General Information
Biofilms are biological aggregates consisting of microorganisms and extracellular polysaccharides that can exist in many environments. Bacterial contamination in medical devices, and infectious diseases such as caries and periodontal disease, are attributed to biofilms. The microorganisms in biofilms are highly resistant to antibiotics; therefore, research into medicines and food ingredients that have anti-biofilm activities is a growing area.
The Biofilm Viability Assay Kit measures the metabolic activity of bacteria in the biofilm to evaluate the bactericidal effect of drugs on biofilm microorganisms. NADH(NADPH)—a coenzyme involved in energy metabolism—reduces WST to colored formazan in the presence of a mediator. This kit utilizes the WST reduction reaction to measure the metabolic activity of the bacteria.
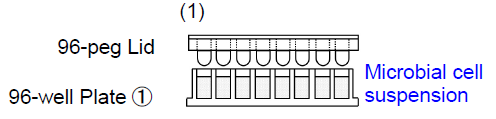
As the biofilm is formed on a peg layer on the lid of a microplate, multiple samples can be easily washed and measured at once without having to peel off the biofilm for each process.
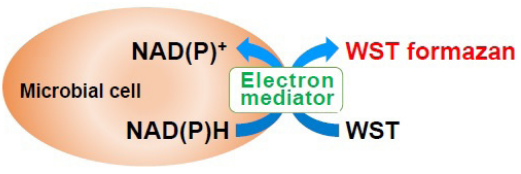
Figure 1. Principle of Biofilm Viability Assay Kit
Kit Contents
| 96 tests | |
| WST Solution | 1 ml x 1 |
| Electron Mediator Reagent | 0.12 ml x 1 |
| 96-peg Lid | x 1 |
| 96-well Plate | x 10 |
Storage Conditions
Store at 0–5°C
Required Equipment and Materials
- Microplate reader (450 nm filter)
- Incubator (37 °C)
- 20-200 μl multichannel pipette
- 100–1000 μl and 20–200 μl micropipettes
- Conical tube
- Sterile physiological saline solution
- Biological safety cabinet
Precautions
- Equilibrate the kit to room temperature prior to use.
- This kit includes 10 sterile 96-well Plates. After opening, please keep the plates under sterile conditions until the experiments and use a new 96-well Plate in each step.
- WST may react with reducing agents to generate WST formazan. Please check the background O.D. if reducing agents are contained in the sample. Please optimize the conditions for the formation of the biofilm prior to measuring the anti-biofilm activity.
- Be careful not to introduce bubbles into the wells as this causes variations in the measurement.
- The incubation time for biofilm formation and coloration time may vary depending on the species of microorganism.
Please optimize the conditions for each experiment. Please refer to table 1. - Use in a biological safety cabinet depending on the species.
General Protocol
Biofilm drug sensitivity test
-
1. Add 180 μl of microbial cell suspension to each well of 96-well Plate ①. Place the 96-peg Lid onto 96-well Plate ① and then incubate the plate at 37°C to form the biofilm on the peg.
- The type of medium for biofilm formation and the in cubation time may vary depending on the species of microorganism. Please optimize the conditions for biofilm formation using the Biofilm Formation Assay Kit (B601).
--
-
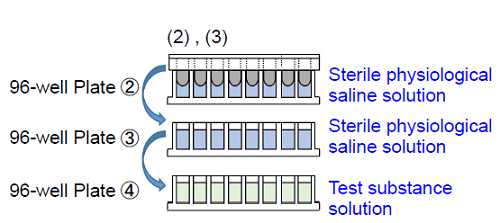
2. Add 200 μl of sterile physiological saline solution to each well of 96-well Plate ② and 96-well Plate ③. Add 200 μl of test substance solution prepared with medium to each well of 96-well Plate ④.
- The medium for the preparation of the test substance solution may vary depending on the species of microorganism.
3. Wash the 96-peg Lid from step (1) by soaking in 96-well plates ② and ③※. Then, place the 96-peg Lid onto 96-well Plate ④ and incubate the plate at 37°C.
- Please soak the lid in saline gently and avoid vigorous shaking.
--
-
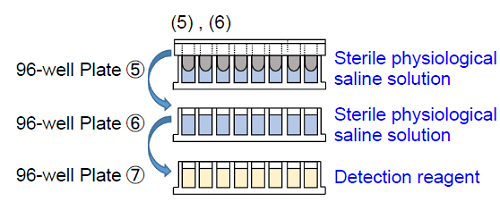
4. Mix 990 μl of WST Solution and 110 μl of Electron Mediator Reagent in a conical tube and add 20.9 ml of Mueller-Hinton broth (MHB) to prepare the detection reagent.
5. Add 200 μl of sterile physiological saline solution to each well of 96-well Plate ⑤ and 96-well Plate ⑥.Add 200 μl of the detection reagent to each well of 96-well Plate ⑦.
6. Wash the 96-peg Lid from step (3) by soaking in 96-well plates ⑤ and ⑥※1. Then, place the 96-peg Lid onto 96-well Plate ⑦. Incubate the plate at 37°C※2.
- Please soak the lid in saline gently and avoid vigorous shaking.
- The incubation time for coloration depends on the species of microorganism and the test substance.
-
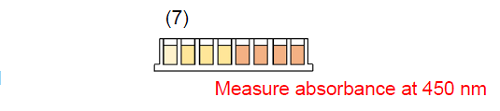
7. Remove the 96-peg Lid and measure the absorbance at 450 nm with a microplate reader.
Experimental Example
Biofilm drug sensitivity test, minocycline : Staphylococcus aureus
- The microbial cell suspension was prepared at approximately 107 CFU/ml with Mueller-Hinton broth (MHB).
- The cell suspension from step 1(180 μl) was added to each well of 96-well Plate ①.
After the 96-peg Lid was placed onto 96-well Plate ①, the plate was incubated at 37°C for 24 hours. - MHB medium (180 μl) was added to each well of 96-well Plate ②. After the 96-peg Lid from step 2 was placed onto 96-well Plate ②, the plate was incubated at 37°C for 72 hours.
- Sterile physiological saline solution (200 μl) was added to each well of 96-well Plate ③ and 96-well Plate ④.
A minocycline solution (1,000 μg/ml) was prepared with MHB medium and sterilized by filtration. A double dilution series of minocycline was prepared with the 1,000 μg/ml minocycline solution and MHB medium on 96-well Plate ⑤ (200 μl in each well).
(e.g.1,000, 500, 250, 125, 62.5, 31.2, 15.6, 7.8, 3.9, 1.95, 0.98, and 0 μg/ml) - The 96-peg Lid from step 3 was washed by soaking in 96-well plates ③ and ④. The 96-peg Lid was then placed onto 96-well Plate ⑤ and the plate was incubated at 37°C for 24 hours.
- The WST soluttion (990 μl) and Electron mediator Reagent (110 μl) were mixed in a sterile conical tube, and MHB medium (20.9 ml) was added it to prepare a detection reagent.
- Sterile physiological saline solution (200 μl) was added to each well of 96-well Plate ⑥ and 96-well Plate ⑦.
200 μl of the detection reagent from step 6 was added to each well of 96-well Plate ⑧. - The 96-peg Lid from step 5 was washed by soaking in 96-well plates ⑥ and ⑦. The 96-peg Lid was then placed onto 96-well Plate ⑧. The plate was incubated at 37°C for 24 hours.
- The 96-peg Lid was removed and the absorbance※ at 450 nm was measured with a microplate reader after incubating for 2–24 hours.
-
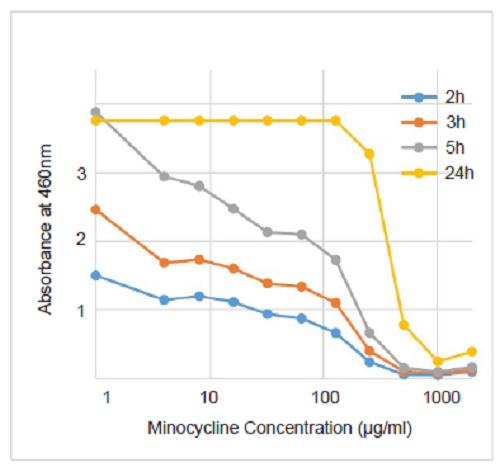
Figure. 2 Biofilm drug sensitivity testing on S. aureus
-
MBEC (minimum biofilm eradication concentration) of minocycline was estimated to be approx. 1,000minocycline 1,000 μ μg/ml.
| Microorganism | Microorganism dilution medium | Microorganism concentration [CFU/ml] |
Incubation time [h] |
Test substance dilution medium | Culture conditions |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Brain heart infusion broth | 106 | 24 | MHB | Aerobic conditions |
| Escherichia coil | Brain heart infusion broth | 107 | 24+72 | MHB | Aerobic conditions |
| Streptococcus mutans | TSB+2%Sucrose | 107 | 24+72 | TSB+2%Sucrose | Anaerobic conditions |
| Porphyromonas gingivalis | Enriched BHI | 107 | 24+72 | Enriched BHI | Anaerobic conditions |
Enriched BHI : Enriched BHI broth (3.7% brain heart infusion, 0.5% yeast extract, and 0.05% cysteine) containing 5 μg/ml of hemin and 0.5 μg/ml of menadione.
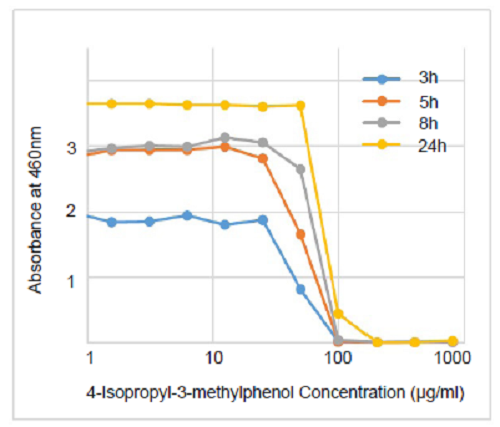
Figure. 3 Biofilm drug sensitivity testing on S. mutans
-
MBEC of 4-Isopropyl-3-methylphenol was estimated to be approx. 250to 250 μ μg/ml.
Reference
- T. Tsukatani, et al., J. Microbiol. Biotech. Food Sci.Sci., 2016, 6, 677-680
This product was developed through joint research within the Biotechnology and Food Research Institute, Fukuoka Industrial Technology Center.
Frequently Asked Questions / Reference
B603: Biofilm Viability Assay Kit
Revised May., 31, 2023


 Hidden sections will not be printed.
Hidden sections will not be printed.