard and test sample solutions to separate wells in a 96-well microplate (Figure 4).
- To obtain accurate data, triplicate measurements are recommended.
- Add 20 μl Glutaminase solution to the glutamine standard and test sample (Glutaminase solution (+)) wells.
- Add 20 μl Reaction Buffer to test sample (Glutaminase solution (-)) wells.
- Incubate the microplate at 37 °C for 15 minutes.
- Add 60 μl working solution to each well.
- Because the enzymatic reaction starts immediately after working solution is added, use a multichannel pipette to minimize time lags in pipetting.
- Incubate the microplate at 37 °C for 30 minutes.
- Seal the microplate during incubation to prevent evaporation.
- Measure absorbance at 450 nm with a microplate reader.
- Calculate the glutamine concentration in each sample from a calibration curve generated from the glutamine standards.
- The glutamine concentration is calculated using the following equation:
glutamine (mmol/l) = (Glutaminase solution (+))-(Glutaminase solution (-)) - Multiply the results by the dilution factor to determine the glutamine concentration in the original sample.
- The glutamine concentration is calculated using the following equation:
-
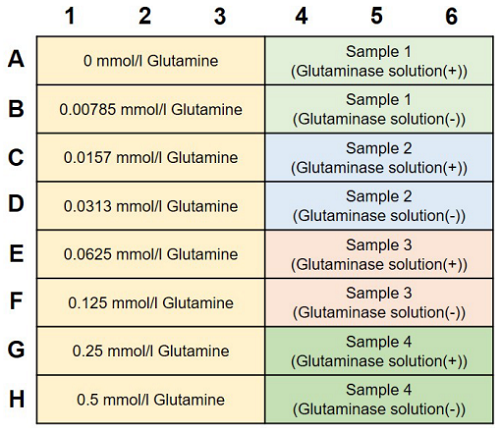
Figure 4. Example of an assay plate format (n=3)
-
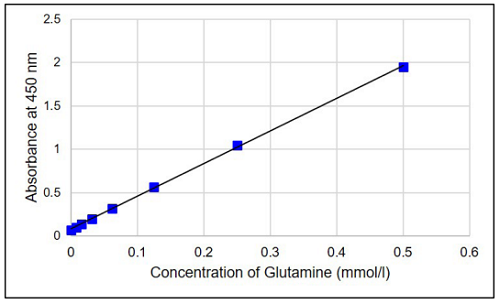
Figure 5. Typical calibration curve generated with glutamine standards
Experimental Example
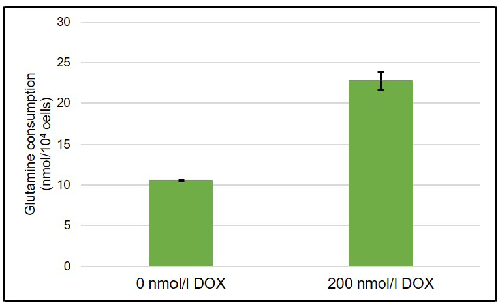
Glutamine consumption of doxorubicin-treated A549 cells
- A549 cells were seeded in a 10-cm dish (2×107 cells/dish in DMEM containing 10% fetal bovine serum and 1% penicillin-streptomycin) and cultured overnight at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 incubator.
- The medium was removed and doxorubicin solution (200 nmol/l in DMEM) was added to the dish.
- The cells were cultured for 2 days at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 incubator.
- The medium was removed and the cells were washed once with 2 ml PBS.
- The cells were trypsinized and collected in a conical tube.
- Doxorubicin-treated A549 cells were seeded in a 6-well plate (1×106 cells/well in DMEM containing 10% fetal bovine serum and 1% penicillin-streptomycin) and cultured overnight at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 incubator.
- Control untreated A549 cells were seeded in a 6-well plate (1×106 cells/well in DMEM containing 10% fetal bovine serum and 1% penicillin-streptomycin) and cultured overnight at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 incubator.
- The medium was removed and 2 ml glutamine solution (2 mmol/l in DMEM) was added to wells.
- The cells were cultured overnight at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 incubator.
- The supernatant (100 μl) was transferred to a 1.5 ml microtube and diluted 15-fold with ddH2O (sample solution). Sample or glutamine standard solutions (40 μl each) were added to individual wells of a 96-well micro plate.
- To determine glutamine consumption, only DMEM containing 2 mmol/l glutamine was also diluted 15-fold with ddH2O.
- Glutaminase solution (20 μl) was added to glutamine standard solutions and sample (only DMEM, doxorubicin-treated A549 cell supernatant and non-treated cell supernatant) (Glutaminase solution (+)) wells.
- Reaction Buffer (20 μl) was added to sample (Glutaminase solution (-)) wells.
- The assay plate was incubated at 37 °C for 15 minutes.
- The working solution (60 μl) was added to each well.
- The assay plate was incubated at 37 °C for 30minutes.
- Absorbance at 450 nm was measured with a microplate reader and the concentrations of glutamine in the samples were calculated from the calibration curve.
glutamine (mmol/l)=(Glutaminase solution (+))-(Glutaminase solution (-)) Glutamine consumption per 104 cells was calculated from the following calculation formula.
glutamine consumption (nmol/104 cells) =
(glutamine in only DMEM (nmol)) (glutamine in doxorubicin-treated supernatant or non-treated (nmol))
cells
- glutamine (nmol)=(glutamine (mmol/l))×(glutamine solution added to wells (2 ml))
-
Figure 6. Comparison of glutamine consumption between doxorubicin (DOX)-treated and non-treated A549 cells
Glutamine consumption level of A549 cells was increased by doxorubicin-treatment.
Reference
- Lingtao, J. et al., Cancer Cell, 2015, 27, 257-270.
Frequently Asked Questions / Reference
G268: Glutamine Assay Kit-WST
Revised May., 17, 2023


 Hidden sections will not be printed.
Hidden sections will not be printed.