LLPS Characterization-dye Set

LLPS Characterization-dye Set
- Dye set for testing the properties of phase separated droplets
- Stain for proteins and amyloids with strong hydrophobic interactions in droplets
- Includes dyes for detection of droplet to aggregate conversion
-
Product codeLL03 LLPS Characterization-dye Set
| Unit size | Price | FUJIFILM Wako Products code |
|---|
What is Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation (LLPS)?
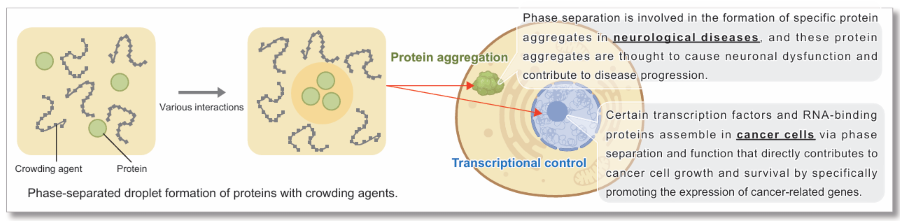
Liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) is a phenomenon in which certain molecules assemble locally within a cell to form aggregates (droplets) of biomolecules with liquid-like properties. In recent years, LLPS has attracted much attention as it has been shown to affect many biological processes in the cell. Although the study of droplets formed by phase separation is still in its infancy, elucidating how these biological phenomena affect cellular functions and the pathogenesis of disease is considered key to the development of new therapeutic strategies.
Reference: E. Dolgin, Nature, 2018, DOI: 10.1038/d41586-018-03070-2.
A set of dyes useful for investigating the properties of phase-separated droplets.
The kit contains four dyes sensitive to hydrophobic interactions between proteins (ANS, SepaFluor) and an amyloid-binding fluorescent dye (Thioflavin T, Congo Red). In addition to hydrophobic interactions, SepaFluor can also be used to observe gelled, phase-separated droplets. The use of these dyes leads to a better understanding of the nature of phase-separated droplets.
*This kit is not suitable for phase separated droplets in cells.
*This kit does not include standard proteins, crowding agents, buffers, etc. Please purchase the separate kit below.
▶ Confirmation of droplet preparation and observation method (standard protein included) LLPS Starter Kit [LL01]
▶ Confirmation of optimal conditions for target protein droplets (crowding agent and buffer included) LLPS Forming Condition Screening Kit [LL02]
▶ This kit
| Components | Feature |
| ANS (8-anilino-1-naphthalenesulfonic acid) | Dye that emits blue fluorescence under hydrophobic conditions |
| SepaFluor |
Dye that emits deep red fluorescence under hydrophobic conditions. |
| Thioflavin T | Amyloid-binding green fluorescent dye |
| Congo Red | Amyloid-binding red fluorescent dye |
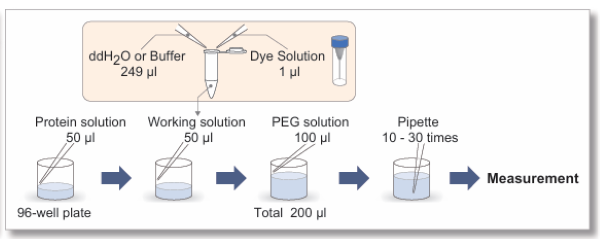
Manual
Q & A
-
Q
How many experiments can I run out of a single kit?
-
A
Approximately 250 tests can be performed when using a 96-well plate.
-
Q
Is there a recommended staining time?
-
A
Staining time depends on the type of phase-separated droplets. When comparing conditions, staining time should be standardized each time. We have experience in staining phase-separated droplets of Tau protein for 10 days using each dye (observation container: glass slides).
-
Q
Is it possible to stain after the formation of phase separated droplets?
-
A
Yes. Add a 1000-fold dilution of the final concentration of each dye in DMSO solution.
-
Q
What kind of 96 well plate can be used?
-
A
For fluorescence microscopy it is recommended to use black plates with a clear bottom.
The following plates have also been used.Manufactures
Product names
Cat No.
ibidi
μPlate 96 well ibiTreat black S 15
ib89626
AGC techno glass
EZVIEW Glass Bottom Culture Plate LB 96well
5866-096
SPL Life Sciences
SPL Cellular Imaging 96 Well Plate Black & Clear Bottom PS
33396
-
Q
Phase-separated droplets are not stained.
-
A
This can be improved by extending the staining time or increasing the staining concentration. However, phase separated droplets are formed by various protein-protein interactions such as hydrophobic interactions, electrostatic interactions, hydrogen bonding, π-π interactions and cation-π interactions. Therefore, some droplets are formed by the interaction of proteins with weak hydrophobic interactions. It is necessary to determine the nature of the interaction from complex data, such as the addition of salts to confirm electrostatic interactions, the addition of urea to confirm hydrogen bonding, or the addition of 1,6-hexanediol to confirm hydrophobic interactions.
Reference:
Manisha Poudyal et al., “Intermolecular interactions underlie protein/peptide phase separation irrespective of sequence and structure at crowded milieu”, Nat. Commun., 2023, 14, 6199.
Handling and storage condition
| Store at -20 °C, protect from light |










