| [Jun. 26, 2024] | Previous Science Note |
|
Endocytosis induction refers to the initiation of the endocytic process, where specific signals trigger the cell to internalize extracellular substances. This induction often involves membrane proteins that can act as receptors to recognize and bind external ligands, initiating the formation of endocytic vesicles. The interaction between ligands and membrane proteins not only triggers endocytosis, but also ensures that the internalized cargo is selectively processed. Thus, membrane proteins are integral to both the initiation and specificity of endocytosis, influencing cellular uptake and signaling pathways. |
|
|
Related Techniques |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Related Applications |
Clear visualization of intracellular vesicular trafficking
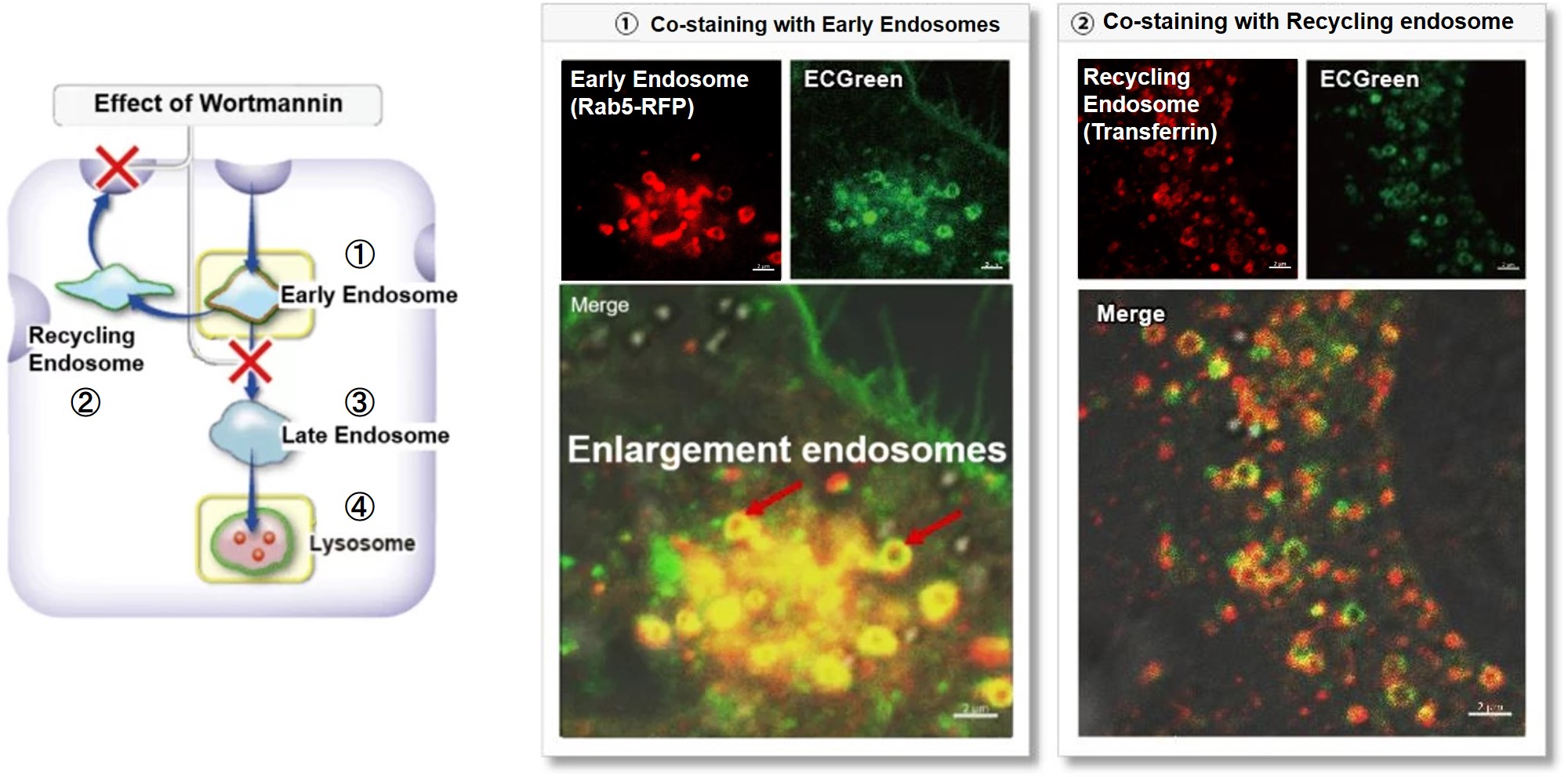
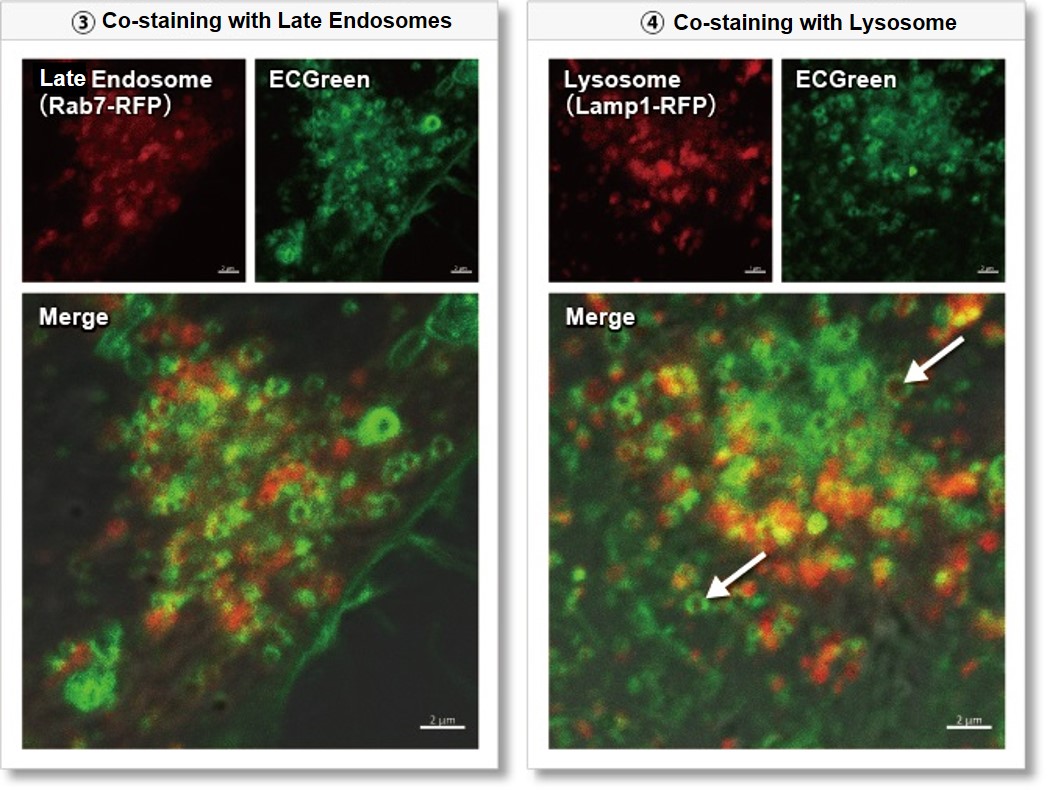
Wortmannin is known to inhibit endosomal recycling and lysosomal translocation, leading to endosomal enlargement. ①Eary endosome: Rab5-RFP (red) As a result, it was confirmed that ECGreen (green) co-localizes only with enlarged early endosomes and recycling endosomes (Fig. ① and ②), but not with late endosomes or Lysosomes (Fig. ③ and ④), supporting Wortmannin's effect. ECGreen can visualize changes in the intracellular vesicular trafficking system and endosome shape. Endosomes (ECGreen, green): Ex. 405 nm / Em. 500 – 560 nm [Experimental Procedure] |