|
Lipid droplets (LDs) play an important role in several diseases, including cancer, neurodegeneration and cellular senescence. In cancer, LD accumulation is often observed and can support rapid cell proliferation by providing essential lipids for membrane synthesis and energy production. Neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's show aberrant lipid metabolism, with excessive LDs contributing to neuroinflammation and neuronal dysfunction. In cellular senescence, lipid droplets sequester polyunsaturated fatty acids to prevent ferroptosis, a type of cell death, thereby impacting aging and age-related diseases.
|
-
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase obstructs CD8+ T cell lipid utilization in the tumor microenvironment
Click here for the original article: Elizabeth Hunt, et. al., Cell Metabolism, 2024.
Point of Interest
- T cells in the solid tumor microenvironment (TME) must catabolize lipids via mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation (FAO) to provide energy during nutrient stress.
- The solid TME activates acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase (ACC) in T cells, causing lipid droplet accumulation in tumor-infiltrating T cells, which inhibits FAO.
- Restricting ACC activity rewires T cell metabolism to maintain energy during TME stress.
-
Cell cycle arrest induces lipid droplet formation and confers ferroptosis resistance
Click here for the original article: Hyemin Lee, et. al., Nature Communications, 2024.
Point of Interest
- Cell cycle arrest suppresses ferroptosis by forming diacylglycerol acyltransferase (DGAT)–dependent lipid droplet to sequester polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs).
- DGAT inhibition reshuffles PUFAs to phospholipids, which resensitizes arrested cells to ferroptosis.
- Some slow-cycling antimitotic drug–resistant cancer cells, such as 5-fluorouracil–resistant cells, have accumulation of lipid droplets and combined treatment with ferroptosis inducers and DGAT inhibitors effectively suppresses their growth.
-
Senescent glia link mitochondrial dysfunction and lipid accumulation
Click here for the original article: China Byrns, et. al., Nature, 2024.
Point of Interest
- Senescent glia in aging Drosophila brains originate from neuronal mitochondrial dysfunction and express AP1, a senescence-associated transcription factor.
- AP1+ senescent glia cause lipid accumulation in non-senescent glia and increase senescence markers.
- Targeting AP1 in senescent glia extends lifespan, but increases oxidative damage in the brain and neuronal mitochondrial function remains poor.
|
| Related Techniques |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Related Applications |
Hepatotoxicity test of drug-induced lipidosis using high-content imaging
Propranolol (a sympathetic β-receptor blocker) was added to a human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line (HepG2 cells), and changes in lipid droplets were observed under a fluorescence microscope. The accumulation of lipid droplets was analyzed by measuring the number, area, and fluorescence intensity of lipid droplets from the acquired microscopic images
|
<Lipid droplet imaging data>
-
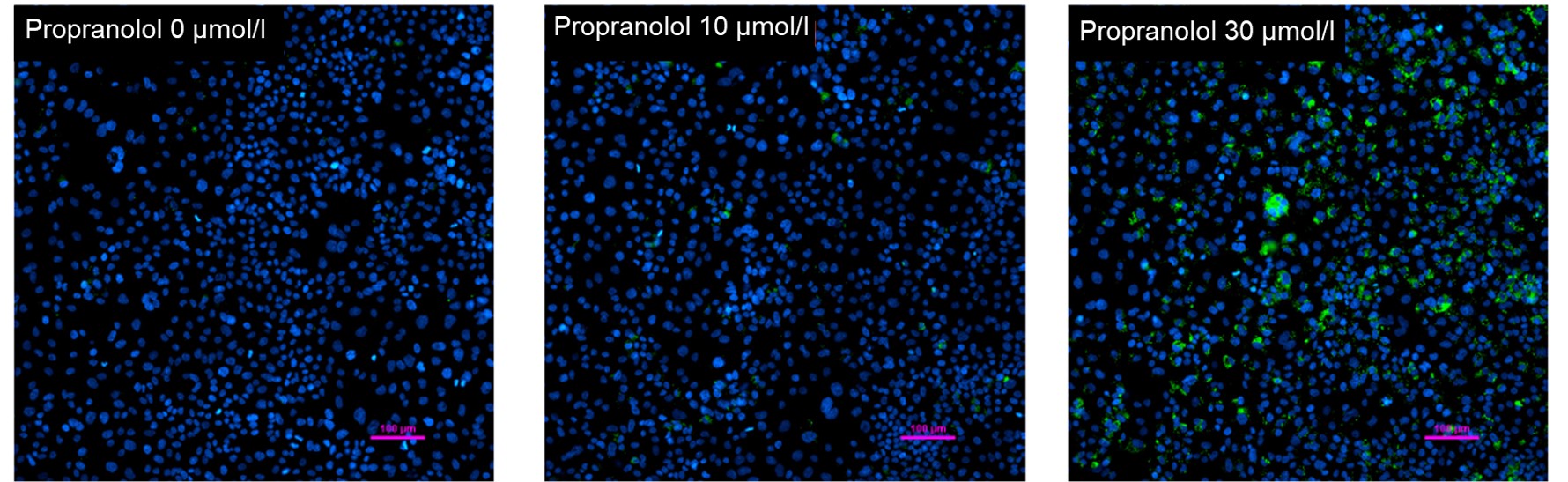
Nucleus (blue: Hoechst 33342 ): Ex 385 nm, Em 460 nm
Lipid droplet (green: Lipi-Green): Ex 475 nm, Em 535nm
-
HepG2 cells were treated with propranolol 0, 10, or 30 μmol/l, lipid droplets were stained with Lipi-Green and nuclei with Hoechst 33342 and observed using a fluorescence microscope (Ti2-E inverted microscope). The results showed that lipid droplets increased in a propranolol concentration-dependent manner.
Related Products
- Lipi-Blue/ Green/ Red/ Deep Red
- Lipid Droplet Assay Kit - Blue / Deep Red
|
<Analysis of lipid droplet accumulation relative to drug treatment concentration>
-
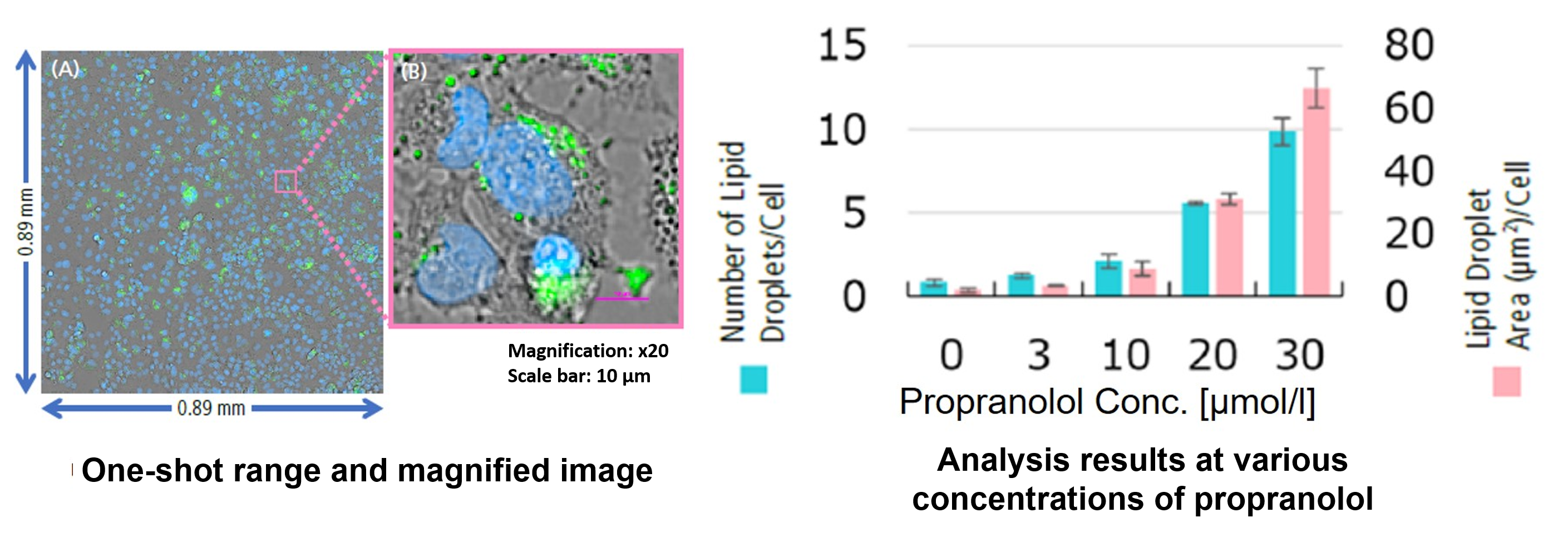
High Content Analysis (HCA) microscope system
(Nikon Corporation : https://www.microscope.healthcare.nikon.com/)
For details of staining and analysis methods, please refer to "APPLICATION NOTE :
Hepatotoxicity test of drug-induced lipidosis using high-content imaging" by Nikon Corporation.
-
From the fluorescence images obtained, the accumulation of lipid droplets per cell was analyzed by measuring cell number from nuclei and area, number, and fluorescence intensity from lipid droplets. The results showed that the number and area of lipid droplets increased in a propranolol concentration-dependent manner, with lipid droplets forming significantly under concentration conditions of 20 μmol/l or higher. The DS-Qi2 camera, which can capture a wide range of cellular areas in a single shot, was used for imaging, and the EDF module of NIS-Elements software, which can acquire focused images of all lipid droplets, was used for analysis, enabling quantitative analysis with highly reliable statistical data. The EDF module of the NIS-Elements software allows for the acquisition of focused images of all lipid droplets.
|

















