General Information
-Bacstain- Bacterial Viability Detection Kits are series of products for fluorescent double-staining of bacteria. By combining different types of fluorescent stain, staining images can be acquired for each index (membrane impairment, respiratory activity, and esterase activity). Bacterial viability is generally assessed by colony formation in nutrient-agar medium. However, this requires a long culturing time, and it is hard to recognize the growth of viable but nonculturable (VNC) bacteria.
However, fluorescent staining does not require bacterial culture, and enables viability assessment by rapid and simple protocols.
-Bacstain- Bacterial Viability Detection Kit – CFDA/PI uses esterase activity of bacteria and bacterial membrane damage as an index.
CFDA is hydrolyzed to carboxyfluorescein―which is fluorescent―by intracellular esterase. PI is a parallel intercalator into the DNA double helix that stains nucleic acids; it passes only through damaged bacterial membranes. Thus, this kit can be used to measure the ratio of bacteria with esterase activity to membrane-damaged bacteria on analysis of the fluorescent images from each stain.
| Code | Product name | Combination |
| BS08 | -Bacstain- Bacterial Viability Detction Kit - DAPI/PI | Nucleic acids/Membrane impairment |
| BS09 | -Bacstain- Bacterial Viability Detction Kit - CTC/DAPI | Respiratory activity/Nucleic acids |
| BS10 | -Bacstain- Bacterial Viability Detction Kit - CFDA/PI | Esterase activity/Membrane impairment |
Kit Contents
| CFDA Solution (in DMSO) | 375 μl × 4 |
| PI Solution | 25 μl × 4 |
Conditions
Store at ≤-20°C
Required Equipment and Materials
- Incubator
- Micropipettes(20 μl and 1,000 μl)
- PBS(-) or saline
- bacteria tend to exhibit lower fluorescence intensity than Gram-positive bacteria because of their cell structure (the outer membrane impedes penetration of CFDA). Thus, the following buffer is recommended for Gram-negative bacteria. NOTE: Gram-negative
0.1 mol/l phosphate buffer (pH8.5), 5% (w/v) NaCl, 0.5 mmol/l EDTA disodium salt.
- bacteria tend to exhibit lower fluorescence intensity than Gram-positive bacteria because of their cell structure (the outer membrane impedes penetration of CFDA). Thus, the following buffer is recommended for Gram-negative bacteria. NOTE: Gram-negative
- Formaldehyde (final concentration 1%–4%)
- Fluorescence microscope
Precaution
Centrifuge the tube briefly before opening the cap because the contents may be on the tube wall or cap.
General Protocol
Each reagent included in this kit is sufficient for 100 samples.
- Equilibrate the CFDA and PI Solutions at room temperature by leaving the tubes for 30 min in the dark.
- Since PI is a potential mutagen, handling and disposal of this reagent should be considered with care.
- Adjust the bacterial suspension to 108–109 bacteria/ml with PBS(-) or saline.
- Transfer 1 ml of the bacterial suspension to a microtube.
- Centrifuge the suspension (5,000 x g, 5 min).
- Remove the supernatant, add 1 ml of PBS(-) or saline, and resuspend the bacteria.
- Repeat steps 4) and 5) twice.
- Add 15 μl of CFDA Solution to the 1-ml bacterial suspension and vortex to mix well (final concentration of CFDA:0.32 mmol/l).
- Incubate the bacterial suspension at 35°C for 5 min.
- If the sensitivity of CFDA staining is insufficient, increase the incubation time.
- Add 1 μl of PI Solution to the 1-ml bacterial suspension and vortex to mix well (final concentration of PI: 1.4 μmol/l)
- Incubate the bacterial suspension at room temperature for 5 min.
- Centrifuge the suspension (5,000 x g, 5 min).
- Remove the supernatant, add 1 ml of formaldehyde (final concentration 1%–4%) and resuspend the bacteria.
- Allow the solution to stand for 10 min at room temperature to fix the cells.
- Centrifuge the cell suspension (5,000 x g, 5 min).
- Remove the supernatant, add 1 ml of PBS(-) or saline, and resuspend the bacteria.
- Observe the bacteria under a fluorescence microscope.
| Component name | Maximum Ex/Em (nm) | Recommended filter | Excitation | Emission |
| CFDA Solution | 493/515 | GFP | 430–510 nm | 475–575 nm |
| PI Solution | 530/620 | TRITC | 520–570 nm | 535–675 nm |
Experimental example-1
Double-staining of Staphylococcus aureus (a Gram-positive bacterium)
- Two test-tubes containing Staphylococcus aureus in 5 ml of liquid medium (TSBYE) were prepared and cultured at 37°C for 14–16 h. One tube was used as a live bacterial sample, and the other was autoclaved at 121°C for 30 min to prepare a sterilized sample.
- The samples prepared in step 1 were diluted with PBS(-) to adjust the bacterial suspension to 108–109 bacteria/ml, then the live and sterilized samples were mixed at a ratio of 7:3.
- One milliliter of bacterial suspension was transferred to a microtube.
- The bacterial suspension was centrifuged at 5,000 x g for 5 min.
- The supernatant was removed and 1 ml of PBS(-) was added to the tube.
- Steps 4 and 5 were repeated twice.
- Fifteen microliter of CFDA Solution was added to the bacterial suspension and mixed well.
- The bacterial suspension was incubated at 35°C for 5 min.
- One microliter of PI Solution was added to the bacterial suspension and mixed well.
- The bacterial suspension was incubated at room temperature for 5 min.
- The bacterial suspension was centrifuged at 5,000 x g for 5 min.
- The supernatant was removed and 1 ml of formaldehyde (final concentration 1%–4%) was added to the tube.
- The bacterial suspension was stood for 10 min at room temperature to fix the cells.
- The bacterial suspension was centrifuged at 5,000 x g for 5 min.
- The supernatant was removed, and 1 ml of PBS(-) was added to tube.
- The bacteria were observed under an epi-illumination fluorescence microscope.
Bacteria with estrase activity are stained by CFDA (green), bacteria with injured cell membrane are stained by PI
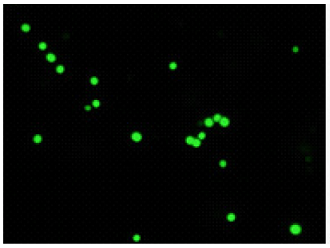
CFDA
excitaition filter 430-510 nm
emission filter 475-575 nm
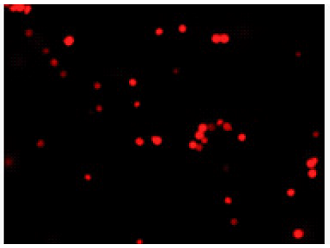
PI
excitaition filter 520-570 nm
emission filter 535-675 nm
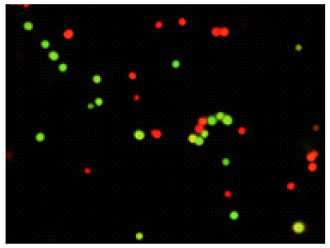
Merge
Experimental example-2
Double-staining of Escherichia coli (a Gram-negative bacterium)
- Two test-tubes containing Escherichia coli in 5 ml of liquid medium (TSBYE) were prepared and cultured at 37°C for 14–16 h. One tube was used as a live bacterial sample, and the other was autoclaved at 121°C for 30 min to prepare a sterilized sample.
- The samples prepared in step 1 were diluted with PBS(-) to adjust the bacterial suspension to 108–109 bacteria/ml, then the live and sterilized samples were mixed at a ratio of 1:1.
- One milliliter of bacterial suspension was transferred to a microtube.
- The bacterial suspension was centrifuged at 5,000 x g for 5 min.
- The supernatant was removed, and 1 ml of 0.1 mol/l -phosphate buffer [0.1 mol/l phosphate buffer (pH8.5), 5% (w/v) NaCl, 0.5 mmol/l EDTA disodium salt] was added to the tube.
- Steps 4 and 5 were repeated twice.
- Fifteen microliter of CFDA Solution was added to the bacterial suspension and mixed well.
- The bacterial suspension was incubated at 35°C for 5 min.
- One microliter of PI Solution was added to the bacterial suspension and mixed well.
- The bacterial suspension was incubated at room temperature for 5 min.
- The bacterial suspension was centrifuged at 5,000 x g for 5 min.
- The supernatant was removed and 1 ml of formaldehyde (final concentration 1%–4%) was added to the tube.
- The bacterial suspension was stood for 10 min at room temperature to fix the cells.
- The bacterial suspension was centrifuged at 5,000 x g for 5 min.
- The supernatant was removed, and 1 ml of 0.1 mol/l phosphate buffer was added to the tube.
- The bacteria were observed under an epi-illumination fluorescence microscope.
Bacteria with esterase activity are stained by CFDA(green), bacteria with injured cell membrane are stained by
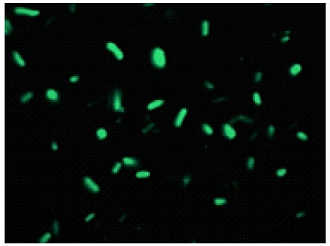
CFDA
excitaition filter 430-510 nm
emission filter 475-575 nm
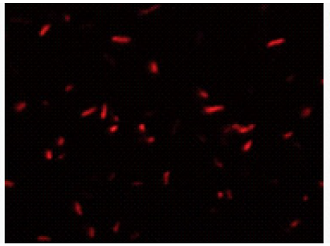
PI
excitaition filter 520-570 nm
emission filter 535-675 nm
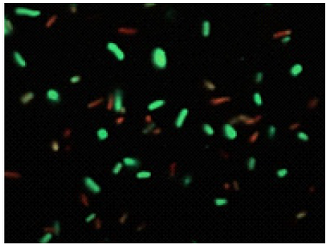
Merge
Frequently Asked Questions / Reference
BS10: -Bacstain- Bacterial Viability Detection Kit - CFDA/PI
Revised Sep., 04, 2023


 Hidden sections will not be printed.
Hidden sections will not be printed.

